Absolute Instability PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title: Absolute Instability
1
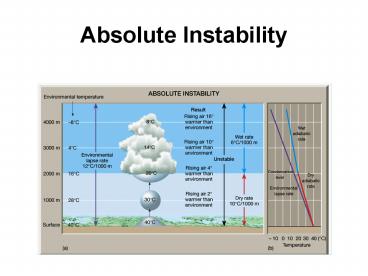
Absolute Instability
2
Absolute Stability
3
Conditional Instability
4
Inversions
- An inversion is defined as any layer of the
atmosphere where the vertical temperature profile
increases with altitude
5
Coriolis Effect
- The Coriolis effect deflects the air flow to the
right in the northern hemisphere and to the left
in the southern hemisphere
6
Geostrophic Wind
- PGF CF winds tend to move parallel to isobars
7
Basic Circulation Patterns
8
Cold Fronts
- Cold air is invading an area of warm air
- The cold air mass is dense and hugs the ground
- The cold air forces the warm air to rise rapidly
9
Warm Fronts
- Warm air is moving into a region of cold air
- The warm air is forced to rise gradually above
the cold air - The rising air cools, creating stratus clouds and
precipitation
10
Occluded Fronts
- Produced when a cold front overtakes a warm front
- The warm air is forced completely off the ground
- Abrupt lifting by the cold air creates
precipitation
11
Global Circulation System
12
Surface Winds
- Hadley Cells
- Hot air rises from the equator and flows to 30
degrees south and north latitudes - At this point the air will cool, and descend back
to the surface, heating due to compression
13
Temperature Layers - Oceans
- The oceans also have a layered structure of
thermal regions - Temperatures are highest at the surface and
decrease with depth - Wave action tends to mix warm surface waters
fairly deeply - Below this warm layer is a thermocline
- Below that is a very cold layer of water that
extends to the ocean bottom It may drop to 0
Celsius - In the Arctic and Antarctic regions the warm
layer and thermocline are absent
14
Deep Currents and Thermohaline Circulation
- Deep currents move ocean water in a slow circuit
across the floors of the ocean - As surface waters in the North Atlantic become
cold and dense, they sink to the bottom of the
ocean and and move along the ocean floor to the
southern ocean where they are brought back to the
surface by upwelling and mixing
15
Deep Currents
- At the same time, there are also broad, slow
surface currents - Together these are referred to as the
thermohaline circulation, because they depend on
the temperature and salinity of ocean water
16
El Nino
- A cyclical disturbance of the ocean and
atmosphere - Occurs at intervals of three to eight years
- Begins in the eastern Pacific and spreads its
influence widely - At the beginning of winter the waters off of the
coast of Peru warm once every few years - This warming occurs at irregular intervals and
reduces the fish population off of the coast,
brings about droughts in some parts of the world,
heavy rainfalls in others, and extremes of
temperatures