Bloodborne Pathogen training - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Bloodborne Pathogen training
Description:
OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIAL (OPIM for short) Saliva in dental procedures Any body fluid visibly contaminated with blood All body fluids in situations where ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:291
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bloodborne Pathogen training
1
(No Transcript)
2
Bonnie DiSalvo, MSASHMUSDA/ARS/NAA
OSHAs Bloodborne Pathogens Standard
3
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
Pathogenic organisms that are present in human
blood and can cause disease in humans. These
include, but are not limited to Hepatitis B
Virus (HBV), HCV and Human Immunodeficiency
Virus (HIV)
4
- Occupational Exposed Worker
- Reasonably anticipated skin, eye, mucous
membrane, or parenteral contact with blood or
other potentially infectious material that may
result from the performance of employee duties.
5
OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIAL (OPIM for
short)
- Saliva in dental procedures
- Any body fluid visibly contaminated with blood
- All body fluids in situations where it is
difficult or impossible to differentiate between
body fluids
6
Standard Requirements
- Written Exposure Control Plan
- Universal Precautions
- Engineering and work practice controls
7
Standard Requirements (cont)
- Basic housekeeping
- Medical prevention plan
- Training
- Labeling requirements and record keeping
- PPE
8
EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN1910.1030(c)
To eliminate or minimize employee exposure, the
employer shall develop a written Exposure Control
Plan that contains
- Employee exposure determination
- The schedule and method of implementing
paragraphs (d) to (h) of the standard - The procedures for evaluating circumstances
surrounding an exposure incident
9
EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN
- Reviewed and updated annually
- Reflect changes in technology that would reduce
or eliminate exposure - Document consideration of devices
10
EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN
- Solicit input from non-managerial employees
- Identification
- Evaluation
- Selection
- Effective engineering and work practice controls
- Document (c)(1)(v)
11
The Written ECP Should Include
- Use of universal precautions
- Engineering and work practice controls
- PPE
- Medical evaluations and vaccinations
- Training
- These elements are required by the standard, but
not necessarily in the ECP
12
November 2000 Law Requires
- Sharps Injury Log
- Documented non-managerial employee input on safer
medical devices - Documented evaluation and implementation of
safer medical devices at least annually
13
UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS
An approach to infection control. According to
the concept of Universal Precautions, all human
blood and body fluids are treated as if known to
be infectious for HIV, HBV, HCV and other
bloodborne pathogens.
14
- Universal/Standard Precautions
- This includes cell or tissue culture, culture
medium, solutions or tissues from humans,
experimental animals infected with HIV/HBV/HCV - For our research facilities, blood and tissue
products are treated under the standard
15
ENGINEERING CONTROLS
- Controls that isolate or remove the hazard from
the workplace - Examples
- Sharps disposal containers, self-sheathing
needles, safer medical devices, such as sharps
with engineered sharps injury protection and
needle-less systems
16
1910.1030(d)(2)(i) ENGINEERING CONTROLS AND WORK
PRACTICES
- Engineering and work practice controls to be
instituted as the PRIMARY means of eliminating or
minimizing exposure. - The employer MUST use engineering and work
practice controls to eliminate exposure or reduce
it to the lowest feasible extent.
17
1910.1030(d)(2)(i) ENGINEERING CONTROLS AND WORK
PRACTICES
- The employer should be using or at least have
considered, and documented in the exposure
control plan why he/she CANNOT use engineering
and work practice controls for work operations
involving exposure to blood or OPIM.
18
- (d)
- Work Practices
- Hand washing
- Personal hygiene
- Personal attire
- Not wearing personal protective equipment (PPE)
out of the work area - Changing PPE when contaminated
- Decontaminating/cleaning regularly after spills
19
(No Transcript)
20
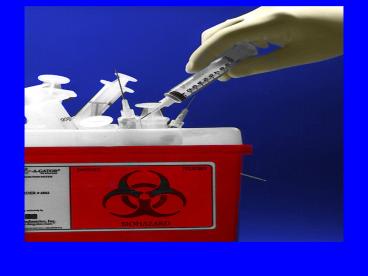
Sharps Disposal Containers
- Must be labeled or color-coded, puncture
resistant, leak-proof, and close-able - Should have well marked fill line, be translucent
or have translucent lid
Classified as medical device (SMDA)
21
Sharps Disposal Containers
- Establish collection schedules
- Provide placement of containers
- Review disposal procedures
22
NEEDLE SHIELDS THAT CONTAIN THE HAZARD
Attached to syringe needle
Attached to holder
Attached to needle
23
- Housekeeping
- Written schedule for cleaning and decontaminating
- Documented eye wash checks
- Material decontamination before exit from lab
- Removal of PPE from lab is prohibited
- Home laundering of PPE is prohibited
- Segregated waste
24
- Medical Prevention Plan
- (f) Vaccination, Post-Exposure Follow-up
- Hepatitis B vaccine made available to all workers
with potential risk of exposure - Offered within 10 days of employment
- No cost to worker
- Declination signed if employee declines
vaccine may accept at a later date
25
- (f) Vaccination, Post-Exposure Follow-up
- Report the incident immediately
- Inform supervisor
- Go to clinic/medical services provider
- Confidential medical evaluation
- Route of exposure
- Circumstances of the incident
- Source known
- Important to start drug therapy within 2 hours
- Testing of victim/source only with consent
(baseline blood stored for 90 days)
26
Decontamination
- What needs to be?
- What does not need to be?
- Create a schedule
- Requirements for medical equipment
- EPA disinfectants, 110 dilutions bleach, 2
glutaraldehyde
27
1910.1030(d)(3) PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
- (d)(3)(i) - PPE must be provided at NO COST to
the employee - (d)(3)(ii) This paragraph addresses that PPE
must be used properly per training received - (d)(3)(iii) - discusses provisions of appropriate
PPE, including hypoallergenic gloves as readily
available alternative to latex
28
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Appropriate PPE
- Testing standards
- ASTM ES 21 and ES 22
- Types
- When used and by whom
- Special needs
- No respiratory protection required
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
- Labeling and Training
- Labels must include universal biohazard symbol
and the term Biohazard - Wherever BBP or OPIM are
- Fluorescent orange-red
- Secured with string, tape, wire, adhesive
- Exceptions Blood products for clinical use,
blood samples in containers, blood drawing tubes
32
- Labeling and Training
- Signs posted at all work area entrances
- Biohazard symbol
- Infectious agent
- Entry requirements
- Name telephone of responsible person
33
- Record Keeping
- Occupational exposure/sharps injury record
- Confidential
- Kept for duration of employment, 30 years
- Includes
- Name social security number
- Vaccination status
- Examination results
34
- Record Keeping
- Training records
- Kept for 3 years
- Dates
- Contents
- Names qualifications of instructors
- Names job titles of students
- Annual documentation
35
Sharps Injury Log Information
- Type and brand of device involved
- Where incident occurred
- Description of how incident occurred
- Employee confidentiality must be maintained
36
Incident Reporting
- Set up a policy
- Record incidents in Sharps Injury Log
- Effective January 2002, Included on OSHA logs
(positives only)
37
Postexposure Evaluation and follow-up Incident
reports
- Document route of exposure
- Identify source
- Test source blood
- Give test results to worker
- Upon consent , test workers blood
38
Postexposure Evaluation(cont.)
- If no consent for HIV tests save blood for 90
days - Advise worker to seek medical attention
- Provide counseling
- Evaluate test results to give treatment if
needed
39
Physician's Written Opinion
- Complete within 15 days
- Worker must be informed of results and risks
- Employers have access to report
40
Types of Prophylaxis
- HBV
- vaccine, serum immunoglobulin
- HIV
- zidovudine
- lamivudine (3TC)
- Indinavir (IDV) when increased risk
- HCV
- None
41
Needlestick Prevention Device Evaluation Program
(NPD)
- Reasons for a program
- Program Components
- NPD Evaluation Criteria
42
Reasons for Program
- Regulatory
- Liability
- Ethics
43
Program Components
- Collect and Analyze Data
- Evaluate Devices
- Implementation
- Collect and Analyze Data
44
Collect and Analyze Data
- Review exposure records
- Target highest risk areas
- Determine device criteria and judgement scheme
45
Criteria to Consider
- Safety
- Healthcare Worker (HCW)
- Patient
- Other Individuals
46
Evaluate Devices
- Involve multiple users in variety of locations
- Use devices in the field
- Prepare cost analysis
47
Criteria to Consider
- Human Factors
- Ease of Use
- Training
- Patient Comfort
48
(No Transcript)
49
BIOHAZARD SYMBOL
BIOHAZARD
50
Treat as regulated medical waste Follow State ,
federal and local regulations For perception
issues on uncontaminated sharps and lab
waste-discuss