Seating Assignments PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 71
Title: Seating Assignments
1
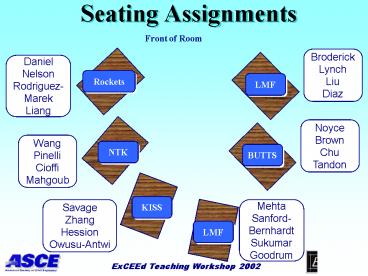
Seating Assignments
Front of Room
BroderickLynch Liu Diaz
Daniel Nelson Rodriguez-Marek Liang
Rockets
6
LMF
1
Noyce Brown Chu Tandon
Wang Pinelli Cioffi Mahgoub
NTK
5
BUTTS
2
KISS
4
Mehta Sanford- Bernhardt Sukumar Goodrum
Savage Zhang Hession Owusu-Antwi
LMF
3
2
Welcome to the ExCEEd Teaching Workshop
Al Estes and the ETW Faculty
3
Excellence in Civil Engineering Education
4
The mind is not a vessel to be filled But a fire
to be kindled. Plutarch, A.D. 46 A.D. 120
My mind is on fire. T.J Cunningham, ExCEEd
Course Assessment, A.D. 2001
The mind is a terrible thing to set on
fire. ETW Group 2, A.D. 2001
5
Congratulations!!!! You have won a Teaching
Fellowship
Your Resume ______ ______
Competed for and won a 2300 Teaching Fellowship
from the American Society of Civil Engineers
6
Our Agenda for Today
- Introduction to ETW
- ASCE welcome overview
- Course organization
- Introduction of participants faculty
- Course administration
- Seminar I Learning to Teach
- Lab I Team-Building Reception and Dinner
7
Why Are We Here?
- Improve our teaching skills.
- Learn and apply theories of teaching and
learning. - Learn teaching assessment skills.
- Meet and interact with other CE educators who are
interested in teaching. - Develop a passion for teaching.
- Learn a little about West Point.
8
The United States Military Academy
Construction
A national treasure...
Construction
Construction
Construction
Construction
You Are Here
Construction
Construction
and an important part of our heritage as
engineers.
9
United States Military Academy
Bicentennial Celebrating 200 Years
10
American Society of Civil Engineers
Celebrating 150 Years Of Service to the
Civil Engineering Profession
Sesquicentennial Birthday
11
Senior?
Senior?
Jim OBrien Senior Director Education
Diversity ASCE
Senior?
Senior?
Senior
Senior?
Senior?
12
Excellence in Civil Engineering Education
13
ExCEEds Roots
- USMA (West Point)
- Department of CME
- Instructor Summer Workshop
- Train rotating military faculty
- 6 weeks
- A 40-year oral tradition
- Mentors All the folks in green plus Dave
Cottrell Jim OBrien
14
ExCEEds Roots
- T4E Short Course at USMA
- NSF-funded
- 1996, 1997, and 1998
- 1-week long
- Incorporated the current body of knowledge on
teaching and learning - Mentors Doug Schmucker Elliot Douglas
15
The ExCEEd Teaching Model
- Structured organization
- Based on learning objectives
- Appropriate to the subject matter
- Varied, to appeal to different learning styles
- Engaging presentation
- Clear written and verbal communication
- High degree of contact with students
- Physical models demonstrations
- Enthusiasm
- Positive rapport with students
- Frequent assessment of student learning
- Classroom assessment techniques
- Out-of-class homework and projects
- Appropriate use of technology
Teacher as Role Model
16
ASCE ExCEEd
- 1995 CE Education Conference
- ASCE Faculty Development Initiative
- ASCE Committee on Faculty Development
17
1999 ExCEEd Workshops
- USMA (Led Klosky)
- Program Development Group
- Effective College Teaching Seminar
18
2000 ExCEEd Workshops
- USMA
- University of Arkansas
- Effective College Teaching Seminar
19
2001 ExCEEd Workshops
- USMA
- University of Arkansas
- Effective College Teaching Seminars
20
2002 ExCEEd Workshops
- USMA
- University of Arkansas
- Northern Arizona University
- Student-Educator-Practitioner Teaching and
Learning Seminar
21
is
Excellence in Civil Engineering Education
22
The Character of this Course
- Focused on planning and delivering classroom
instruction - A little theory, a lot of practice
- No theory without application
- High challenge, low threat
- Collaborative
- Collegial
- Fun
23
Course Organization
1
- Seminars
- All participants together
- Room B-19 Mahan Hall
- Presentations, discussion, and small group work
- Demonstration Classes
- All participants together
- Room B-23 Mahan Hall and 444 Thayer Hall
- Participants role-play as students
24
Course Organization (contd)
- Labs
- 6 groups
- 4 participants
- 1 mentor
- 1 assistant mentor
- Individually assigned classrooms
- Individual work, small group work, and practice
classes
25
COURSE SCHEDULE
SUNDAY
MONDAY
TUESDAY
WEDNESDAY
THURSDAY
FRIDAY
Admin Gift
Admin Gift
Admin Gift
Admin Gift
Admin Gift
800
Demo Class I
Lab III Practice Class 1
Lab IV Practice Class 2
Lab V Practice Class 3
Interpersonal Rapport
Principles of Teaching Learning
ASCE Programs
1000
ETW Assessment
Learning Objectives
Graduation
1200
Lunch
Lunch
Lunch
Lunch
Teaching Assessment
Lab IV (continued)
Design of Instruction
Planning A Class
200
Demo Class II
Non-verbal Communi- cation
Chalkboard
Demo Class III
Communi- cation Skills
Intro To ETW
Lab II Objectives
400
Instructional Technology
Learning To Teach
Working Dinner Class Prep
600
Hudson River Cruise
Lab I Team- Building
26
Team Assignments
2
27
Team 1
- Participants
- Greg Broderick
- Jason Lynch
- Yusef Mehta
- Manuel Diaz
- Mentor Fred Meyer
- Assistant Mentor
- Jim Kohl
- Craig Quadrato (Head Assistant Mentor)
28
Team 2
- Participants
- David Noyce
- Kris Brown
- Bella Chu
- Hesham Mahgoub
- Mentor Elliot Douglas
- Assistant Mentors
- Hank Thomsen
29
Team 3
- Participants
- Carl Liu
- Kristen Sanford Bernhardt
- Natarajan Sukumar
- Paul Goodrum
- Mentor Daisie Boettner
- Assistant Mentors
- Dave Borowicz
30
Team 4
- Participants
- Bruce Savage
- Yunfeng Zhang
- Cully Hession
- Emmanuel Owusu-Antwi
- Mentor Dave Cottrell
- Assistant Mentors
- Mike McKay
31
Team 5
- Participants
- Jamie Wang
- Jean-Paul Pinelli
- Tony Cioffi
- Vivek Tandon
- Mentor Doug Schmucker
- Assistant Mentors
- Steve Braddom
32
Team 6
- Participants
- Jo Daniel
- Tom Nelson
- Adrian Rodriquez-Marek
- Xu Liang
- Mentor Led Klosky
- Assistant Mentors
- Dawson Plummer
33
Other Folks You Should Know
- Principal Seminar Instructors
- Al Estes
- Steve Ressler
- Ron Welch
- Mark Evans
- ASCE Staff
- Tom Lenox
- Jim OBrien
- Ty Booker
2
- Special Guests
- Joe Dietrich
- Jim McDonald
- Pete Jenkins
- Judy Stallnaker
- Janet Sanders
- Tom Jackson
34
Homework Assignment 1
Not later than 2100 this evening, create a
mutually agreeable name for your group
and post it on your team sign.
You will announce your results at the banquet
35
Course Administration
36
Course Administration
- Wear your name tag!
- Travel orders
- Workshop assessment
- Getting to class
- Breakfast options
- Grant Hall (opens 0700)
- McDs (opens 0630)
- Hotel Thayer (opens 0700)
11
Take the 0713 shuttle!
37
More Course Administration
- Lunch options
- West Point Club (1100 1330)
- Grant Hall (Until 1400)
- Breaks B-12 Mahan Hall 441 Thayer Hall
- Telephone number (845) 938-2600
- Internet access 204 Mahan Hall
- DOMAIN CME.Dean
- USERID exceed
- PASSWORD password
- Extra supplies B-22 Mahan Hall
38
And Yet Even More Course Administration
- Watching your videotape options
- Your classroom
- Your hotel room (select few)
- Tension/Torsion Lab across the hall
- Gymnasium usage
- Hotel Thayer
- Family Fitness Center
- Arvin Gymnasium
39
Welcome to the ExCEEd Teaching Workshop
Any questions?
40
Getting to Know You...
- Update your personal data.
- ETW Pre-Assessment.
- As you leave the room
- Stop in front of the video camera.
- Face the camera.
- Clearly say your first and last name.(Use the
nickname you prefer to be called.) - Take a break!
- Be back here for Seminar I at _____.
41
Seminars on Teaching and Learning
Al Estes Steve Ressler Ron Welch
42
Classroom Procedures
- Bring ETW Notebook Calculator to class
- Course textbooks
- Bring prepared materials for the practice class
you will teach on the following day. - Hard-copies of slides
- Electronic copies of slides
- Food and drink
- Breaks
- Rest rooms
- Questions discussion
- After-hours access to classrooms
Wankat Oreovicz
Lowman
4
43
Seminars on Teaching and Learning
Seminar I
Learning to Teach
Al Estes
44
Why Learn to Teach?
- 1990 Seymour Hewitt study
- Why do undergrads leave SME?
- Studied 335 students at 7 institutions
- Findings
- 40 of engineering undergrads switch to other
non-SME disciplines. - Losses are disproportionately higher among women
and minorities. - No significant difference in the intellectual
abilities of switchers and non-switchers.
45
Why Learn to Teach
- Findings about Teaching
- 41 of switchers cited poor teaching as a
factor in the decision to switch. - 98 of switchers cited poor teaching as a
concern. - 86 of non-switchers also cited poor teaching
as a concern. - Next lowest non-switcher concern was 53.
We have a problem.
46
Why Learn to Teach?
- Students perceived that SME faculty
- Do not like to teach
- Do not value teaching as a professional activity
- Lack any incentive to teach well
- Conclusion
- Switchers and non-switchers were virtually
unanimous in their view that no set of problems
in S.M.E. majors was more in need of urgent and
radical improvement than faculty
pedagogy. -Seymour and Hewitt
We REALLY have a problem.
47
What Makes A Bad Teacher?
- Students cited specifics
- Preoccupation with research
- Indifferent to academic difficulties
- Took no responsibility for student learning
- Sarcasm, ridicule, degradation, aloof, forbidding
- Inadequate preparation
- No logical sequence or structure
- Unable to explain ideas coherently
- Material and tests at too high a level
- No practical application for material
- Boring presentation read from book, silent
teaching - No fit between class material, homework, tests
- Do not understand how people learn
- Curve-grading
- Address their own intellectual needs not
students
48
Homework Assignment 2
Prepare a short (lt5-minute) skit illustrating the
worst teaching you have ever experienced.
Skits will be performed throughout the day
tomorrow.
49
Group Activity
(1) How did you learn to teach? (List the 3 most
common activities or experiences of your group
members.) (2) What would have made the learning
process more effective?
50
Why Learn to Teach?
- Students in the study offered three suggestions
- Teacher training programs
- Senior faculty mentoring
- Reward good teaching
If you are not convinced and still need a reason
51
Why Learn to Teach?
- The NSPE Code of EthicsEngineers shall perform
services only in the areas of their competence.
Teaching when you are not competent to do so is
unethical.
52
How should welearn to teach?
How should our students learn engineering?
Different questions Same answer
53
A Design Project
- Given
- A complex engineering concept, with a variety of
important applications - You know nothing about it
- Resources
- A textbook that covers the topic
- 6 hours
- 2 one-hour blocks of classroom time with a
subject-matter expert - 4 hours on your own, outside of class
- Required Design a sequence of activities that
will help you learn the concept and its
applications most effectively.
You have 7 minutes
54
Some Possible Activities
- Read the textbook.
- Receive a lecture on the concept from the expert.
- Watch the expert solve an example problem.
- Describe your own understanding of the concept to
the expert, and get feedback on how well you
really understand it. - Discuss the concept with your peers.
- Solve a practice problem with assistance from the
expert. - Solve a practice problem on your own, then get
feedback from the expert on how well you did. - Solve a practice problem with your peers.
55
A Model Instructional Strategy
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking about the subject.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance and provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
56
Two Key Definitions
- Assessment and Evaluation
- Assessment - A measurement of performance, for
the purpose of improving future performance. - Evaluation - A measurement of performance against
a set of prescribed standards, usually for the
purpose of reward or punishment.
57
Types of Assessment
- Assessment of a Program
- Assessment of a Course
- Assessment of Teaching
- Assessment of Student Learning
Well talk about all four in ETW
58
Classroom Assessment Technique 1
Background Knowledge Probe
59
A Model Instructional Strategy
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance and provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
60
(No Transcript)
61
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance and provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
62
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance and provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
63
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance and provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
64
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
65
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
66
Learning to Teach in ETW
- Provide an orientation
- Why is this important?
- How does it relate to prior knowledge?
- Provide learning objectives.
- Provide information.
- Stimulate critical thinking.
- Provide models.
- Provide opportunities to apply the knowledge
- In a familiar context.
- In new and unfamiliar contexts.
- Assess the learners performance provide
feedback. - Provide opportunities for self-assessment.
67
Learning Objectives
- Explain what constitutes effective teaching.
- Apply Felders learning styles model to the
organization and conduct of a class. - Use Classroom Assessment Techniques to assess
student learning. - Organize a class.
- Deliver classroom instruction.
- Assess a class from a students perspective.
- Self-assess your own class.
68
Tomorrow
- 0745 - Course Admin ASCE Gift
- Here
- Eat breakfast before class.
- 0800 - Demonstration Class I
- Instructors Steve Ressler
- Course EM302 Statics Dynamics
- Subject Truss Analysis 1
- Bring your calculator.
69
Role-Playing
- For all classes
- View the class from the perspective of an
undergraduate engineering student. - Answer questions accordingly.
- Ask questions accordingly.
- Why?
- Make classes as authentic as possible.
- Focus on student learning.
- Basis for assessment.
70
Dont Forget
- Homework Assignment 1
- Homework Assignment 2
- Bring all prepared materials for your first
class. - Wear your name tag!
7
71
Seminar I
Learning To Teach
5
Im Hungry Time for Dinner!