Good X PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
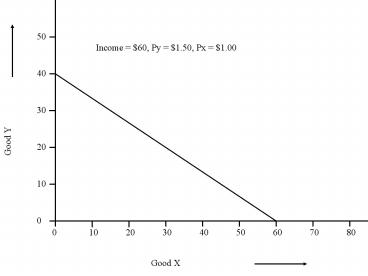
Title: Good X
1
50
Income 60, Py 1.50, Px 1.00
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
2
Consumer chooses her optimal bundle
40
Good Y
14
0
0
60
39
Good X
3
50
The price of Good X rises to 2.00 resulting in a
rotation of the budget line.
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
4
The consumer chooses her best bundle on the new
budget line.
40
Good Y
20
0
15
0
30
Good X
5
50
The total effect of the price increase on the
consumers optimal bundles.
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
6
The dashed line represents a hypothetical budget
line that is parallel to the new budget line
(reflecting the new prices) and is tangent to the
original indifference curve.
50
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
7
The substitution effect of the increase of the
price of good X.
40
32
Good Y
0
21
0
60
Good X
8
The income effect of the increase in the price of
good X.
50
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
9
The total effect is the sum of the substitution
effect and the income effect.
50
40
30
Good Y
20
10
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
70
60
80
Good X
10
How much additional money is needed to compensate
the consumer for the price rise? Is X a normal
good? Is Y a normal good?
11
32
Good Y
20
14
0
21
15
0
39
Good X
12
30.00 If her income is increased by 30 to 90
then, at the new prices, the dashed line will be
her budget line. The best choice on the dashed
line allows her to have the same level of utility
as she did initially. Both Y and X must be normal
goods. The income effect results in a decrease of
both goods.
13
The effect of the increase in price of good X on
purchases of good X.
- Substitution effect X decreased by 18 units.
- Income effect X decreased (normal good) by 6
units. - Total effect -18 -6 -24
X decreased by 24 units
14
32
Good Y
20
14
0
21
15
0
39
Good X
15
The effect of the increase in price of good X on
purchases of good Y.
- Substitution effect Y increased by 18 units.
- Income effect Y decreased (normal good) by 12
units. - Total effect 18 -12 6
Y increased by 6 units.
16
32
Good Y
20
14
0
21
15
0
39
Good X
17
Income and substitution effects
- Example 2 A decrease in the price of good X
18
I 300, Py 1, Px 5
500
400
300
Good Y
200
100
0
140
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Good X
19
Price of good X falls to 2.00 The budget line
rotates in a counter-clockwise direction around
the y intercept
500
400
300
Good Y
200
100
0
140
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Good X
20
The total effect is the sum of the substitution
effect and the income effect.
500
400
300
Good Y
200
100
0
140
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Good X
21
Good Y
81
0
0
56
Good X
22
How much money is the consumer willing to pay to
get a price of 2.00 instead of 5.00? If the
firm selling good X charged that fee, to lower
the price of good X to 2.00 from 5.00 will its
revenue increase? Will its profit? Is X a normal
good? Is Y a normal good?
23
107. Yes. The consumer ends up buying less of
good Y. Since its price hasnt changed, the
consumer is spending less overall on good Y and
hence more on good X. Y is a normal good. The
positive income effect results in an increase in
good Y. X is an inferior good. The positive
income effect results in a decrease in good X.
Note however that the total effect on good X is
an increase.
24
The Direction of the Substitution Effect
What is the direction of the substitution effect
of a relative price increase (decrease) of good X
on good X? on good Y?
25
It is always in the opposite direction to the
price change.
Good Y
0
0
Good X
26
The Direction of the Income Effect
What is the direction of the income effect of a
relative price increase (decrease) of good X on
good X? on good Y?
27
It depends on whether the goods are normal or
inferior
Is a giffen good inferior?