CAD/CAE Modeling - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
CAD/CAE Modeling
Description:
Engineer friendly terms ( fillets, boss, slots etc.,) used in modeling/design workbench ... Geometric Modeling Features. Rules and Data for Features ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:720
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CAD/CAE Modeling
1
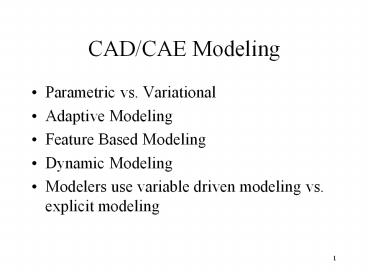
CAD/CAE Modeling
- Parametric vs. Variational
- Adaptive Modeling
- Feature Based Modeling
- Dynamic Modeling
- Modelers use variable driven modeling vs.
explicit modeling
2
Dynamic Vs. Static modeling
- PTC introduced commercial version of variable
modeling - Uses dimensions and constraints
- Feature Based design
- Uses primitives and parameters rather than
coordinates and orientation - Features are directly placed in models
3
Modeling Modes
- Issue How to capture/define parameters
- Issue How to capture design intent and translate
to variables - Issue After capture, how to maintain
parameters/variables - Explicit modelers use geometry. Changes are
expensive (time and effor) - Combines wires, sheets, solids
4
Variable Driven
- Design intent is captured
- Allows users to explore various design
alternatives - Two popular sub-methods in use are parametric and
variational modeling methodologies
5
Parametric Modelers
- Transaction history is captured
- Order dependent and hierarchical model creation (
ordered steps to follow) - Solution speed is a great advantage to this
method - Must FULLY constrain before next element is
defined (every step) - DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) modeling
6
Variational Modelers
- Solves set of simultaneous equations
- Driving dimensions can be based on complex
equations Eg Dimensions based on material
properties - No specific order dependency.
- Constraints dimensional, geometric, algebraic
- Eg Parallel lines A and B can both move
7
Adaptive Modelers
- CSG tree based
- Boolean operators
- Parameters alter the CSG primitives
- Euclid (MDV) used this method
- Changes are still expensive due to boolean
operator costs
8
Dynamic Modelers
- Use Feature Recognition Technology
- No prerequisite knowledge of models assumed
- HP PE solid designer uses this method
- No inter-relations available between features.
This could be a limitation
9
Feature Based Modelers
- Features are named entities which follow rules
- Engineer friendly terms ( fillets, boss, slots
etc.,) used in modeling/design workbench - Topological integrity must be maintained (
through holes remain after higher thickness) - Follow rules. Process information is captured for
manufacturing and applications
10
Sketches in Modeling
- Contributes to how easy to edit and recreate
designs - 2D-gt 3D can be done using extrude, revolve, sweep
operations - Automatic parameterisation is more common in 2D.
3D problem domain is much more complex
11
Geometric Modeling Features
- Rules and Data for Features
- Solid 3D models and features use DATUM feature in
Pro/E - Changes and Edits are critical to evaluate for
ease of use and speed - Variable Driven modeling is a must for all future
systems
12
Advanced Modeling
- Assembly models are collection of parts with
position and orientation - Positional variables are used to relate parts
- Stresses, Volumes, Geometric contraints are
placed in assembly context - Tolerance Analysis application uses variables to
help simulation/manufacturing