THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
1 / 20
Title: THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
1
THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
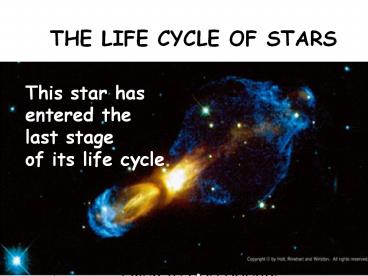
This star has entered the last stage of its
life cycle
2
- The first stage of star formation is NUCLEAR
FUSION - Gravity pulls clouds ofgas and dust (nebulae)
together into a sphere as it becomes denser, it
gets hotter and the hydrogen changes to helium.
3
- Stars are classified by
- Size
- Brightness
- Mass
- Color
- Temperature
- Spectrum
- Age
4
TYPES OF STARS
- MAIN SEQUENCE STARS this is the second phase
and the longest phase - Energy is generated in the core as hydrogen atoms
fuse into helium atoms - Stars are about 98 Hydrogen and Helium
- The sun in this stage (10 million yrs. to become
this stage has been shining for 5 billion years
) Earth is 4.6 billion years old
5
GIANTS AND SUPERGIANTS
- Third stage RED GIANT
- RED GIANT A large reddish star late in its life
cycle - a star that expands and cools once it
uses all of its hydrogen - Eventually will shrink
- When shrinks atmosphere grows large and cools
to a red giant or red supergiant - In 5 billion years the sun will become a red
giant
6
- Red giants 10 or more times bigger than the
sun. - Red Supergiants at least 100 times bigger than
the sun.
7
WHITE DWARFS AND RED DWARFS
- WHITE DWARF a small, hot, dim star that is the
leftover center of an old star - No hydrogen left
- Can shine for billions of years before they cool
completely - RED DWARF low-mass stars
- Oldest stars in the universe
8
BLUE STARS
- BLUE STARS very massive blue stars are not in
the main sequence very long. - They quickly use up the hydrogen in their cores
- Expand and turn into giants or supergiants
9
SUPERNOVAS
- A main sequence star with a mass of more than
about 10 Suns experiences a spectacular end. - It swells into a red supergiant with cooling,
expanding outer layers. - Eventually its core collapses, causing a huge
explosion known as a supernova
10
- A gigantic explosion in which a massive star
collapses and throws its outer layers into space
11
NEUTRON STARS and PULSARS
- NEUTRON STAR a star that has collapsed under
gravity to the point that the electrons and
protons have smashed together to form neutrons - If the core of a supernova has relatively low
mass, the core will be crushed into a tiny, super
dense neutron star - PULSAR a spinning neutron star
12
BLACK HOLE
- A volume of space in which gravity is SO GREAT
that nothing can escape, not even light, although
objects can fall in - If the core of a supernova has a mass of more
than about two Suns, its own gravity will squash
it further, into a black hole.
13
HR Diagram (page 592 593)Shows the
relationship between a stars surface temperature
and absolute magnitude.
14
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- The temperature is given along the bottom of the
diagram.
15
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- The absolute magnitude (brightness) is given
along the left side.
16
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- The Hot (blue) stars are located on the LEFT
- The Cool (red) stars are located on the RIGHT.
17
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
- The BRIGHT stars are at the TOP.
- The DIM stars are at the BOTTOM.
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
- The DIAGONAL pattern where most stars lie is the
MAIN SEQUENCE. - The SUN is located in the middle of the diagram.
- Average stars like the sun become giants or
supergiants (Right) and then down to the left to
become white dwarfs.