Elements of Life - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Elements of Life
Description:
Some energy is used to form the bonds, but the net result is a release of energy (heat) http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255enz/activation_energy .jpg ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:568
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Elements of Life
1
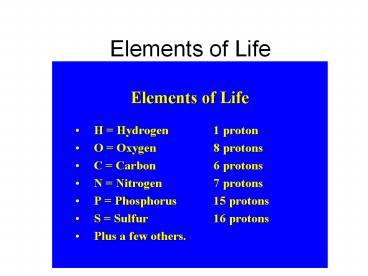
Elements of Life
- Chapter 2
2
Ecology
- The scientific study of relationships between
organisms and their environment - Every organism is a chemical factory that
captures matter and energy from its environment
and transforms them into structures and process
that make life possible.
http//www.texascenter.org/almanac/Land/m.ecolgy.g
if
3
Matter
- Everything that takes up space and has mass
- Solid, liquid, gas and plasma (4 states)
- Matter is neither created nor destroyed but
rather recycled over and over again (Conservation
of matter) - If everything goes somewhere, where do the things
we dispose of go after the garbage truck leaves?
4
Elements
- Substances that cannot be broken down into
simpler forms by ordinary chemical reactions - 115 known (92 natural)
- N, C, H, O 96 of the mass of most living
organisms
http//www.corrosionsource.com/handbook/periodic/p
eriodic_table.gif
5
Atoms
- The smallest particles that exhibit the
characteristics of the element - Protons (), Neutrons, Electrons (-)
- Protons Neutrons Nucleus (Atomic Mass)
- Atomic Number number of protons
- Isotopes different number of neutrons within
the same element (15N , 14N) - Unstable isotopes may spontaneously emit
electromagnetic energy, or subatomic particles,
or both. (Radioactive waste, nuclear energy)
6
Compounds
- Joined atoms
- A pair of group of atoms that can exist as a
single unit is known as a molecule - Ionic bonds opposite charges attracting
(NaCl-) - Covalent bonds sharing of electrons (H2O) Polar
molecules - Oxidized atom gives up an electron (Oxidation
reaction oxygen usually takes the electron) - Reduced atom gains an electron (Reduction
reaction)
7
Forming bonds requires Energy
- Activation energy energy needed to initiate the
reaction - Some energy is used to form the bonds, but the
net result is a release of energy (heat)
http//fig.cox.miami.edu/cmallery/255/255enz/acti
vation_energy20.jpg
8
Electrical Charge
- Ions charged particles
- Negatively charged atoms anions ?Cl-
- Positively charge atoms cations ?Na
- Substances the readily give up hydrogen ion in
water (Acids HCl ? H Cl-) pH lt 7 - Substances the readily bond with H ions (Bases
NaOH ? Na OH-) pH gt 7
9
pH Scale
- pH 7 is neutral
- pH 6 represents ten times more hydrogen ions in
solution than pH 7 - Buffers solutions that accept or release
hydrogen ions. - Alkaline rocks can buffer acidic precipitation
http//www.dreddyclinic.com/images/ph_scale.jpg
10
Water
- Polar molecule
- Only inorganic liquid that exists under normal
conditions at temperatures suitable for life - Cohesive (stick together) lets it exhibit
capillary action - Expands when it crystallizes
- High heat of vaporization (sweating is a good way
to get rid of excess heat) - High specific heat a lot of heat is absorbed
before it changes states
11
Organic Compounds
- Chains and rings of carbon form the backbone of
organic compounds - Lipids (fats and oils) store energy for the
cells, and they provide the core of cell
membranes and other structures (hydrocarbons)
http//www.eccentrix.com/members/chempics/Slike/Li
pids/1Lipids.jpg
12
Organic Compounds
- Carbohydrates (sugars, starches, cellulose)
store energy and provide structure to cells
(glucose)
http//images.google.com/imgres?imgurlhttp//www.
eccentrix.com/members/chempics/Slike/Lipids/1Lipid
s.jpgimgrefurlhttp//www.eccentrix.com/members/c
hempics/Lipids.htmlh480w640sz62hlenstart
2tbnidvBwzZRaFKKKyXMtbnh103tbnw137prev/im
ages3Fq3Dlipids26svnum3D1026hl3Den26lr3D2
6client3Dfirefox-a26rls3Dorg.mozillaen-USoffi
cial_s26sa3DN
13
Organic Compounds
- Proteins (amino acids) formed by chains of
amino acids, provide structure for the cell and
countless cell functions (enzymes, identify
disease causing microbes, make muscles move,
transport oxygen, regulate cell activity)
http//images.google.com/imgres?imgurlhttp//www.
eccentrix.com/members/chempics/Slike/Lipids/1Lipid
s.jpgimgrefurlhttp//www.eccentrix.com/members/c
hempics/Lipids.htmlh480w640sz62hlenstart
2tbnidvBwzZRaFKKKyXMtbnh103tbnw137prev/im
ages3Fq3Dlipids26svnum3D1026hl3Den26lr3D2
6client3Dfirefox-a26rls3Dorg.mozillaen-USoffi
cial_s26sa3DN
14
Organic Compounds
- Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) complex molecules
made of a five-carbon sugar (ribose or
deoxyribose), ore or more phosphate groups and an
organic nitrogen-containing base called either a
purine or pyrimidine
http//www.swbic.org/products/clipart/images/nacol
lage.jpg
15
Cells
- Fundamental units of life
- Minute compartments within which the processes of
life are carried out - Can contain organelles
- Enzymes molecular catalysts that regulate
chemical reactions without being used up or
inactivated in the process - Metabolism the multitude of enzymatic reactions
performed by an organism
http//training.seer.cancer.gov/module_anatomy/ima
ges/illu_cell_structure.jpg