Weather - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Weather
Description:
It was Friday, August 13th. ... At about 9am, Hurricane Charley started 'wobbling' to the east. ... People felt the walls shake around them as Charley moved inland. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:108
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Weather
1
Weather
You Are Here
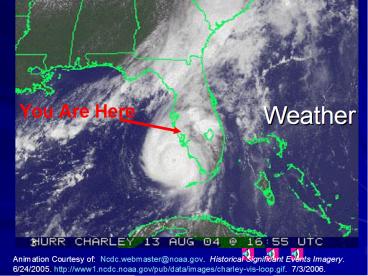
Animation Courtesy of Ncdc.webmaster_at_noaa.gov.
Historical Significant Events Imagery.
6/24/2005. http//www1.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/imag
es/charley-vis-loop.gif. 7/3/2006.
2
A Weather Story
- It was Friday, August 13th. The morning was calm
and peaceful typical of a summer day in the
Sunshine State. Yet unlike most days, towns in
this part of Florida were fairly deserted because
a relatively minor hurricane was churning in the
Gulf of Mexico, a little too close for comfort.
It was a Category 1 then a Category 2. But it
wasnt supposed to come here. Hurricanes just
dont hit here
3
Preparation
- The storm was headed for the Tampa Bay area which
caused nearly 1.4 million people living there to
evacuate ahead of it. But in our area, people
still were able to get in some morning jogs.
They put the final touches on their storm
shutters and diligently put on the news to watch
the storm forecast closely.
4
A Wobble?
- At about 9am, Hurricane Charley started
wobbling to the east. Meteorologists in this
area stared at live satellite images to see if
Charley was indeed wobbling or making that
predicted northeasterly turn a bit early. By
11am, local emergency personnel and everyone else
in the area was wide awake, staring at Hurricane
Charley. That wobble became a turn, sparing
heavily populated Tampa Bay and aiming right at
our paradise.
5
It Intensifies
- Still a Category 2, Charley was an unwanted and
dangerous nuisance. Around 230pm, people in the
area gritted their teeth as they saw the report
from the weather service that Charley had
strengthened to a Category 3 storm. But, before
they could come to terms with this, Charley
strengthened to a powerful Category 4 around
300pm.
6
Just Before the Storm
- Some sought safety in shelters. Others went to
relatives or friends homes. As the winds
steadily increased in our area, people prepared
for the worst. They climbed into bathtubs, hid
beneath mattresses, and huddled in closets.
7
Charley Strikes
- Charley first nailed Cayo Costa, west of Cape
Coral, at 345pm, before moving toward Charlotte
Harbor with sustained winds of 145mph. People
felt the walls shake around them as Charley moved
inland. Roofs were torn off above their heads as
trees toppled all around. The roaring and
howling of Charleys winds were deafening.
8
The Aftermath
- Mighty trees had been uprooted. Roofs had been
ripped off. Cars had been lifted. Street signs
and stoplights were missing. Power lines were
tangled and poles broken. Hurricane Charley
killed 31 people. It also caused an estimated
6.8 billion in damage. But, it could have been
much worse.
Some Story Excerpts Taken From Arnold, C.
(2004). Charley threatens paradise,
residents brace for the wrath. Port
Charlotte, FL Sun Newspapers.
9
The Science of Weather
- Many, many heroes emerged on that fateful day and
meteorologists were definitely among them - A meteorologist is a scientist who studies
weather - The predictions and tracking information they
provided helped save countless lives
10
Air Masses
- Much of weather predicting relies on the study of
the movements of air masses - Weather changes are caused by the movement and
interaction of air masses - An air mass is a large body of air where
temperature moisture content are similar
throughout it
11
Fronts
- Air masses that form from different areas often
do not mix because warm air is less dense than
cold air - When 2 air masses meet, warm air rises and cold
air sinks - A front is the area where 2 types of air masses
meet
12
4 Types of Fronts
- 1. Cold front forms when cold air moves under
warm air, pushing the warm air up. - Cold fronts move quickly and bring thunderstorms,
heavy rain, or snow. - Cooler weather usually follows a cold front
because the air mass behind the cold front is
cooler and drier than the air mass that it is
replacing.
13
(No Transcript)
14
- 2. Warm front forms where warm air moves over
cold, denser air. - Warm fronts generally bring drizzly rain.
- Warm air gradually replaces the cold air causing
clear and warm weather to follow a warm front.
15
(No Transcript)
16
- 3. Occluded front forms when a warm air mass
is caught between two colder air masses. - Occluded fronts bring cool temperatures and large
amounts of rain and snow.
17
(No Transcript)
18
- 4. Stationary front forms when a cold air mass
meets a warm air mass but both air masses dont
have enough force to lift the warm air mass over
the cold one so they remain separated. - Stationary fronts often bring many days of
cloudy, wet weather.
19
(No Transcript)
20
You Be The Meteorologist!
- On the next few slides, read through the
descriptions of the weather conditions to come up
with a general weather forecast.
21
- A warm air mass is stuck between two colder air
masses. - 1. What type of front is this?
- 2. What type of weather will it bring?
1. ANS OCCLUDED FRONT
2. ANS COOL TEMPERATURES LOTS OF
RAIN/SNOW
Click screen to check answer
22
A cold air mass has met a warm air mass but they
dont have enough energy to lift the warm air up.
1. ANS STATIONARY FRONT
- 1. What type of front is this?
- 2. What type of weather will it
bring?
2. ANS DAYS OF
CLOUDY, WET WEATHER.
Click screen to check answer
23
Links to Lean More
- Click on the links below to learn more about
weather. - www.brainpop.com
- Select Science, then Weather and Weather
Advanced - http//www.oar.noaa.gov/k12/html/forecasting2.html
- Explore this site for info on weather forecasting
24
Your Assignment
- On the following slides, choose Tornadoes,
Lightning, or Hurricanes to do an in depth study
of severe weather. - Use the information to create an informational
poster about that particular form of sever
weather. - Be prepared to present your poster to the class.
25
Tornadoes
- DIRECTIONS Gather information about the
following and put it on a poster to present. The
research links are on my website. - What causes them?
- How do they form?
- What are the environmental clues?
- Clearly explain the following
- Tornado Watch,
- Tornado Warning
- Severe Thunderstorm Watch
- Severe Thunderstorm Warning
- List some facts and myths about tornadoes.
- List the months of peak occurrence for Florida
and 4 other states of your choosing. - Explain 5 interesting facts about tornadoes that
you discovered during research. - Include a drawing of a tornado.
26
Lightning
- DIRECTIONS Gather information about the
following and put it - on a poster to present. The research links are
on my website. - What are the causes of lightning and thunder?
- Explain the following
- How far away from a storm can lightning strike?
- What is the 30-30 rule?
- Where does lightning usually strike?
- Draw the types of lightning and explain about
each. - Find out if Florida really does have the most
lightning strikes in the U.S. If not, who does? - List 5 other states that have frequent lightning
strikes. Be sure to indicate the number of
strikes for each. - Hypothesize why most lightning fatalities occur
at the beginning or end of a thunderstorm, rather
than during the worst part of the storm. - List 5 interesting facts you found during your
research.
27
Hurricanes
- DIRECTIONS Gather information about the
following and put it on a poster to present. The
research links are on my website. - Explain the difference between a tropical
depression, a tropical storm, and a hurricane. - Describe each hurricane level on the
Saffir-Simpson Scale. - Describe and explain the 3 things that must occur
for a hurricane to get stronger. - Describe and explain the dangers of hurricanes to
include - storm surge
- Flooding
- Danger from heavy winds
- Tornadoes
- Where are areas at risk?
- Write an explanation about the Hurricane Hunters
to include - The history
- What they do
- List 5 interesting facts you found during your
research. - Include a drawing of a hurricane.