1ms PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title: 1ms
1
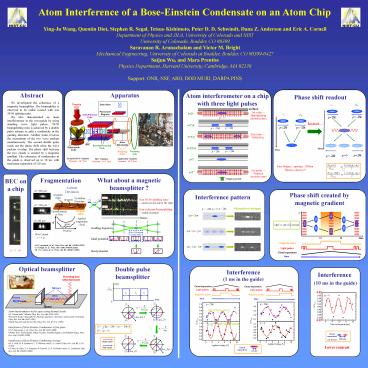
Atom Interference of a Bose-Einstein Condensate
on an Atom Chip
Ying-Ju Wang, Quentin Diot, Stephen R. Segal,
Tetsuo Kishimoto, Peter D. D. Schwindt, Dana Z.
Anderson and Eric A. Cornell Department of
Physics and JILA, University of Colorado and
NIST University of Colorado, Boulder, CO
80309 Saravanan R. Arunachalam and Victor M.
Bright Mechanical Engineering, University of
Colorado at Boulder, Boulder, CO
80309-0427 Saijun Wu, and Mara Prentiss Physics
Department, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA
02138 Support ONR, NSF, ARO, DOD MURI, DARPA
PINS
Apparatus
Abstract
Atom interferometer on a chip with three light
pulses
Phase shift readout
We investigated the coherence of a magnetic
beamsplitter. The beamsplitter is observed to be
radial excited with non 50/50 splitting ratio.
We also demonstrated an atom interferometer in
the waveguide by using standing wave light
pulses. 50/50 beampslitting ratio is achieved by
a double pulse scheme to split a condensate in
the guiding direction. Another pulse reverses the
momentum of the two wave packets simultaneously.
The second double pulse reads out the phase shift
when the wave packets overlap. The phase shift
between the two clouds is created by a magnetic
gradient. The coherence of condensates in the
guide is observed up to 10 ms with maximum
separation of 120 mm.
?a
?b
Trapping Laser
Gate Valve Permanent Magnets
surface
1st pulse --- Beamsplitting (double pulse)
t0
?a
?b
Ioffe-Pritchard Coils
Instead
tT/4
2nd pulse --- Reflecting
tT/2
Atom Waveguide
BEC
Slowing/Focusing Coils
Quadrupole Coils
time
t3T/4
time
Focusing Coil
Stopping Coils
Pyramid MOT Chamber Pressure 10-9 Torr
Application Chamber Pressure 10-10 Torr
BEC Chamber Pressure 10-11 Torr
tT-
Fine fringes spacing 200nm Hard to observe!!
3rd pulse --- Readout (double pulse)
tT
What about a magnetic beamsplitter ?
Fragmentation
BEC on a chip
imaging pulse
Current Deviation
d 150 mm
Phase shift created by magnetic gradient
Interference pattern
Irregular Edge
Crystalline Boundary
- Non 50/50 splitting ratio
- ---Atoms on one side or the other
- Non-coherent beamsplitting
- --- radial excitation
Impurity
1ms
d 103 mm
Absorption images
5ms
Copper Wire
Current density in Wire
x
190 mm
Applied longitudinal field
Position
10ms
d 82 mm
B
6 mG
Guiding trajectory
Position
Zero Curvature (Loose Trap)
Wire Current
I 1 A
t1
time
t2
Ideal potential
15ms
Magnetic pulse
- A.E. Leanhardt, et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 90,
100404 (2003) - J. Fortágh, et. al., Phys. Rev. A 66, 041604
(2002) - M. P. A. Jones, et. al., Phys. Lett. 91, 080401
(2003)
Light pulses
N 7 . 104
Real potential
Cloud separation
time
Optical beamsplitter
Double pulse beamsplitter
Interference (1 ms in the guide)
Interference (10 ms in the guide)
Atom chip
Incoming and reflected beam
Cloud separation
Cloud separation
Mirrors
Light pulses
Light pulses
0.52
Magnetic pulse
Magnetic pulse
BEC
Wires
0.50
Atoms
0.48
time
time
time
0
0.46
N/Ntotal
0.44
Tunnel
0.42
0.40
100 contrast ratio line
- Atom interferometers in free space using thermal
clouds - O. Carnal and J. Mlynek, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66,
2689 (1991) - David W. Keith, Christopher R. Ekstrom, Quentin
A. Turchette, and David E. Pritchard, Phys. Rev.
Lett. 66, 2693 (1991) - Mark Kasevich and Steven Chu, Phys. Rev. Lett.
67, 181 (1991) - Interference of Bose-Einstein Condensates in free
space - J. E. Simsarian, et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 85,
2040 (2000) - Yoshio Torii, Yoichi Suzuki, Mikio Koauma,
Toshiaki Sugiura, and Takahiro Kuga, Phys. Rev. A
61, 041602 (2000) - Interference of Bose-Einstein Condensates in
traps - D. S. Hall, M. R. Matthews, C. E. Wieman, and E.
A. Cornell, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1543 (1998) - Y. Shin, M. Saba, T. A. Pasquini, W. Ketterle, D.
E. Pritchard, and A. E. Leanhardt, Phys. Rev.
Lett. 92, 050405 (2004)
0.38
0.36
0.34
0.32
N/Ntotal
N/Ntotal
8
9
10
11
12
100 contrast ratio line
Time in the guide ms
Cloud separation (at 10 ms)
120 ?m
State vector
Applied voltage V
Applied voltage V
Lower contrast
Rabi vector