Myocardial infarction : Overview, Causes, Symptoms, treatment and diagnosis PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Myocardial infarction : Overview, Causes, Symptoms, treatment and diagnosis
1
Myocardial infarction
2
Myocardial infarction
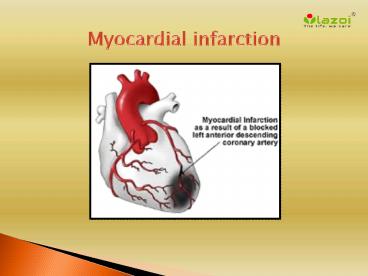
- Myocardial infarction is the medical name for
a heart attack. Heart attacks occur when the flow
of blood to the heart becomes blocked. They can
cause tissue damage and can even be
life-threatening. - The heart requires its own constant supply of
oxygen and nutrients, like any muscle in the
body. - The heart has three coronary arteries, two of
them large, branching arteries that deliver
oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. - If one of these arteries or branches becomes
blocked suddenly, a portion of the heart is
starved of oxygen, a condition called "cardiac
ischemia." - If cardiac ischemia lasts too long, the starved
heart tissue dies. This is a heart attack
3
Symptoms
- Symptoms of myocardial infarction
- In many cases there may be no symptoms, but 25
of the heart attacks show symptoms. Treating the
symptoms at correct time can always rescue
patients. Symptoms may include - Tightness in the chest
- Pain in the chest, back, jaw, and other areas of
the upper body that lasts more than a few minutes
or that goes away and comes back (this may be the
most early sign of heart attack) - Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Anxiety
- Dizziness
- Fast heart rate
4
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
- Physical test of the heart beat is the primary
test which is done to know if the heart is
working properly. - Stress test may also be done to see the beating
of heart during any intense physical exercise. - Measuring of blood pressure
- An electrocardiogram, to measure the hearts
electrical activity - An angiogram, to look for the areas where the
arteries are blocked - An echocardiogram, to look for the areas of the
heart that arent working properly.
5
Causes of myocardial infarction
- Most of the heart attacks are the result of
atherosclerosis or "hardening of the arteries," a
condition that clogs coronary arteries with
fatty, calcified plaques over time. - Inflammation may also be the cause of heart
attack, coronary artery walls become inflated
over time, further increasing the build up of
fatty plaques. - Bad cholesterol- Bad cholesterol, also
called low-density lipoprotein (LDL), is one of
the leading causes of a blockage in the arteries. - Saturated fat-Saturated fats also contribute to
the build up of plaque in the coronary arteries.
This fats are mostly found meat and dairy
products, including beef, butter, and cheese - Trans fat- Another fat which can lead to the
clogging of arteries are trans fat or
hydrogenated fat which is artificially created.
6
Risk factors of myocardial infarction
- Though anyone can have myocardial infarction, but
there may be some risk factors. This may include - High blood pressure
- Hugh cholesterol level
- High triglyceride level
- Age (Men are at higher risk after age 45 and
women after 55) - Obesity
- Diabetes/ High blood sugar level
- Family history
- Smoking
7
Treatment
- Treatments of myocardial infarction
- Heart attack in most cases are emergency, in such
cases surgical methods are used - Procedure called angioplasty may be used to
unblock the arteries that supply blood to the
heart. - In some cases coronary artery bypass graft
(CABG) is done. In this procedure, the surgeon
will reroute the veins and arteries so the blood
can flow around the blockage. - Certain medications can also be used to treat
heart attack, which may include - Blood thinners, such as aspirin, are often used
to break up blood clots and improve blood flow
through narrowed arteries.
8
Treatment
Continue
- Thrombolytics are often used to dissolve clots.
- Antiplatelet drugs, such as clopidogrel, can be
used to prevent new clots from forming and
existing clots from growing. - Nitroglycerine can be used to widen the blood
vessels. - Beta-blockers lower the blood pressure and relax
the heart muscle. This can help limit the
severity of damage to the heart. - ACE inhibitors can also be used to lower blood
pressure and decrease stress on the heart.
9
Complications of myocardial infarction
- Depending on the severity of the heart attack,
certain other complications can alaso occur, such
as - Heart failure
- Arrhythmias or abnormal heart rhythms
- Cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death, where the
heart stops beating. - Cardiogenic shock, where the heart is so damaged
from the heart attack that a person goes into
shock, which may result in damage of other vital
organs like the kidneys or liver - Death
- Myocardial infarction can be treated, and
certain fatality can be minimized if the symptoms
are treated as early as possible.
10
CONNECT WITH US
- Logon to
- www.lazoi.com
- Like us on Facebook
- https//www.facebook.com/LazoiTheLife
- Follow us on Twitter
- https//www.twitter.com/lazoithelife
- Follow us on Pinterest
- https//www.in.pinterest.com/lazoithelife