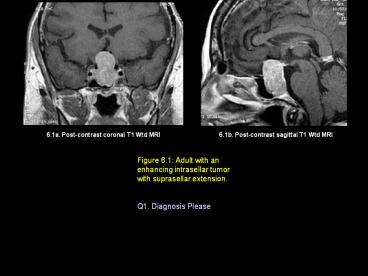
6.1a. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
Title:
6.1a. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
Description:
Figure 6.1: Adult with an enhancing intrasellar tumor with suprasellar extension. ... as eosinophilic adenoma giving rise to gigantism/acromegaly and ACTH producing ... –
Number of Views:137
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 6.1a. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
1
6.1a. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
6.1b. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.1 Adult with an enhancing intrasellar
tumor with suprasellar extension.
Q1. Diagnosis Please
2
6.2. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.2 A child with cystic suprasellar
tumor.
Q2. Diagnosis Please
3
6.3a. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
6.3b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.3 A child with nausea, vomiting and
ataxia.
Q3. Diagnosis Please
4
6.4c. Pre-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
6.4a. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.4b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.4 A child with nausea, vomiting and
ataxia.
Q4. Diagnosis Please
5
6.5c. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
6.5a. Pre-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.5b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.5 A child with nausea, vomiting and
ataxia.
Q5. Diagnosis Please
6
6.6b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.6a. Pre-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.6 An adult with a cranial nerve
deficit produced by a tumor.
Name the cranial nerve deficit _____________ Name
the tumor ____________
Q6. Diagnosis Please
7
6.1a. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
6.1b. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.1
Findings
A homogeneously enhancing tumor is seen within
the sella (yellow arrow in figures A, B) with
suprasellar extension (red arrow in figures A, B)
producing optic chiasm compression.
Diagnosis
- PITUITARY ADENOMA
- Non-hormone secreting pituitary macro adenomas
greater than 1cm in size, grow silently until
they produce optic chiasm compression giving rise
to visual field defects. - Hormone secreting tumors such as eosinophilic
adenoma giving rise to gigantism/acromegaly and
ACTH producing tumor resulting in Cushings
Syndrome are usually smaller in size measuring
less than 1cm in size (microadenoma).
Microadenomas tend to be small in size and are
recognized early due to the hormone secreting
features.
8
6.2. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.2
Findings
A large cystic suprasellar tumor (yellow arrow)
with a rim of peripheral enhancement (red arrow).
Diagnosis
- CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA
- Common suprasellar tumor in a child
- Tumors can be cystic/solid
- Common calcified tumor, calcification within the
tumor can be seen as high as 90
9
6.3b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.3a. Post-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.3
Findings
An enhancing intra IV ventricular tumor (yellow
arrow in figures A, B) is seen. Red arrows point
to expanded IV ventricle.
Diagnosis
- EPENDYMOMA OF THE IV VENTRICLE
- Common pediatric brain tumor
- Enhancing tumors. Calcification can be seen in
50 of tumors.
10
T
6.4c. Pre-contrast sagittal T1 Wtd MRI
6.4a. Pre-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.4b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.4
Findings
An enhancing tumor (yellow arrow in B) seen
posterior to the IV ventricle. Pre-contrast
sagittal T1-weighted MR image (figure c) shows
tumor (T) and its location posterior inferior to
the IV ventricle (yellow arrow).
Diagnosis
- MEDULLOBLASTOMA
- Common pediatric brain tumor
- Common location is posterior to the IV
ventricle, involving the vermis. - Tumor enhances with contrast.
11
6.5c. Post-contrast coronal T1 Wtd MRI
6.5a. Pre-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.5b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.5
Findings
Left cerebellar tumor with cystic (yellow arrow
in A,B,C) and a solid enhancing tumor nodule (red
arrow in B,C).
Diagnosis
- JUVENILE PILOCYTIC. ASTROCYTOMA
- Common pediatric brain tumor
- Common locations include cerebellum and cerebral
hemispheres. - Tumors demonstrate solid and cystic components
12
6.6b. Post-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
6.6a. Pre-contrast axial T1 Wtd MRI
Figure 6.6
Findings
An enhancing tumor within the left
cerebello-pontine angel (red arrow) with
extension into the internal auditory canal
(yellow arrow)
Diagnosis
- Vestibular (8th nerve) Schwannoma
- Tumor recognized by its location.
- Tumor intensely enhances with contrast.