Comparing Business Organizations PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title: Comparing Business Organizations
1
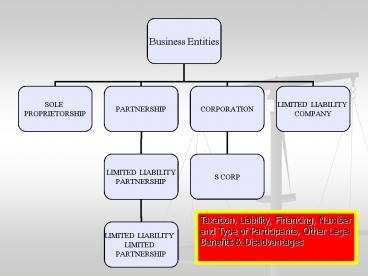
Taxation, Liability, Financing, Number and Type
of Participants, Other Legal Benefits
Disadvantages
2
General Partnerships
- Benefits
- NO DOUBLE TAXATION (Pass Through Taxation).
- Individuals Business Entities Can Be Partners.
- No Formal Process Required for Formation.
- Disadvantages
- Unlimited Liability
- UPA (Uniform Partnership Act)
- Articles of Partnership
3
Formation of a Partnership
- Voluntary
- Association of two or more persons
- Carrying on Business
- For Profit
- As Co-Owners
- Share Profits Losses and Important Management
Decisions - But see Creditors, Landlords
- No Express or Specific Intent Required.
4
Existence of a Partnership?
- FACTS Sweet was an hourly employee at Vohland
Nursery. After serving in the military Sweet
came back to work at the Nursery. There was no
written partnership agreement. Sweet did not
contribute any capital to the Nursery. Sweet
claims Vohland and him verbally agreed that Sweet
would have a 20 partnership interest in the
Nursery. Sweet Vohland sat down together on an
irregular basis every several weeks to determine
the Nurserys net profit. Sweet was then given a
check for 20 of the Nurserys net profit. No
social security or income taxes were withheld
from Sweets checks. Sweet claimed himself as
self-employed on his personal tax return paid
self-employment taxes. Vohland managed the
finances while Sweet managed the physical
operations of the Nursery. Sweet brings suit to
dissolve the partnership and collect his 20 of
the Nurserys inventory. - Q Did Vohland and Sweet enter into a
Partnership? - Q What if Sweet had received a pay-check every
two weeks that withheld social security and
income taxes?
5
Contributions Partnership Property
- Contributions of Capital, Labor, Assets
- Partnership Property
- Business v. Personal Use
- Majority of partners must agree to personal use.
- Personal Property Used in Business
- Partnership Property v. Personal Property
- RULE Totality of the circumstances.
- Presumptions
- Listed as an asset on Partnerships Books
- Partnership Paid Insurance on It
- Partnership Paid Taxes on It
6
Facts Allen bought a laptop from Best Buy with
his own personal money. Each day Allen brings
the laptop to work and allows the Partnerships
secretary to use it. Each night Allen takes the
laptop back home.
- Q Is the laptop Partnership property or
personal property being used by the Partnership? - A Personal property being used by Partnership.
- Q What if the Partnership paid for insurance on
the laptop? - A Could be personal or Partnership property.
7
Standard Partnership Provisions
- Partnership Name
- Voice in Management
- Equal Right to Participate in Management
(default) - Majority Rulegenerally partnersship decisions
only require majority of partners consent. - Unanimous Consent RequiredFor actions that are
contrary to Partnership Agreement or
fundamentally change the nature of the business.
8
FACTS Allen, Bob Carl formed a partnership
for the purpose of designing and selling tennis
shoes. The Partnership bought a retail shop
downtown. Bob hears the market in real estate is
really booming right now and wants to sell the
building for a profit. Bob convinces Allen that
the Partnership should sell the building. Carl
objects. Q Can Carl prevent Allen Bob
from selling the Partnerships downtown retail
building?
- ANSWER Unanimous Consent Required to
- Sell all of Business Inventory or Business
Building. - Guarantee Debts of a Partner.
9
Partnership Rights Duties
- Right to Compensation
- Profits Losses shared EQUALLY.
- Not entitled to wages, rent, interest.
- Duty to Inform.
- Duty to Account.
- Duty of Care in Partnership Business.
- Duty of Loyalty Good Faith
- Must not compete with or injure partnership.
- May not make secret profits.
10
FACTS Levy and Disharoon formed a partnership
for the purpose of purchasing a jet and operating
a charter airline service. Disharoon located a
jet and informed Levy that it could be purchased
for 963,000. After securing Levys approval,
Disharoon arranged to have the partnership borrow
975,000 to make the purchase. Unbeknownst to
Levy, Disharoon had actually contracted to buy
the jet for 860,000. Disharoon paid 860,000
for the jet and deposited 103,000 in his
personal bank account. Upon discovering
Disharoons misrepresentation, Levy sued for both
actual and punitive damages on a theory of breach
of loyalty and good faith.
- Q What duties did Disharoon breach, if any?
- A Duty to inform
- Duty of loyalty good faith
- Duty to account (maybe)
11
Partnership Authority
- Express Authority Partnership Agreement.
- Partnership Agreement can limit a partners
actual authority. - Implied Authority Every Partner is an Agent of
the Partnership. - Apparent Authority When 3rd Party Justifiably
Relies on Partners Implied Authority. - Partnership By Estoppelindividuals can be
estopped from leading 3rd parties to believe they
are partners when in fact they are not.
12
Partnership By Estoppel
- FACTS Leslie has not agreed to be partners with
Jamie, but Leslie accompanies Jamie to the Bank
where they speak with a loan officer. Jamie tells
the loan officer that she Leslie are going to
open a Bar together. Leslie does not correct
Jamie. The Bank loans Jamie 50,000. Leslie
does not share in the losses or profits from the
Bar and does not make any management decisions.
Jamie later defaults on the loan. The Bank sues
both Jamie Leslie to collect the debt. - Q Is Leslie Liable for the 50,000 loan?
- Q What if the Bank found out Leslie was not a
partner before loaning Jamie the 50,000?
13
Unlimited Liability
- Contract Liability
- Only jointly liable.
- Indemnification
- Tort Liability
- Partners jointly severally liable.
- Criminal Liability
- Partnership
- Individual Partners
14
FACTS Jose Joseph were both medical doctors
who were partners in a medical practice. Both
doctors treated Elaine Zuckerman during her
pregnancy. Her son was born with severe physical
problems. Zuckerman sued both Jose Joseph for
malpractice. The jury found Jose guilty, but
Joseph not guilty. The jury granted Zuckerman 4
million in damages.
- Q Can Zuckerman collect tort damages from
Joseph? - Answer Partners are jointly severally liable
for torts committed in the commission of the
partnerships business.
15
FACTS Jose Joseph were both medical doctors
who were partners in a medical practice. Both
doctors treated Elaine Zuckerman during her
pregnancy. Her son was born with severe physical
problems. Zuckerman sued both Jose Joseph for
malpractice. The jury found Jose guilty, but
Joseph not guilty. The jury granted Zuckerman 4
million in damages.
- Q If Jose was held criminally liable for
practicing medicine without a license would the
Partnership be liable? Would Joseph be liable? - Answer Partnership is liable, but Joseph is not
as long as Joseph did not directly participate in
or encourage the criminal behavior.
16
Facts Davis Mitchell formed a General
Partnership to purchase rental property for
investment purposes. The Partnership purchased
real property from Kemmler Foundation on credit.
Davis signed a 150,000 promissory note to the
Foundation as Cliff W. Davis, Partner. Before
executing the note, Davis Mitchell entered into
an agreement that provided only Davis AND NOT
Mitchell would be personally liable on the note.
Foundation had no knowledge of the agreement.
The Partnership defaults on the note.
- Q Is Mitchell Liable for the Note?
- Answer Mitchell is liable because Foundation
justifiably relied on Mitchells implied
authority. - Q What if the Foundation knew about the
agreement? - Answer Mitchell is not liable, because
Foundation did not justifiably rely on Mitchells
implied authority.
17
Liabilities of Outgoing Incoming Partners
- Liability of Outgoing Partners
- Continuation of Partnershipdeparting partner not
liable for any new debts obligations after
notifying creditors of his or her departure. - Novationagreement between creditors and
continuing partners to release withdrawing
partner from liability. - Liability of Incoming Partners
- Liable for existing debts obligations only to
the extent of his or her capital contribution. - Liability not limited as to debts obligations
incurred after becoming a partner.
18
Dissolution of Partnership
- Dissolution
- Types of Dissolution Non-Wrongful, Wrongful,
Automatic, By Court Order. - Terminates partners actual authority to enter
into contracts and act on behalf of the
partnership. - DOES NOT terminate Partnerships or personal
liability. - Partnership at Will v. Partnership for a Term
- Power to Withdraw at any time.
- Right to Withdraw Wrongful Dissolution
- Notice of DissolutionFailure to properly notify
3rd parties may create liability based on
apparent authority. - Actual Notice (3rd parties that actually dealt
with partnership) - Constructive Notice (3rd parties that had
knowledge of partnership) - No Notice (3rd parties that had no knowledge of
partnership) - Continuation of Partnership After Dissolution
19
Winding Up Partnership
- Distribution of Assets
- Outside Creditors of the Firm.
- Debts owed to Partners.
- Return of each partners Capital Contribution.
- Remaining assets divided as profits according to
Articles of Partnership. - Compensation for Winding Up
- Only upon death of a partner are surviving
partners entitled to compensation.
20
Limited Partnership
- (Revised) Uniform Limited Partnership Act RULPA
- Requires General Partner(s) Limited Partner(s)
- General Partnersmanage business, personally
liable. - Limited Partnerscan not manage business, but
limited in liability to only invest capital. - Any person or business entity can be a general or
limited partner. - Corporations as General Partnerliability limited
to its assets. - FormationCertificate of Limited Partnership
- Filed with secretary of state and, sometimes, in
counties where LP conducts business. - LP name, general character of business, principle
place of business, names addresses
distinction of each partner, dissolution date,
description amount of each partners capital
contribution, etc.
21
Partners Liability in aLimited Partnership
- Liability
- General Partnersunlimited liability
- Limited Partnersliable only to extent of
investment - Exceptions
- Limited Partners actions led 3rd party to
reasonably believe the limited partner was a
general partner - Personal Guarantees
- Rights
- Limited Partnersno right to act on LPs behalf
22
Limited Partnership
- Defective Formation
- Certificate not properly filed.
- Defects in Certificate.
- Other statutory requirements not met.
- Limited Partners become liable as General
Partners - Liable to 3rd parties who transact business with
the enterprise before defective formation is
corrected. - Correcting Good Faith Defective Formation (2
options) - Cause appropriate certificate to be filed.
- Withdraw from any future equity participation and
file certificate showing withdrawal.
23
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- All partners are limited partners (no general
partners) - No Personal Liability beyond capital investment.
- Government filing required (Domestic LLP v.
Foreign LLP) - Liability insurance required.
- Restricted to Certain Professions (most states)
24
Comparing Business Organizations