Primary IDS: Single gene Defects Xlinked PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title: Primary IDS: Single gene Defects Xlinked
1
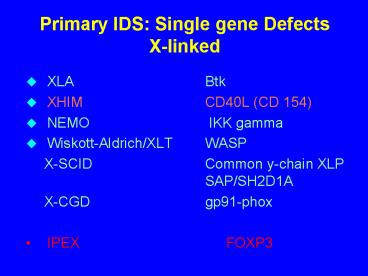
Primary IDS Single gene Defects X-linked
- XLA Btk
- XHIM CD40L (CD 154)
- NEMO IKK gamma
- Wiskott-Aldrich/XLT WASP
- X-SCID Common y-chain XLP SAP/SH2D1A
- X-CGD gp91-phox
- IPEX FOXP3
2
Primary IDS Single gene Defects autosomal
recessive
- Ragl/Rag2 deficient SCID, Omenn Syndrome
- Jak3 Zap 70 MHCII deficiency.
- ADA, PNP deficiency.
- AT (ATM) NBS (NBS 1)
- FAS FAS-L Caspase 3 Caspase 10 deficiency.
- LAD 1 (CD 18 deficiency)
- Agammaglobulinemia (mH, l5, Iga)
- Autosomal CGD (p22 p47 p67-phox)
- Hyper IgE STAT3 Tyk2
- CVID ICOS TACI CD19 CD21 BAFF-R
- IgM Hyper and normal CD40L CD40 AID UNG
3
Hyper IgM Syndromes (HIGM)
- X-linked HIGM CD40L mutations
- CD40 mutation
- Activation induced cytidine deaminase
- (AID) deficiency
- Uracil-DNA Glycosylase (UNG) deficiency
- NEMO deficiency (associated with hypo- hidrotic
ectodermal dysplasia) - Unknown gene(s)
- Misdiagnosis Btk (XLA), SH2D1A/Birc4 (XLP),
CVID, - ATM (AT)
4
X-LINKED HYPER-IgM SYNDROME (HIGM1)
A rare primary immunodeficiency characterized by
- recurrent bacterial and opportunistic
infections - neutropenia - very low serum
IgG/IgA, with normal/high IgM - normal T and B
lymphocyte counts - impaired germinal centers
formation - impaired generation of memory B
cells - reduced somatic hypermutation - impaired
T -lymphocytes/DC cross-talk Caused by
mutations in the TNFSF5R (CD40L) gene
5
X-linked Hyper-IgM Syndrome
- Evidence suggesting broader T cell dysfunction
- Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (43)
- Cryptosporidium infection (52)
- Stomatitis, Neutropenia
- Lymphoid hyperplasia, Malignancy
6
KAPLAN-MEIER SURVIVAL CURVE IN 126 XHIM
PATIENTS
100
80
Survival ( )
60
40
20
0
0 5 10 15 20
25 30 35 40
106 75 39 22 6
2 1
At risk
Time ( y )
7
REDUCED NUMBER OF MEMORY B CELLS (BOTH SWITCHED
AND UNSWITCHED) IN HIGM3
switched memory B cells
unswitched memory B cells
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
Hyper IgM syndromes
T
Cytokines IL- 4
CD40L
CD4O
AID
NEMO
NEMO-IKK
UNG
Germinal Center Formation
NF-?B
CSR-def
SHM
CSR
B
IgAEG
11
THREE FAMILIES WITH AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE HYPER-IgM
SYNDROME TYPE 3 (HIGM3)
Pt. 1 (Italy)
Pt. 4
Pt. 2
Pt. 3
(Turkey)
(Saudi Arabia)
12
Clinical and laboratory features in 4 children
with autosomal-recessive hyper-IgM syndrome type
3 (HIGM3)
sex age IP chronic scler. FTT neutropenia
eosinophilia (mo) diarrhea cholang. Pt. 1 F
4 no no
no no yes
(PCP) Pt. 2 M 60 no no no
no yes no Pt. 3 F 84
no no yes no yes Pt.
4 F 12 yes yes
no yes (RSV) (Crypt.)
13
Immunological features in 4 children with
autosomal-recessive hyper-IgM syndrome type 3
(HIGM3)
IgG IgA IgM CD3 CD19 PHA (mg/dl)
(mg/dl) (mg/dl) () () (cpm
x10 ) Pt. 1 180 lt6.6 81 73
16 124 Pt. 2 120 lt6.6 400 75
19 122 Pt. 3 135 lt6.6 200 76
20 138 Pt. 4 lt150 lt6.6 80 56
35 128 n.v. 351-1916 17-178 48-347
71?7 18 ?6 116-188
-3
14
Activation Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID)
Deficiency
- Very low IgG, A, E
- Normal or IgM
- Hyperplasia of lymph nodes and tonsils
- Neutropenia never
- CPC never
- Malignancies incidence not increased
15
AID DEFICIENCY CLINICAL AND MOLECULAR FEATURES
Genetics autosomal recessive disease,
due to mutations of
the Activation Induced
cytidine
Deaminase (AID) gene Clinical features recurrent
URTI and LRTI of bacterial origin,
tonsils and lymph
node enlargement Immunology very low serum IgG
and IgA, normal
to increased IgM,
giant germinal centers,
lack of memory B cells, impairment of
somatic hypermutation
16
AID
- Expressed in germinal center B cells and in
B-LCLs - Class switch recombination
- Somatic hypermutation of Ig's
- If mutated, B cell defect (HIM2)
17
(No Transcript)
18
AID GENE MUTATIONS IN 28 FAMILIES WITH HIGM2
2
4
3
1
5
non sense mutation
Cytidine deaminase domain
missense mutation
deletion, frameshift
deletion, in frame
19
Uracil-DNA glycosylase Deficiency (UNG)
- Low IgG, A, E
- Elevated IgM
- Late onset of symptoms
- Hyperplasia of lymphoid organs
- /- autoimmunity
- Neutropenia/PCP never
- Malignancies not increased
20
Cytokines (TNF, IL-1b, IL-18)
CK-R bacterial infections (LPS,
peptidoglycans) TLR4, TLR2 CD154
(activated T cells)
CD40
P
P
IKKa
IKKa
IKKg
IKKg
IKKb
IKKb
P
P
P
P
RelA
RelA
IkB
IkB
p50
p50
Ub-Ub-Ub-Ub-Ub
P
RelA
P
p50
IkB
Ub-Ub-Ub-Ub-Ub
26S proteasome
NF-kB responsive gene
RelA
p50
CK, CC, adhesion molecules, receptors cell
proliferation, cell differentiation (including
peripheral B cell maturation)
21
X-LINKED HYPOHIDROTIC ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA WITH
IMMUNODEFICIENCY
Clinical features hypodontia, conical teeth
inability/impairment to sweat, dry skin sparse
hair (variable) recurrent bacterial and
opportunistic infections Laboratory features
variable Ig levels (often low IgG and
normal to increased IgM) Genetics defects
in the NEMO (IKK-gamma) gene, mapping at Xq28
22
IL-2 IL-4 IL-7 etc.
IL-Rgc
BCR
Ag
Btk
CD40L
CD40
Hyper mutation
MCHII
TRAFs
JAK3
T
IL-Rgc
TCR
B7
AID
CD28
NAKB NFAT
CD40L
IL-2 IL-4 IL-7 etc. IFNg
IgM
CD40
IgG IgA IgE
IL-1 TNFa IFNa,b
MØ
IL-Rgc
IFNgR
23
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- X-linked recessive disorder
- Thrombocytopenia/small platelets
- Eczema
- Recurrent infections
- Abnormal B and T cell functions
- Autoimmune diseases
- Malignancies
24
(No Transcript)
25
When to suspect WAS / XLT
- Positive family history (ITP) and
- Congenital bleeding tendency
- Petechii, bruises, post circumcision bleed
- Perinatal brain hemorrhage
- Bloody diarrhea as infant
- Eczema that is difficult to treat
- Allergies
- Ear and other infections, bad pneumonia
26
(No Transcript)
27
WAS/XLT PLATELETS NUMBER AND SIZE
-9
28
Intermittent XLT phenotype
- Thrombocytopenia, intermittent (50-300K), no
history of bleeding except for intermittent
petecchiae, - Small platelet volume
- Infections none or mild, common
- Autoimmunity none
- Malignancy none
- WASP mutation missense, WASP
29
(No Transcript)
30
WAS / XLT / XLN
- WAS Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- XLT X-linked Thrombocytopenia
- IXLT Intermittend XLT
- XLN X-linked Neutropenia
31
(No Transcript)
32
WASP Mutation scores
- Score "0" no WAS/XLT findings, e.g. XLN
- Score lt1 intermittent XLT (IXLT)
- Score 1-2 XLT
- Score 3-4 classic WAS
- Score 5 progression from score 1-2 (rare) or
from score 3-4 (frequent)to Autoimmune Disease,
Malignancy
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
WASP PROTEIN EXPRESSION BY FLOW CYTOMETRY
control isotype
3F3 (anti-WASP)
Control
WAS
XLT
36
(No Transcript)
37
A Diagnosis of WAS/XLTWhat can be done?
- Early Diagnosis a must
- Adjust Diet Food Allergies
- Antibiotics some times prophylactic
- IVIG if Antibody Production is deficient
- Skin care, may need Prednisone
- Platelet Transfusion, only if serious Bleed
- Splenectomy?
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Bone Marrow Cord Blood
- Gene Therapy (pre-clinical)
38
(No Transcript)