B.P.R. PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: B.P.R.
1
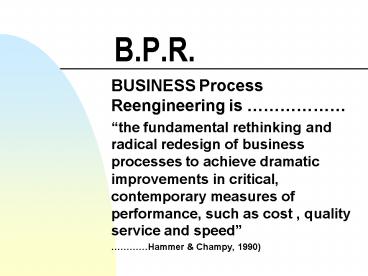
B.P.R.
- BUSINESS Process Reengineering is
- the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign
of business processes to achieve dramatic
improvements in critical, contemporary measures
of performance, such as cost , quality service
and speed - Hammer Champy, 1990)
2
Change
- Management practices have changed from the system
first identified by Adam Smith in the 1700s
where - workers performing small, specialised tasks in a
mass production process
3
Principles of BPR
- Operations Should Be Organised Around the Total
Process Which Adds Value for Customers Rather
Than the Functions Which Perform the Various
Stages of Value Adding - Rethink Business Processes in a Cross-functional
Manner Which Organises Work Around the Natural
Flow of Information. - Strive for Dramatic Improvements
- Integrate Functions
- Do Not Separate Those Who Do the Work From Those
Who Control and Manage the Work
4
What is Reengineering?
- To Reengineer a Process Try to Combine Tasks and
Eliminate Steps - Look for Opportunities to Boost Worker Efficiency
With Technology - Start From Scratch - Forget Ho Youve Handled the
Process So Far and Decide How Best to Handle Them
in the Future
5
Take Broader View
- Companies That Focus on Task Often Lose Sight of
Their Larger Objectives. They May Measure Workers
Ability to Handle Individual Tasks, but Dont
Look at Efficiency, Cost, Purpose of an Entire
Process Etc.
6
How Reengineering Works
- A reengineering team carefully examines the
outputs and inputs of a process - Asks how it might streamline, combine or
eliminate inputs while adding value to the
outputs - Example Kodak (1987)
7
Kodak vs Fuji (1987)
- Fuji Announces New Single-use Preloaded Camera.
- Customer Takes Picture, Return Camera to Fuji Who
Process the Film, Breakdown the Camera and
Salvage Parts for Reuse.
- Kodaks Two Existing Design Processes Couldnt
Meet the Need for Rapid Turnaround - Kodaks Traditional Design Process Would Take 70
to Produce a Rival Camera - Rather Than Look at Org Chars, Kodak Focussed on
the Design Process Itself - Brought in CAD/CAM - New Technology Replaced Drafting Tables and
Allowed Collaboration and Access to Latest Data - Development Time Halved
8
The Reengineers
- Leader
- Authorises and Motivates the Overall Effort
- Persuades the Organisation and Employees That
Radical Change Is Worthwhile - Feels a Passion to Reinvent the Company
- Process Owner
- Senior Level Manager Responsible for Specific
Process and the Reengineering on It - Assembles a Reengineering Team
- Inspire and Motivate the Team
- Obtain Resources for Team
9
The Reengineers - contd
- Reengineering Team
- 5 - 10 Individuals
- Examine the Existing Processes and Oversee the
Redesign and Implementation - Consists of Insiders and Outsiders (Consultants
or People From Different Functions - Objectivity) - One Team Reengineers One Process at a Time
- 75 of Their Time Committed
- Duration One Year
10
What new processes look like
- Several Jobs Are Combined Into One
- The Steps in a Process Are Performed in a Logical
Order Instead of the Artificial Sequence Imposed
by Mass Production - Processes Can Have Multiple Versions
- Work Is Performed Where It Makes the Most Sense
- Checks and Controls Are Reduced
11
Think Inductively
- Deductive Thinking Involves Defining a Problem
and Then Seeking Solutions - Inductive Thinking - Instead of Searching for One
Correct Answer, You Search for As Many Promising
Answers As Possible - It Helps You Find Better Processes and Ways to
Exploit the Latest Technology
12
Changing the Culture
- Executives Assess the Current Culture Authority,
Values, Norms, Rewards and Sanctions - Where Are the Problems Areas
- Identify the Way Changes Can Be Made to Do Things
More Attractively. - Simultaneous Loose-tight Properties I.E.Culture
Demanded Compliance, Performance and Obedience to
Key Norms and at the Same Time It Permitted
Freedom to Take Risks and Innovate ( Peters and
Waterman, In Search of Excellence)
13
Creativity
- The Important thing is not to stop questioning
- Albert Einstein
14
Characteristics of Creativity
- Mental Flexibility - Ability to Keep Your Mental
Outlook Changeable - Option Thinking - the Way to Have Good Ideas Is
to Have Plenty of Them - Big Picture Thinking - Helicopter View They
Have Ability to Envision the Impact of a Solution
to a Problem - Selling Your Ideas - Get Inside the Head of
Others and Rearrange Their Understanding - Intellectual Courage - Push Your Idea in the
Face of Apathy, Rejection, Bigotry and Hostility
15
Making the Move
- How Do You Make the Organisation Creative and
Adaptive? - Define Your Culture
- Communicate the Need
- Remodel the Reward System
- Remodel the Structures
- Preach the Gospel
16
Break the Rules
- Inductive Thinkers Use New Technology to Break
Rules That Limit How They Conduct Their Work - Today Information Can Appear in Several Places at
One Time - Computer Networks and Database
Technology - Relatively Unskilled People Can Operate Computer
Technology - Expert-systems Technology Captures
the Expertise of Specialists in Computer Software
17
What to Reengineer?
- Three Criteria for Selection
- Need Processes in Trouble, a Product
Development Process Hasnt Delivered a New
Product in Five Year Employees Type Data From a
Computer Printout Into a Computer Terminal - Importance - Processes With Greatest Impact on
Customer E.G Cost, On-time Delivery Features - Feasibility Estimate the Likelihood of Success
for Reengineering Effort.
18
Implementation of BPR
- Steering Committee Established
- Define Improvement Objectives and Develop a
Vision Statement for the Process - Manage the Project Against Agreed Timescales
- Provide Resources and Ensure Appropriate People
Are Involved in the Project - Ensure People Involved Have Right Set of Skills
- Identify Issues and Resolve Them
- Challenge the Status Quo
- Resolve Functional Conflicts
19
Process Design Team
- Team Comprises 6-8 Members
- Identify and Map the Current State of the Process
Under Review - Define and Understand the Existing Processes
- Identify the Critical Process
- Challenge All Assumptions Associated With the
Process - Accept No Boundaries and Demarcations
- Find Breakthrough Improvements
- Design New Process
- Ensure People Affected Are Involved in the
Process - Decide How the Changes Will Be Measured and
Assessed - Pilot Changes and Modify the Design As
Appropriate - Present Recommendations to Project Sponsor and
Steering Committee - Communicate With Those Affected by the Change.
20
Benefits of BPR
- Increased Customer Focus
- Improved Profitability
- Improved Quality and Control
- Improved Corporate Flexibility
- Increased Speed of Service Delivery and
Responsiveness - Improved Measurability Within the Process
21
Criticisms of BPR
- Can Be Seen As a Management Fad
- Seen As an Excuse to Get Rid of Staff by Putting
Short Term Interests of the Shareholder Above
Long Term Employee and Organisational Interests - Core Experience Lost From Operation.