South Korea 45'1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
South Korea 45'1
Description:
Often blurts out answers before question completed. ... Using language to acquire new skills, understand jokes and riddles. Enlarged memory capacity. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:45
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: South Korea 45'1
1
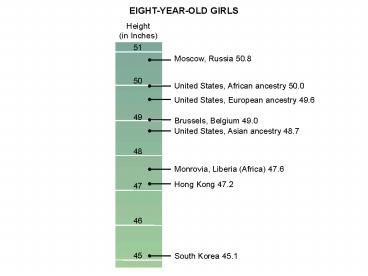
EIGHT-YEAR-OLD GIRLS
Height (in Inches)
51
Moscow, Russia 50.8
50
United States, African ancestry 50.0
United States, European ancestry 49.6
49
Brussels, Belgium 49.0
United States, Asian ancestry 48.7
48
Monrovia, Liberia (Africa) 47.6
Hong Kong 47.2
47
46
South Korea 45.1
45
2
Obesity in Childhood
- 80 of obese children become obese adults.
- Obese children generally have obese parents.
- Early excessive fat storage leads to
overabundance of fat cells. - Obese individuals are more responsive to external
eating signals. - Obese individuals eat faster and chew less.
- Mothers of obese children interpret all
expressions as a need for food, and use food as a
reward. - Obese children are less active.
- Social consequences of obesity include
- Behavior problems
- Depression
- Lowered self-esteem
3
Physical Effects of Childhood Athletics
Negative
Positive
Sports-related injuries
Better physical fitness Improved motor
coordination
Psychological Effects of Childhood Athletics
Negative
Positive
Training in achievement motivation (e.g.,
bettering previous running times)
Competition (e.g., more concern with winning than
with performance as such) Excessive pressure
from adults to practice, perform well and win
4
males
females
males
females
RUNNING
THROWING
200
7.6
180
7.2
160
6.8
140
6.4
Yards per Second
120
Feet
6.0
100
5.6
80
5.2
60
4.8
40
4.4
20
4.0
0
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Age
Age
5
Ages 5 - 14 Girls
Ages 15 - 24 Boys
Ages 15 - 24 Girls
Ages 5 - 14 Boys
150
135
120
60
Frequency per 100,000 children
45
30
15
0
All causes
Motor vehicle accidents
Drownings, fires, poisons
Other accidents
Infections
Cancer (all kinds)
Heart diseases
Homicides
Suicides
Accidents
Diseases (selected)
Violence
Cause of Death
6
Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity
Disorder
- Often fidgets with hands or feet, or squirms in
seat. - Difficulty remaining seated when required.
- Easily distracted by extraneous stimuli.
- Difficulty awaiting turn in games or groups.
- Often blurts out answers before question
completed. - Difficulty following through on instructions (not
due to lack of comprehension) fails to finish
chores. - Difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play.
- Shifts from one incomplete activity to another.
- Difficulty playing quietly.
- Often talks excessively.
- Often interrupts or intrudes on others.
- Often doesnt listen to what is said to him or
her. - Often loses things needed at home or school
(pencils, books, assignments) - Often engages in dangerous activities without
considering possible consequences. - Source Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of
Mental Disorders (IV). (1994). American
Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC.
7
Characteristics of Concrete Operational Thought
- Conservation has developed.
- Classification and categorization have developed.
- Ability to resolve contradictions.
- Comprehension of past, present, and future.
- Understanding of reversibility child has control
and flexibility. - Using the alphabet for organization.
- Ability to verbalize directions.
- Ability to transpose (i.e., see things from
anothers viewpoint). - Comprehension of relational terms.
- Can use simple logic.
8
Original Setup
Alter as Shown
Ask Child
Usual Answer
Which has more liquid?
Conservation of liquid
Has more
Do they both weigh the same, or does one weigh
more than the other?
Conservation of mass
Weighs more
Are there still as many pennies as nickels, or
more of one than the other?
Conservation of number
More
Are they the same length, or is one longer?
Conservation of length
Is longer
Is one pencil as long as the other, or is one
longer?
Conservation of length
Is longer
9
Developmental Changes in Recall Memory
10
9
8
7
Digit Span
6
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
adults
Age
10
Spanish
Other languages
Total non-English language
Asian language
16
13.8
14
12
11.0
10
Percentage
7.5
8
6
5.3
4.6
4.4
4
1.9
2
1.1
0
1980
1990
11
Second Language Learning as a Function of Age
276
270
260
250
240
Mean score
230
220
210
Native
3 - 7
8 - 10
11- 15
17 - 39
Age of arrival
12
The Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
Examples
Realm of Intelligence
Coding and representing information planning and
executing solutions to problems Skills with
novel problems and familiar problems in novel
settings skill at solving problems automatically
as they become familiar Deliberate adaptation,
alteration, and selection of learning
environments to facilitate problem solving
Componential Experiential Contextual
13
GARDNER'S THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES
- Language skill
- Musical skill
- Logical skill
- Spatial skill
- Kinesthetic, or body balance, skill
- Interpersonal and intrapersonal skills
14
Summary of Middle Childhood Physical Development
- Growth has slowed down.
- Increased endurance
- Improved running, throwing, swimming, bicycling,
and skating. - Better motor control.
15
Summary of Middle Childhood Cognitive Development
- Reach Piagets concrete operational thought
stage. - Becoming logical.
- Using language to acquire new skills, understand
jokes and riddles. - Enlarged memory capacity.
- Understand arithmetical concepts.