Apoptosis Mechanism Necrosis Pyroptosis Apoptosis: friend or - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Apoptosis Mechanism Necrosis Pyroptosis Apoptosis: friend or
Description:
Apoptosis Mechanism Necrosis Pyroptosis Apoptosis: friend or foe Chlamydia species PowerPoint Presentation Chlamydia modulates apoptosis Chlamydia both induces ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:694
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Apoptosis Mechanism Necrosis Pyroptosis Apoptosis: friend or
1
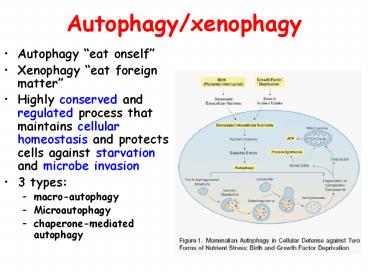
Autophagy/xenophagy
- Autophagy eat onself
- Xenophagy eat foreign matter
- Highly conserved and regulated process that
maintains cellular homeostasis and protects cells
against starvation and microbe invasion - 3 types
- macro-autophagy
- Microautophagy
- chaperone-mediated autophagy
2
Manipulating host responses
- Autophagy
- Apoptosis
3
Autophagic process
- Cytoplasmic organelles and portions of cytoplasm
sequestered in double membrane-bound vacuoles - Source of membrane multifactorial (ribosome-free
ER?) - Fuse with lysosomes
Nature reviews microbiology 2004 2301
Science 2004 306990
4
3 Stages
- Initiation nutrient starvation, growth
factor-mediated starvation - Execution
- Maturation
Nature reviews microbiology 2004 2301
5
InitiationSignaling pathways
- Trimeric G proteins
- Growth receptors
- PI3K (classes I III)
- protein phosphatases
- mTOR
6
Execution
- Requires covalent-conjugation pathways
- Requires Atg3, Atg7, Atg10
- Homologs of ubiquitinylation proteins
- Modifies pathway components but does not target
them for degradation
7
Execution (cont)
- Production of PIP3 via hVPS34 (class III PI3K)
- Inhibited by wortmanin, 3-Methyladenine
- Promotes proteolysis-gtproduction of amino acids
- Complex formed between hVPS34, Atg14, Atg6
(Beclin-1) which is necessary for downstream
recruitment and localization of Atg5 Atg12 - Covalent linkage of Atg5 and Atg12 on
pre-autophagosomal membrane - Protease cleavage of Atg8 (MAP1 Light chain 3
(LC3), followed by covalent lipidation to
phosphatidylethanolamine and translocation to
autophagosome membrane
8
Fusion
- Autophagosomes fuse with endosomes
- Acquire characteristics of lysosomes
- LAMP1 2
- Accessible to DAMP
- Cathepsins, acid phosphatases
- Vesicle fusion mediated by Rabs (Rab24)
9
Assays for autophagy
- EM
- Marker labeling
- Atg5 early autophagosomes
- Atg8/LCM3 early late
- Lysosomal markers (DAMP, lysosotracker)
- Monodansylcadaverine-fluorescent marker staining
- Genetically tractable organisms
- Knockout cells (Atg-5)
- Inhibitors (wortmannin, 3-MA)
- Inducers (amino acid starvation, rapamycin,
IFN-gamma)
10
Involved in many processes
- ATG6/Beclin 1 tumour suppressor gene
- Deleted in sporadic breast, ovarian, prostate CA
- Dauer formation in C. elegans
- ATG5 ATG7 Dictyostelium nitrogen starvation
- Prevent premature senescence
- Host defense against pathogen invasion
11
Microbes autophagy
- Diverse strategies
- Host defense
- Bacterial manipulate it to survive intracellularly
Nature reviews microbiology 2004 2301
12
Intracellular bacteria can by killed by autophagy
- Listeria (?ActA)
13
Legionella
- pregnant pause hypothesis
- Initially enter into autophagosomes
- Require type IV effector to delay maturation into
lysosomes
14
Legionella
- Membranous vacuole surrounded by double membrane
- Contains ER protein (BiP)
- Contains LAMP1, cathepsin D
- Dot/ICM mutants enter late endosomes/lysosomes
- Controversial
- ER membrane
- Inhibited by DN SAR1 ARF1, involved in ER-golgi
trafficking - Normal intracellular development in dictyostelium
Atg1, atg5, atg6, atg7, atg8 genes
15
Streptococcus pyogenes aka Group A Strep (GAS)
- Sore throat
- Glomerulonephritis
- Rheumatic fever and valvular heart disease
- Toxin-mediated skin infections
- Impetigo
- Scarlet Fever
- Necrotizing fasciitis (flesh eating bacteria)
- Toxic shock-like syndrome
16
GrpA strepAutophagy as host defense
- Binds to ECM produces toxins
- Invades non-phagocytic cells-gtvacuolar
escape-gtdegraded by autophagy - Initially enters early endosome (EEA1)
- Requires SLO to escape and enter autophagic
pathway - Vacuolar escape mutant (?SLO) avoids autophagy
- Atg5 deficient cells
- Vacuolar escape
- Avoids autophagic destruction
- Modest increase in intracellular bacterial titers
- Host cell ultimately undergo apoptosis
17
(No Transcript)
18
M. Tb
- Induction of autophagy (AA starvation, rapamycin)
augments phagolysome acidification - Blocked by Wortmannin 3-MA
- Induction of autophagy promotes maturation of
phagolysosome - Acquisition of cathepsin D, Lamp-1, vacuolar
ATPase, LBPA - Induction of autophagy promotes co-localization
of autophagic markers (LC3, beclin-1) - Induction of autophagy inhibits mycobacterial
survival - Mimicked by IFN-gamma
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
Shigellaa bug that disarms autophagyOgawa et al
Science 2005
Atg5
No autophagy
VirG
Atg5
?IcsBautophagy
IcsB
?VirG no autophagy
22
There are many ways to die
23
Apoptosis
- Programmed cell death
- Type I caspase mediated
- Type II autophagy-mediated
- Entire cell dismantled within membrane-enclosed
vesicles - Taken up by phagocytes, preventing release of
intracellular components from dying cells - Normal morphogenesis, removing genetically
damaged cells, proper tissue homeostasis,
invading microbes
24
Mechanism
- Sequential activation of cysteine proteases
(caspases) - Caspase 1-related 1,4,5,13,14
- Cytokine processing and pro-inflammatory cell
death - Initiator caspases 2, 8, 9, 10
- Effector caspases 3,6,7
- Regulated process
- Extrinsic stimulation of Fas or TNFR surface
receptors - Intrinsic altered mitochondrial membrane
integrity
25
Necrosis
- Cell swelling and rupture
- Release in intracellular components
- Activation of inflammatory response
- Can be regulated
- Can occur in concert with or instead of apoptosis
(e.g. if apoptosis is blocked)
26
Pyroptosis
- Caspase-1-dependent cell death
- Convert IL-1B and IL-18 to active forms
- Induced by Shigella IpaB and Salmonella SipB
27
Apoptosis friend or foe
- Host view
- Apoptosis is bad unless it takes away a
privileged intracellular niche - Pathogen view
- Inhibit apoptosis to provide for intracellular
niche (Chlamydia) - Promote apoptosis (Yersinia, Shigella)
- Dismantle host defense
- Promote microbe dissemination
- Many bacterial molecules can modulate apoptosis
- Toxins
- Type III secreted proteins
28
Chlamydia species
- Obligate intracellular bacteria
- Interesting intracellular life cycle
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Major cause of STDs in US and trachoma in
developing countries - Chlamydia pneumoniae
- Important cause of upper and lower respiratory
infections - Possible association with atherosclerotic heart
disease
29
- Diverges from endoctyic pathway immediately
- Acquires characteristics of golgli
- Sphingomyelin
- Cholesterol
- Rab1 (ER to golgi trafficking), Rab 11 (recycling
endosomes, TGN, plasma membrane), Rab 6 (Golgi-ER
trafficking, EE to TGN transport)
30
Chlamydia modulates apoptosis
- Chlamydiae-infected cells are protected against
mitochondria-dependent cell death but not
caspase-3 mediated cell death - Inhibits cytochrome C release
- Destroys pro-apoptotic BH3 domain containing
proteins (Bim/Bod, Puma, Bad) which are upstream
of Bax/Bak
31
Chlamydia both induces and inhibits apoptosis
- Chlamydia protein associated with death domains,
that interacts with death domains of TNF
receptors to activate apoptotic caspases
32
Salmonella-induced cell death is complicated
- Mutiple mechanisms
- Appears heterogeneous
- Apoptosis, necrosis, pyrotosis
- SPI-1-dependent caspase-1 dependent cell death
- Rapid
- Caspase-1 dependent
- Caspase-3 independent
- SipB-dependent
- SipB forms complex with Caspase-1
33
- SPI-1 dependent caspase-1 independent cell death
- Slower
- SipB-dependent
- Expression of SipB in caspase-1 deficient cells
lead to formation of lamellar structures..autophag
osomes? Fusing to mitochondria - SipB has fusogenic properties
34
SPI-2-dependent macrophage cell death
- Prolonged incubation (24 hrs)
- Caspase-1-dependent
- Caspase-1-deficient mice are resistant to
Salmonella infection
35
(No Transcript)