SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
1
(No Transcript)
2
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
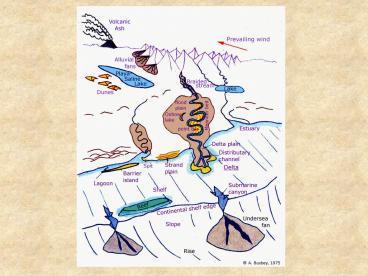
Marine Environment
3
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
Continental Shelf Flat, smooth regions that
fringe continents Few km to 300 km wide Low
tide to 200 m depth Similar to continental
deposits Shelf planed off by changes in sea
level
4
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
Continental Shelf Most eroded continental materi
al ends up here Primarily sand, silt,
clay Carbonates develop where clastic influx is
low In shallow marine biologic impact is great
5
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
6
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
Steeper slope than shelf 300 to 3200 m deep Zone
of erosion as material from shelf moves to
abyssal plain Turbidity currents (Waterville
Fm.) Mostly fine sand, silt, clay
Continental Slope
7
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
Continental Slope
Turbidity Currents
8
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
More gradual slope at base of continental
slope
Continental Rise
9
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Marine Environment
Depths gt3200 m Only fine clay, volcanic ash and
calcareous and siliceous oozes
accumulate Carbonate compensation depth Oozes
are skeletal remains Coarse-grains Slumps
Ice-rafted debris
Deep Marine Abyssal Plain
10
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environments
Represents the margin between the oceans and
contintents (Shorelines and coasts)
Clastic sediments
11
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Carbonate sediments
12
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Deltas ?
13
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Mississippi River Delta
Deltas Prograding Delta Deposition gt
Erosion Upward progression of fines to
coarse Subsiding basin Contain organic
matter Petroleum producing
14
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Deltas
15
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Deltas Deposition Erosion Concentric
enlargement of delta
Niger River Delta
16
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Deltas Erosion gt Deposition No visible delta
Kennebec River
17
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Barrier Islands
18
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Usually sandy Organisms include bivalves,
gastropods, echinoids, and crustaceans
Barrier Islands
19
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Lagoon Shallow areas land- ward of
barrier islands Can be protected
inlets Sediments usually silty
20
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Lagoon
21
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Tidal Flats
22
SEDIMENTARY ARCHIVES
Transitional Environment
Tidal Flats Exposed and covered by tides Harsh
environment Alternating wet and dry Generally
fine-grained Diversity is low Includes bivalves,
gastropods, crustaceans, worms, and
cyanobacteria