Comment on: PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 97
Title: Comment on:
1
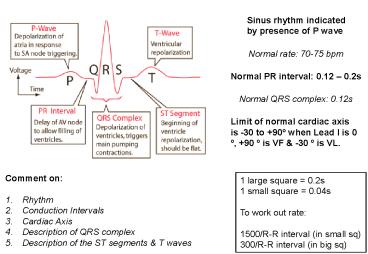
Sinus rhythm indicated by presence of P wave
Normal rate 70-75 bpm
Normal PR interval 0.12 0.2s
Normal QRS complex 0.12s
Limit of normal cardiac axis is -30 to 90º when
Lead I is 0 º, 90 º is VF -30 º is VL.
- Comment on
- Rhythm
- Conduction Intervals
- Cardiac Axis
- Description of QRS complex
- Description of the ST segments T waves
1 large square 0.2s 1 small square 0.04s To
work out rate 1500/R-R interval (in small
sq) 300/R-R interval (in big sq)
2
ECG Changes following an MI
3
Heart Murmurs
4
Myocardial Infarction
5
Myocardial Infarction continued
6
Thromboembolism
7
Thromboembolism continued
8
Angina Pectoris
9
Angina Pectoris continued
10
Cardiac Failure
11
Cardiac Failure continued
12
COPD
13
COPD continued
14
Adult Asthma
15
Adult Asthma continued
16
Acute Abdomen
Ruptured spleen GU Aortic Aneurysm Perforated
colon L pneumonia Pyelonephritis
Pancreatitis MI Peptic ulcer Acute
cholecystitis Perforated oesophagus
Intestinal Obstruction Acute pancreatitis Early
appendicitis Mesenteric thrombosis Aortic
aneurysm Diverticulitis
Acute cholecystitis DU Hepatitis Congestive
hepatomegaly Pyelonephritis Appendicitis R
pneumonia
Sigmoid diverticulitis Salpingitis Ectopic
pregnancy (ruptured) Strangulated
hernia Perforated colon Crohns
disease Ulcerative colitis Renal/ureteric stone
Appendicitis Salpingitis Ectopic pregnancy
(ruptured) Renal/ureteric stone Strangulated
hernia Meckels diverticulitis Crohns
diseases Perforated caecum
17
Acute Pancreatitis
18
Acute Pancreatitis continued
19
Urea metabolism by H. pylori tests available
for detection
Control of acid secretion
Main reflux mechanisms
Clinical presentation of gallstones
20
GORD
21
GORD continued
22
Gallstones
23
Gallstones continued
24
Acute Appendicitis
25
Peptic Ulcer
26
Peptic Ulcer continued
27
IBD Differences between Crohns/UC
28
Causes of clubbing
29
IBD Crohns Disease
30
IBD Crohns Disease continued
31
IBD Ulcerative Colitis Disease
32
IBD Ulcerative Colitis continued
33
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
34
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
35
Diverticular Disease
36
Diverticular Disease continued
37
Intestinal Obstruction
38
Renal Ureteric Colic
39
Ectopic Pregnancy
40
Blood Pressure Ranges
- Ideal - Systolic lt140 mmHg Diastolic lt85 mmHg
- Diabetic/Renal Disease Systolic lt130 mmHg
Diastolic lt80 mmHg - If Systolic gt220 mmHg or Diastolic gt120 mmHg
treat immediately, also if there is accelerated
(malignant) hypertension (with papilloedema,
fundal haemorrhages or exudates) or impending
cardiovascular complications. - If Systolic 180-219 mmHg or Diastolic 110-119
mmHg confirm over 1-2 weeks then treat. - If Systolic 160-179mmHg or Diastolic 100-109 mmHg
with CV complications, end-organ damage or
diabetes mellitus (type I/II), confirm over 3-4
weeks treat is sustained. - If Systolic 160-179mmHg or Diastolic 100-109 mmHg
without CV complications, end-organ damage or
diabetes mellitus (type I/II), advice lifestyle
changes, reassess weekly treat if values
sustained over 4-12 weeks. - If Systolic 140-159mmHg or Diastolic 90-99 mmHg
with CV complications, end-organ damage or
diabetes mellitus (type I/II), confirm over 12
weeks treat is sustained. - If Systolic 140-159mmHg or Diastolic 90-99 mmHg
without CV complications, end-organ damage or
diabetes mellitus (type I/II), advise lifestyle
changes, reassess monthly treat mild
hypertension if the 10-year coronary heart
disease risk is gt15. - In the elderly treatment is consider when
systolic gt160 mmHg or diastolic gt90 mmHg over 3-6
months. Benefit lt evident gt 80 yrs, although each
case should be treated individually, longevity
considered
41
Keith-Wagener classification of fundoscopy
- Fundoscopy is an essential part of hypertensive
examination. The grading system is according to
the Keith-Wagener classification - Grade 1 tortuosity (twisted shape or position)
of the retinal arteries with increased
reflectiveness (silver wiring) due to arteriolar
narrowing - Grade 2 grade 1 plus appearance of
arteriovenous nipping (arching of the vein)
produced when thickened arteries pass over the
retinal veins is due to sclerotic changes. Also
spasms of the vessels. - Grade 3 grade 2 plus flame-shaped haemorrhages
soft cotton wool exudates (due to small
infarcts) - Grade 4 grade 3 plus papilloedema (blurring of
the margins of the optic disc) - Grade 3 4 are diagnostic of malignant
hypertension. The above picture shows
haemorrhages, exudates papilloedema.
42
Systemic Hypertension
43
Systemic Hypertension continued
44
(No Transcript)
45
Stroke
46
Stroke continued
47
Stroke continued
48
(No Transcript)
49
Pulmonary Embolism
50
Pulmonary Embolism continued
51
Colles Fracture
52
Femoral Neck Fracture
53
Rheumatoid Arthritis
54
Rheumatoid Arthritis continued
55
Osteoarthritis
56
Osteoarthritis continued
57
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
58
SLE continued
59
Septic Arthritis
60
Alcohol Misuse
61
Alcohol Misuse continued
62
Bacterial Pneumonia
63
Bacterial Pneumonia continued
64
Cystic Fibrosis
65
Cystic Fibrosis continued
66
Jaundice
67
Jaundice continued
68
(No Transcript)
69
Approach to patient with jaundice
Causes of jaundice
Cause of acute parenchymal cell damage
70
(No Transcript)
71
Viral Hepatitis
72
Viral Hepatitis continued
73
Cirrhosis
74
Cirrhosis continued
75
Acute Renal Failure
76
Acute Renal Failure continued
77
Chronic Renal Failure
78
Chronic Renal Failure continued
79
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
80
Urinary Incontinence in Males
81
Urinary Incontinence in Females
82
Rectal Bleeding
83
Rectal Bleeding
Spotting
Mixed with stool
Separate from stool
Haemorrhoids inflammatory disease polyps, cancer
Haemorrhoids inflammatory disease diverticular
disease
Haemorrhoids anal tear
Proctoscopy
Flexi-sigmoidoscopy OR Colonoscopy
84
Dyspnoea
85
Persistent Cough
86
Adult Obesity
87
Dementia
88
Adult Visual Impairment/Cataracts
89
AVI / Cataracts continued
90
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PIV)
91
Hip Replacement and PO infection
92
Knee Replacement
93
List of core cases
- Colles Fracture
- Femoral Neck Fracture
- Hip/Knee replacement and PO infection
- Rectal Bleeding
- Persistent cough
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Renal uteric colic
- Dyspnoea
- Acute/Sub-acute Intestinal Obstruction
- Alcohol Misuse
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Jaundice
- Hepatitis A, B C
- Liver cirrhosis complication
- Acute renal failure
- Chronic renal failure
- Male/Female urinary incontinence
- Cataracts/ Adult Visual Impairment
- Myocardial Infarction
- Thromboembolism
- Angina Pectoris
- Cardiac Failure
- COPD
- Adult Asthma
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Peptic Ulceration
- GORD
- Gallstones
- Acute appendicitis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohns Ulcerative
Colitis) - Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Diverticular Disease
- Systemic Hypertension
- Stroke
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Osteoarthritis
1 to go
94
Reference Ranges
95
(No Transcript)
96
Cranial Nerves
- Olfactory
- Optic
- Oculomotor
- Trochlear
- Trigeminal
- Abducens
- Facial
- Vestibulocochlear
- Glossopharyngeal
- Vagus
- Accessory
- Hypoglossal
- Some
- Say
- Money
- Matters
- But
- My
- Brother
- Says
- Big
- Boobs
- Matter
- More
KEY S Sensory M Motor B Both
97
(No Transcript)