Microbial pathogens - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Microbial pathogens
Description:
Number of possible binary states of system of n genes is 2n ... Outbreak in Burkina Faso has reported a total of 7146 cases including 1058 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:149
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Microbial pathogens
1
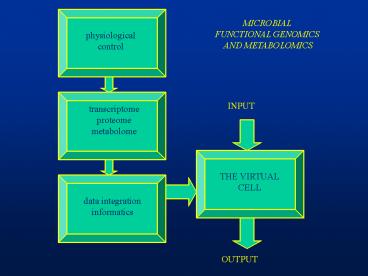
MICROBIAL FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS AND METABOLOMICS
physiological control
INPUT
transcriptome proteome metabolome
THE VIRTUAL CELL
data integration informatics
OUTPUT
2
Complexity and microbes
- Microbes have the smallest genomes 0.5 9Mbases
with 500 few thousand genes. - In a genome of n genes, the number of possible
intra-gene binary interactions increases as
n(n-1)/2. - Number of possible binary states of system of n
genes is 2n - Modelling of eukaryotic cells with tens of
thousands of genes is far beyond existing
computing power. - Modelling of simpler microbial cells may soon be
a tractable problem.
3
Frazier et al 2003
4
The burden of infectious Diseases
5
Tuberculosis
- One third of the worlds population infected
- Responsible for 3-4 millions deaths per year
- Biggest cause of adult death in the developing
world
6
Meningitis
- Caused by bacteria, viruses, funghi and protozoa
- About 1.2 million cases of bacterial meningitis
occur each year and about 10 of them are fatal - Major epidemics of meningitis are caused by the
meningococcus - Outbreak in Burkina Faso has reported a total of
7146 cases including 1058 deaths since January
2003 - 2-3,000 cases in the UK mostly group B
7
Diarrhoeal Disease
- Biggest cause of infant mortality worldwide
- Responsible for about 1.5 million deaths each
year - Caused mainly by bacteria and viruses
8
Emerging and re-emerging infections
- SARS
- HIV
- TB
- West Nile Virus
- W135 meningococcus
- Bioterrorism
9
Microbial genomes
- Genomes of all major pathogens have now been
sequenced - Viruses
- TB bacillus
- Meningococcus
- Campylobacter
10
Functional Genomic capability in the Group/School
- Advanced robotics for microarray production and
analysis - Microarray scanners
- MALDI-tof
- Automated sequencer
- Confocal microscope
- FACS scanner
- Additional mass specs for metabolomics (eg. ion
trap)
11
Functional Genomics of Microbial Pathogens at
Surrey
- Bacteria
- Meningococcus
- Tubercle bacillus
- Campylobacter
- Viruses
- Astroviruses, caliciviruses
- Control of viral translation
- Drug targets
- Vaccines
- Diagnostics
- Vectors
12
Continuous Culture to Study Bacterial Pathogens
- Transcriptome
- Proteome
- Metabolome
- But, problems
- Physiological Control
- Reproducibility
- Continuous Culture
RPM
O2
0C
pH
13
Continuous culture of bacterial pathogens
P3 Chemostat Facility
transcriptome
MALDI-tof
RPM
O2
0C
pH
proteome
metabolome
Mass spec NMR
14
Identification of metabolic pathways that are
active during persistence in M. tuberculosis
New Drug Targets
- M. tuberculosis can persist in the host for many
years - Drug regimes have to be maintained for at least 6
months - Chemostat ? populations of cell growing at
different rates. - Proteome and transcriptome analysis of fast and
slow-growing cells ? identify metabolic pathways
active during persistence - NEW DRUG TARGETS
15
Functional genomics to identify virulence genes
in the meningococcus
regulated virulence genes
a)
New Vaccine Candidate antigens
b)
16
Microbial Functional Genomics
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Protozoa
- Funghi
- Algae
- Microbial Products
- Microbial Pathogenicity
- Microbial Ecology