Monocytes PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title: Monocytes
1
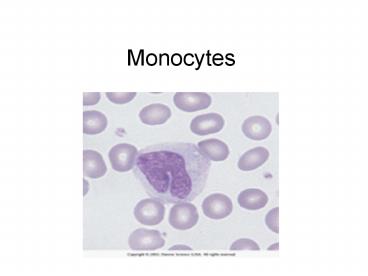
Monocytes
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Monocytes / Macrophages
- Bone marrow
- Lymph nodes
- Kidney (glomerular mesengial)
- Brain (microglial)
- Liver (kupffer)
- Spleen (sinus)
- Lung (alveolar)
6
Function
7
(No Transcript)
8
Monocytosis gt1.0 x 109/L adults
- Reactive Monocytosis
- Chronic infections (i.e. TB)
- Transiently in recovery from tissue injury (MI)
- Sarcoidosis
- Hodgkins nonHodgkins lymphoma
- Splenectomy
- Recovery from acute infection agranulocytosis
9
Monocytosis
- Circulating Neoplasmic Monocytes
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Acute myelomonocytic leukemia (AML-M4)
- Acute monocytic leukemia (AML- M5)
- Malignant histiocytosis
10
Eosinophils Basophils
11
Learning Objectives
- Describe the role of basophil mast cells
- Explain the mechanism of basophil degranulation
and the role of the biologically active materials
lipid mediators. - Describe the role of eosinophils in the killing
of parasites. Explain the role of IL4, IL5, C3b3. - Understand the causes of basophilia,
eosinophilia, eosinopenia and basopenia.
12
Hypersensitivity Classification
13
Hypersensitivity Classification contd
14
Hypersensitivity
- Type I IgE mediated hypersensitivity
- Antigen cross-linkage of IgE bound to mast cells
basophils causes release of vasoactive
mediators - reactions typically take 2-30 minutes
- symptoms may include
- anaphylaxis
- hay fever
- hives
- asthma
- food allergies
- eczema
15
Basophils
16
Function of Basophils
17
Basos vs. Masts
18
Whats on the Outside of a Baso?
19
Stages of Activation of Basos Masts
- 1. degranulation
- 2. production of lipid mediators
- 3. cytokine excretion
20
Granules
- Granules contain many substances that are
involved in vasodilation, bronchoconstriction,
stopping clotting and altering tissues - important examples
- histamine vasodilation
- Chondoitin SO4 packages basic proteins into
granules, binds and stabilized proteases - slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis
- Eosinophil chemotactic factor
- Prostaglandin D2
21
Cytokines secreted by Basos Masts
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
- IL4
- IL3, GMCSF
- others
- IL1
- Il5
- IL6
22
Remember the cytokines
23
Review of Basos
- 1. inflammation immediate hypersensitivity
- 2. leukotriene cytokine release
- 3. degranulation
24
Basophilia (gt0.2 x 109/L)
- allergy or inflammation
- infections
- neoplasms
- following radiation exposure
25
Basopenia (lt0.01 x 109/L)
- steroids
- thyroid hormones
- Acute infection
- stress
26
Eosinophils
27
Eosinophils
- Granules
- Primary Granules
- Charcot leyden protein lysophospholipase
- Eosinophil peroxidase
- Secondary Granules
- Eosinophil peroxidase
- Major Basic Protein disrupts membranes
- histaminase inhibits histamine
- Eosinophil cationic protein destroys membranes
28
The Occupation of Eosinophils
extracellular killing O2 independent O2
dependent
- C3b
control the masts basos removal of fibrin can
phagocytize
29
Eosinophilia (gt0.6 x 109/L)
- parasitic disease
- drug reactions
- allergies
- Cutaneous disorders
- immune deficiencies
- malignancies
- sarcoidosis
- connective tissue disorders
30
Eosinopenia (lt0.04 x 109/L)
- acute inflammatory response
- Administration of corticosteroids
- Cushings syndrome
- Acute stress (glucocorticoid adrenaline)