Knowledge Acquisition PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Knowledge Acquisition
1
Knowledge Acquisition
see Course Readings Extracting expertise from
Experts Methods for Knowledge Acquisition p. 35
2
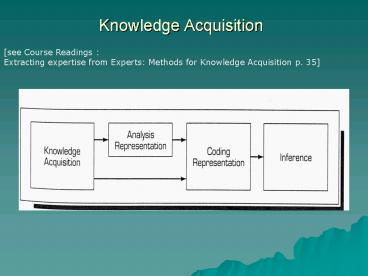
Knowledge Acquisition
- Knowledge is elicited from the expert (or other
sources), represented and then coded into the
knowledge base. - elicitation techniques
- manual
- semi-automated
- automated
- representation schemes could be
- decision trees
- influence diagrams
- rule matrices
- conceptual graphs
3
Elicitation techniques manual approaches
- unstructured/structured interviews
- good for identifying facts and procedures in the
problem domain. - can gain confidence, normally used at the
beginning of the acquisition phase. - documented by transcripts leading to a graphical
representation using a technique such as
conceptual graph/influence diagram
4
Elicitation techniques manual approaches
- protocol analysis
- the expert performs the task and verbalises the
decision making (documented by transcripts). - Several strategies are possible
- perform familiar or common tasks, then make it a
bit harder - perform familiar tasks but withhold some
information - perform familiar tasks under a time constraint
- perform difficult tasks by using tough data
5
Elicitation techniques manual approaches
- Advantages and disadvantages of protocol analysis
- expert consciously considers decision making
heuristics - but this requires an awareness on the part of the
expert - expert consciously considers decision
alternatives, attributes and values - but this requires that the expert can
categorize major decision alternatives - developer can observe and analyze decision making
behaviour - but this requires the expert is able to verbalize
the attributes and values of a decision variable
6
Elicitation techniques manual approaches
- Advantages and disadvantages of protocol analysis
- and finally
- the developer can later check the decision making
behaviour with the expert - but is this all a subjective view. Does the
explanation match the actual reasoning? or
does it matter
7
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- These approaches are sometimes referred to as
indirect methods - The expert is not being asked to express their
knowledge directly, instead they carry out
tasks' and from the results a structure for the
problem domain can be determined. - The methods themselves are taken from Cognitive
Psychology.
8
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- 1. Multidimensional Scaling
- Trying to establish similarity between
concepts/objects across a number of dimensions. - The expert estimates similarity b/w each
possible pair on some scale (0 - 1, 0 9, 1
-16 etc) - Analysis of similarity matrices leads to the
concepts/objects being clustered in space - The expert can inspect and describe this
diagram.
9
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- 1. Multidimensional Scaling
- example
- the concepts Farm domestic animals goat,
cow, sheep, pig, horse, dog, rabbit - dimension size i.e. how similar are they in
terms of size? - A similarity matrix can be constructed
10
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- The higher the number the less similar the
concepts are
11
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- Many more similarity matrices could be formed
using different dimensions e.g. behaviour,
temperment, suitability for human consumption etc - A clustering algorithm is then applied to the
matrices to produce a diagram that shows how
similar (in an overall sense) the concepts are. - See figures 7, 8 9 on pages 41-42 of the course
readings
12
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- 2. Repertory grid analysis
- The focus is now on difference as well as
similarity - from clinical psychology - personal construct
theory - important objects/concepts are identified
- The concepts are represented to the
client(expert) in groups of three - The expert is asked which one is different from
the other two? and then in what way? (the
answer to the 2nd question provides a construct) - The expert is then asked to rate the other
concepts in terms of the construct - (on some lickert style scale)
13
Elicitation techniques semi-automated approaches
- 2. Repertory grid analysis
- This process continues until a series of
constructs are built up. A rating grid can then
be produced (e.g. see fig 19 p. 47) - From this a distance matrix and a hierarchy chart
can be developed (see figures 20 21 p.47)
14
Elicitation techniques Summary
- Activity identifying general decision making
heuristics and concepts. - Technique structured interviews.
- Activity identifying routine tasks or
procedures during the decision making. - Technique structured interviews, protocol
analysis. - Activity identifying major concepts,
relationships i.e a semantic view of the problem
domain. - Technique semi-automated approaches such as
multi-dimensional scaling, repertory grid
analysis.