Hydrocyclone Separation of Industrial Glaze Waste PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title: Hydrocyclone Separation of Industrial Glaze Waste
1
Hydrocyclone Separation of Industrial Glaze Waste
Concept Develop a pilot hydrocyclone system to
separate glaze components from Pb-containing
manufacturing glaze waste so the materials can be
reused.
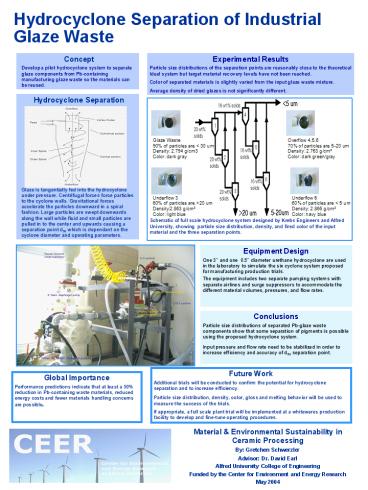
Experimental Results Particle size distributions
of the separation points are reasonably close to
the theoretical Ideal system but target material
recovery levels have not been reached. Color of
separated materials is slightly varied from the
input glaze waste mixture. Average density of
dried glazes is not significantly different.
Hydrocyclone Separation Glaze is
tangentially fed into the hydrocyclone under
pressure. Centrifugal forces force particles to
the cyclone walls. Gravitational forces
accelerate the particles downward in a spiral
fashion. Large particles are swept downwards
along the wall while fluid and small particles
are pulled in to the center and upwards causing a
separation point d50 which is dependant on the
cyclone diameter and operating parameters.
Schematic of full scale hydrocyclone system
designed by Krebs Engineers and Alfred
University, showing particle size distribution,
density, and fired color of the input material
and the three separation points.
Equipment Design One 3 and one 0.5 diameter
urethane hydrocyclone are used in the laboratory
to simulate the six cyclone system proposed for
manufacturing production trials. The equipment
includes two separate pumping systems with
separate airlines and surge suppressors to
accommodate the different material volumes,
pressures, and flow rates.
Conclusions Particle size distributions of
separated Pb-glaze waste components show that
some separation of pigments is possible using the
proposed hydrocyclone system. Input pressure
and flow rate need to be stabilized in order to
increase efficiency and accuracy of d50
separation point.
Future Work Additional trials will be conducted
to confirm the potential for hydrocyclone
separation and to increase efficiency. Particle
size distribution, density, color, gloss and
melting behavior will be used to measure the
success of the trials. If appropriate, a full
scale plant trial will be implemented at a
whitewares production facility to develop and
fine-tune operating procedures.
Global Importance Performance predictions
indicate that at least a 50 reduction in
Pb-containing waste materials, reduced energy
costs and fewer materials handling concerns are
possible.
Material Environmental Sustainability
in Ceramic Processing By Gretchen
Schwerzler Advisor Dr. David Earl Alfred
University College of Engineering Funded by the
Center for Environment and Energy Research May
2004