Capacitors PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title: Capacitors
1
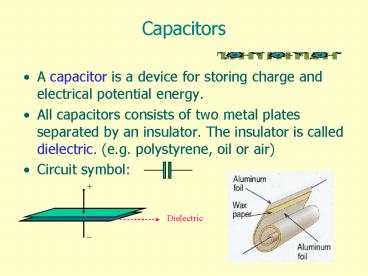
Capacitors
- A capacitor is a device for storing charge and
electrical potential energy. - All capacitors consists of two metal plates
separated by an insulator. The insulator is
called dielectric. (e.g. polystyrene, oil or air) - Circuit symbol
2
Examples of Capacitors
- Paper, plastic, ceramic and mica capacitors
- Non-polarized types can be connected either way
round. - Electrolytic capacitors
- Polarized types must be connected so that there
is d.c. through them in the correct direction. - Air capacitors
- The capacitance is changed by varying the
interleaved area.
3
Formation of a Capacitor
- Capacitors are formed all of the time in everyday
situations - when a charged thunderstorm cloud induces an
opposite charge in the ground below, - when you put your hand near the monitor screen of
this computer.
4
Charged Capacitor
- A capacitor is said to be charged when there are
more electrons on one conductor plate than on the
other.
When a capacitor is charged, energy is stored in
the dielectric material in the form of an
electrostatic field.
5
Capacitance (1)
- Consider any isolated pair of conductors with
charge Q
Capacitance is defined as
Unit farad (F)
Where Q charge on one conductor V potential
difference between two conductors
6
Capacitance (2)
- The smaller the change in potential of the
conductor when a certain charge is transferred to
it, the more charge it can store before breakdown
occurs. - In electronics, the microfarad (µF) and the
picofarad (pF) are usually used to measure
capacitance.
7
Capacitance of a Capacitor
- Note that Q is not the net charge on the
capacitor, which is zero. - Capacitance is a measure of a capacitor's ability
to store charge. - The more charge a capacitor can hold at a given
potential difference, the larger is the
capacitance. - Capacitance is also a measure of the energy
storage capability of a capacitor.
8
Capacitance of Metal Plates
- Consider a metal plate A which has a charge Q as
shown. - If the plate is isolated, A will then have some
potential V relative to earth and its capacitance
C Q/V.
- Now suppose that another metal B is brought
- near to A.
- Induced charges q and q are then obtained
- on B. This lowers the potential V to a value V.
- So C Q/V gt C.
9
Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Suppose two parallel plates of a capacitor each
have a charge numerically equal to Q.
- As C Q/V
- Where QeoEA and
- VEd
? C eoA/d
- C depends on the geometry of the conductors.
10
Action of Dielectric (1)
- A molecule can be regarded as a collection of
atomic nuclei, positively charged, and surrounded
by a cloud of negative electrons.
no field no net charge
- When the molecule is in an electric field, the
nuclei are - urged in the direction of the field, and the
electrons in - the opposite direction.
- The molecule is said to be polarized.
11
Action of Dielectric (2)
- When a dielectric is in a charged capacitor,
charges appear as shown below. - These charges are of opposite sign to the charges
on the plates.
- The charges reduce the electric
- field strength E between the plates.
- The potential difference between
- the plates is also reduced as E V/d.
- From C Q/V, it follows that C is
- increased.
12
Functions of Dielectrics
- It solves the mechanical problem of maintaining
two large metal plates at a very small separation
without actual contact. - Using a dielectric increases the maximum possible
potential difference between the capacitor
plates. - With the dielectric present, the p.d. for a given
charge Q is reduced by a factor er and hence the
capacitance of the capacitor is increased.
13
Relative permittivity and Dielectric Strength
- The ratio of the capacitance with and without the
dielectric between the plates is called the
relative permittivity. or dielectric constant.
- The strength of a dielectric
- is the potential gradient
- (electric field strength) at
- which its insulation breakdown.
14
Relative permittivity of some dielectrics
15
Combination of Capacitor (1)
- In series
The resultant capacitance is smaller than the
smallest Individual one.
16
Combination of Capacitors (2)
- In parallel
The resultant capacitance is greater Than the
greatest individual one.
17
Measurement of Capacitance using Reed Switch
- The capacitor is charged at a frequency f to the
p.d V across the supply, and each time discharged
through the microammeter.
During each time interval 1/f, a charge Q CV is
passed through the ammeter.
18
Stray Capacitance
- The increased capacitance due to nearby objects
is called the stray capacitance Cs which is
defined by - C Co Cs
- Where C is the measured capacitance.
- Stray capacitance exists in all circuits to some
extent. While usually to ground, it can occur
between any two points with different potentials.
- Sometimes stray capacitance can be used to
advantage, usually you take it into account but
often it's a monumental pain.
19
Measurement of Stray Capacitance
- In measuring capacitance of a capacitor, the
stray capacitance can be found as follows
20
Charging of Capacitors (1)
- As a capacitor becomes charged, the current flow
decreases because the voltage developed by the
capacitor increases over time and opposes the
source voltage.
21
Charging a Capacitor (2)
- Voltage-charge characteristics
- Current flow
22
Discharging of Capacitors (1)
- The charged capacitor is the source of voltage
for the current flow. The current will cease
flowing when the charges of the two plates are
again equal, meaning that the capacitor is
completely discharged.
23
Discharging a Capacitor (2)
- Voltage-charge characteristics
- Current flow
24
Time Constant (?)
- ? CR
- The time constant is used to measure how long it
takes to charge a capacitor through a resistor. - The time constant may also be defined as the time
taken for the charge to decay to 1/e times its
initial value. - The greater the value of CR, the more slowly the
charge is stored. - Half-life
- The half-life is the time taken for the charge in
a capacitor to decay to half of its initial
value. - T1/2 CR ln 2
25
Energy Stored in a Charged Capacitor
- The area under the graph gives the energy stored
in the capacitor.
26
Applications of Capacitors (1)
- The capacitance is varied by
- altering the overlap between
- a fixed set of metal plates
- and a moving set. These are
- used to tune radio receiver.
- Press the key on a computer keyboard reduce the
capacitor spacing thus increasing the capacitance
which can be detected electronically.
27
Applications of Capacitors (2)
- Condenser microphone
- sound pressure changes the spacing between a thin
metallic membrane and the stationary back plate.
The plates are charged to a total charge - A change in plate spacing will cause a change in
charge Q and force a current through resistance
R. This current "images" the sound pressure,
making this a "pressure" microphone.
28
Applications of Capacitors (3)
- Electronic flash on a camera
- The battery charges up the flashs capacitor over
several seconds, and then the capacitor dumps the
full charge into the flash tube almost instantly. - A high voltage pulse is generated across the
flash tube. - The capacitor discharges through gas in the the
flash tube and bright light is emitted.