Microbe of the Week PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title: Microbe of the Week
1
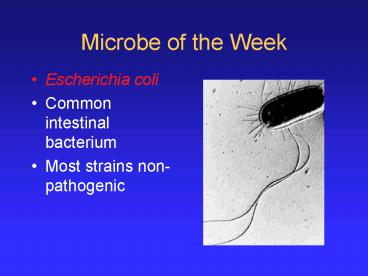
Microbe of the Week
- Escherichia coli
- Common intestinal bacterium
- Most strains non-pathogenic
2
Escherichia coli
3
Escherichia coli
- Gram negative rod
- Divides in 20 minutes under optimal conditions
- Widely used in molecular biology
4
Escherichia coli
- Some strains produce exotoxins that cause
intestinal damage - Example E. coli 0157
5
Prokaryotes
- Functional Anatomy
6
Escherichia coli
- Ferments lactose to produce acid
- Indicator organism for fecal contamination of
water or food
7
Prokaryotes
- Cell walls usually peptidoglycan, a complex
polysaccharide - Divide by binary fission
- No internal membrane-bound organelles
- Include bacteria and archaea (no peptidoglycan)
- Unicellular
8
TOPICS
- External structures
- Cell Envelope
- Internal Structures
- Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes
- Classification
- Archaea
- Biofilms
9
(No Transcript)
10
External Structures
- Flagella
- Pili and fimbriae
- Glycocalyx
11
Flagella
- Flagella (singlular flagellum)
- Composed of protein subunits
- Motility (chemotaxis)
- Varied arrangement
- Monotrichous - single flagellum
- Lophotrichous - small bunches
- Amphitrichous - both poles of the cell
- Peritrichous - randomly over cell surface
12
(No Transcript)
13
Flagella Structure
14
Chemotaxis
15
Proteus vulgaris Swarming(due to peritrichous
flagella)
16
Axial Filament of Spirochetes
- Spirochete bacteria have their flagella embedded
in the membrane
17
Diagnostic Use of Flagella
- H antigen differs within a species and can be
used to distinguish a serovar (serotype) - Example E. coli O157H7 makes a potent toxin that
causes gastroenteritis
18
Pili and Fimbriae
- Fimbriae are used for attachment
19
Pili and Fimbriae
- Pili are used for mating (conjugation)
20
Glycocalyx
- Polysaccharide or polypeptide coat that surrounds
cells - also called extracellular polysaccharide
(EPS) - Made inside cell and secreted
21
Function of Glycocalyx
- Virulence factor (disease severity)
- avoid phagocytosis (being engulfed and killed by
WBC) - Attachment to surfaces
- Protection from drying, viruses
- Provide nutrients
22
Capsule
- Capsule organized and tightly attached to cell
wall
23
Slime Layer (EPS)
- Slime layer unorganized, loosely attached to
cell wall
24
Biofilms
- Biofilm a microbial community attached to a
surface - May be one or several organisms
25
Environmental Biofilms
26
Environmental Biofilms
27
Environmental Biofilms
28
Infectious Disease Biofilms
29
Infectious Disease Biofilms
- On implants
30
Some Medically Important Biofilms
- CDC estimate 65 of human bacterial infections
are associated with biofilms in vivo - Dental plaque
- Infectious kidney stones
- Endocarditis
- Catheters
- Cystic Fibrosis
31
Cell Envelope
- Cell Wall
- classification
- shape
- Cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane
32
Cell Wall
- Located just outside plasma membrane
- Functions
- maintains cell shape
- protects cell from rupturing when water pressure
is higher inside cell - anchors flagella
- Differentiated by Gram stain
33
Peptidoglycan (PG)
- Repeating disaccharide of N-acetylglucosamine
(NAG) and n-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) - Cross linked by polypeptides
- Penicillin blocks peptidoglycan cross-linking
- Lysozyme breaks peptidoglycan
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
Gram Positive Cell Wall
- Many layers of peptidoglycan
- Teichoic acid
- Regulate positive ion flow
- Protect wall from breakdown
- Antigen specificity of cells
37
(No Transcript)
38
Gram Negative Cell Wall
- Thin peptidoglycan, no teichoic acid
- Outer membrane (OM) contains lipopolysaccharide
(LPS) endotoxin ( O antigen) - Protects cell from penicillin, lysozyme
- Contains porins that form channels to allow
passage of nutrients
39
LPS
40
(No Transcript)
41
Gram Positive and Negative Cell Walls
42
Cytoplasmic membrane
- Lipid bilayer
- Phoispholipids
- Proteins
- Functions
- Regulates transport
- Site of ATP synthesis
43
Atypical Cell Walls
- Acid-Fast Staining wall
- Mycobacteria (TB, leprosy)
- Very thick outer lipid layer - acid fast
- Slow nutrient exchange
- Slow growth
44
Atypical Cell Walls
- No cell wall
- Mycoplasma lack cell wall - pleiotropic
45
Damage to Cell Walls
- Digested by lysozyme
- Gram positive bacteria become protoplasts, lyse
in distilled water by osmotic lysis - Gram negative cells become spheroplasts
46
Damage to Cell WallsProtoplasts, Spheroplasts
47
To Be Continued
- Internal Structures
- Cell shapes and arrangements
- Classification
- Archaea