Today - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 45
Title:
Today
Description:
... is needed to handle messages (this is a set of macros, so it does not follow ... CWinApp constructor stores this object's address as the entry point as WinMain ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:31
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Today
1
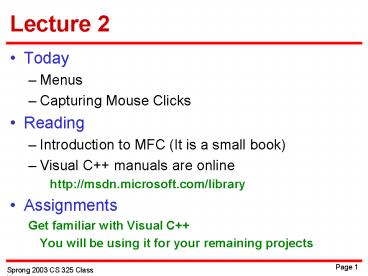
Lecture 2
- Today
- Menus
- Capturing Mouse Clicks
- Reading
- Introduction to MFC (It is a small book)
- Visual C manuals are online
- http//msdn.microsoft.com/library
- Assignments
- Get familiar with Visual C
- You will be using it for your remaining projects
2
CS Supplemental Instruction
Association for Computing Machinery
- Have additional questions from class?
- Stuck on a spot in a project?
- Want additional practice problems?
- Want to compare your notes to old tests?
Where AIME Behind Ferg. Parking Lot Across
from Paty Hall When Monday Wednesday
Nights CS 124 530 630 CS 114 630-730 CS 325
730-830
Coming Soon www.cba.ua.edu/mis/mentoring
3
Before we dive into MFC
- Three initial comments
- MFC has a set of classes defined (see next slide)
that does most things for you automagically - Microsoft (as well as other commercial vendors)
uses a unique naming convention notation, once
you understand this reading other peoples code
becomes easier - No main in windows applications (build off of
existing Microsoft classes instead)
4
Comment 1 MFC Hierarchy
- CObjectCGdiObject CPen CBrush CFont CBitmapC
MenuCCmdTarget CWnd CDialog
CStatic CButton CListBox
CComboBox CFrameWnd CWinThread
CWinApp
- MFC base classgraphical device class class used
for drawing patterns/colors class used for fill
patterns/colors class for fonts class for
bitmap imagesmenu classbase class for targeting
event messages windows base class class for
dialog box windows class for static
items class for buttons (controls) class for
list boxes class for combination boxes class
for frame windows base class for task
threads windows application class
5
Comment 2 Hungarian Notation
- Leading part of variable identifies type of the
variable - Eliminates guessing
- Standard formats
- Examples
- Guess the following
- m_dAverage
- sName
- m_arData
- CStack
- m_pNext
- Array ar
- Char c
- Double d
- Integer n or i
- Boolean b
- Pointer p
- String s
- Class C
- Class member m_
- Static class member s_
6
Comment 3 No main
- Users normally interact with windows program by
events - Move the mouse, click the mouse, click a button,
press a key, etc. - These events generate messages that are sent to
the windows program - MFC provides a wrapper that hides the details
of capturing/interpreting these events from the
programmer - Program responses to events
7
Build an MFC application
- In VC
- File/New, Win32 Application, Empty project,
Finish - File/New, C Source File, ltgive file a namegt
- Insert the code from the web (snippit2)
- Compile it
- Build, build ltproject namegt.exe
- Two errors while linking
- nafxcwd.lib(thrdcore.obj) error LNK2001
unresolved external symbol __endthreadex - nafxcwd.lib(thrdcore.obj) error LNK2001
unresolved external symbol __beginthreadex - Debug/demo1.exe fatal error LNK1120 2
unresolved externals - Fix this error
- Project/Settings, MFC, Use MFC in a shared DLL
8
Class Exercises
- The code in our project should really be in two
files - Class declaration in header file (xxx.h)
- class CWelcomeWindow public CFrameWnd
- public
- CWelcomeWindow()
- CWelcomeWindow()
- private
- CStatic m_pGreeting
- Rest of code in C source file (xxx.cpp)
- Fix this so we have a header source file
9
What does this code mean/do?
- Header File (example1.h)
- Declares a new class that builds off of CFrameWnd
- CFrameWnd gives basic window functionality
(resize the window, move the window, close the
window, etc.) - Class has constructor, destructor, one data
member - class CWelcomeWindow public CFrameWnd
- public
- CWelcomeWindow()
- CWelcomeWindow()
- private
- CStatic m_pGreeting // static block of text
(text box) in window
10
What does this code mean/do?
- include ltafxwin.hgt
- include "example1.h"
- CWelcomeWindowCWelcomeWindow()
- Create(NULL, "Hello CS 325", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW
, CRect(100,100,400,400) ) - m_pGreeting new CStatic
- m_pGreeting-gtCreate("Welcome to Visual C in CS
325", WS_CHILD WS_VISIBLE WS_BORDER
SS_CENTER, CRect(20,20,100,100), this) - CWelcomeWindowCWelcomeWindow() delete
m_pGreeting
- MFC Header file needed
- Our class declaration
- Our class constructor
- Create a new window, second parameter is title,
third is style of window, fourth is
location/size - Declare a new CStatic (block of text)
- Initialize text block with Create method (text to
display, style of display, location/size, parent) - Our class destructor
11
What does this code mean/do?
- class CWelcomeApp public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance()
- m_pMainWnd new
- CWelcomeWindow()
- m_pMainWnd-gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)
- m_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow()
- return TRUE
- welcomeApp
- Class that drives program
- InitInstance starts app
- Creates the window
- Makes window visible
- Forces a refresh of screen
- Reports success
- As welcomeApp instantiates
- Calls constructor, CWinApp constructor, which
registers w/WinMain as entry point - WinMain calls InitInstance
- InitInstance creates window
- Window creates static block
12
Class Exercises
- Using help in VC
- Search for CFrameWnd, look up Create method
- Only look in Visual C documentation
- Search for CFrameWnd
- Want to find document called CFrameWndCreate
- Read the parameters that Create takes
- Check out the style attributes for dwStyle
- Search for CStatic
- Look up how the Create function works in CStatic
13
Adding Menus
- Most windows have a set of menus across the top
of them (various actions users perform) - Can custom-build menus in an application
- Use some built-in MFC features to make it easier
to develop menus - Utilize MFC macro to declare a message map
- This is a data structure that maps message
identifiers to the appropriate message handling
method - Walk through a sample menu program
14
Windows menu example
- Two menus
- First allows user to exit
- Second allows user to toggle text on screen
- Basic construction
- Routines OnExit and OnToggle do processing of
menu items - String variables hold the two messages
- Need the DECLARE stanza in header
- // demo.h file
- include ltafxwin.hgt
- include ltstringgtusing namespace std
- class CMenuWin public CFrameWnd
- publicCMenuWin()afx_msg void
OnExit()afx_msg void OnToggle() - privateint m_iTogglestring m_sOnestring
m_sTwoDECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
15
Body of the menu program (1)
- include demo.h"
- include "menus.h"
- CMenuWinCMenuWin() m_sOne("Roll"),m_sTwo("Tid
e"),m_iToggle(0) - Create(NULL, Menu example",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, CRect(100,100,500,500),
NULL, "MyMenus") - afx_msg void CMenuWinOnExit()
SendMessage(WM_CLOSE)
- Include files
- demo.h from previous slide
- menus.h contains definitions (see shortly)
- Constructor code
- initialize three variables
- create a window, note the one additional
parameter that defines how menus are to look in
this window (will see the MyMenus definition
later) - Function detailing what to do when you process an
exit request (you quit the program)
16
Body of the menu program (2)
- afx_msg void CMenuWinOnToggle() CClientDC
dc(this)string sTextif (m_iToggle)
sTextm_sOne m_iToggle0dc.SetTextColor(
RGB(255,0,0))else sTextm_sTwo
m_iToggle1dc.SetTextColor( RGB(0,255,0))dc.
TextOut(50,50, sText.c_str() )
- Function detailing what to do when the user
selects the toggle menu option - A method for referring to the current window (dc
device context), enables drawing in the window - Check state of variable
- Either set text message to string one or string
two, set color to either red or blue - Copy the string to the window at location
specified
17
Body of the menu program (3)
- // new, this is needed to handle messages (this
is a set of macros, so it does not follow
standard C syntax) - // identify a message and the routine that should
process it - BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP (CMenuWin, CFrameWnd)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_EXIT, OnExit)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_TOGGLE, OnToggle)
- END_MESSAGE_MAP()
- // already seen the following in the previous
example, its role in this program is the same - class CMenuApp public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance() m_pMainWnd new
CMenuWinm_pMainWnd-gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)m
_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow()return TRUE - menuApp
18
Need two more files
- // menus.rc file
- // defines menu and associates identifiers with
message items - include ltafxres.hgt
- include ltmenus.hgt
- MyMenus MENU
- POPUP "File"
- MENUITEM "Halt", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Stop", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Quit", IDM_EXIT
- POPUP "Options
- MENUITEM "Toggle", IDM_TOGGLE
- // menus.h file, links identifiers in our
resource file with the C code - define IDM_EXIT 5050
- define IDM_TOGGLE 5500
19
Summary of menu program
- Declare a derived class from CFrameWnd
- Basic idea same as before (last program)
- Contains macros for defining menus and what
methods in the class are to process menu items - Declare a resource file for menu format
- menus.rc, outlines what menus are in program
- Declare mnemonic names for messages
- menus.h, clean way to refer to messages in pgm
- Declare a derived class from CWinApp
- Same as before, sets program starting point
20
Class Exercises
- Build our menu program (from previous slides)
- demo.h
- demo.cpp
- menus.h
- menus.rc
- Create a new VC project and insert these files
into this project. Run the program - Modify the program so it initially displays some
message (either roll or tide) when the
program starts (add lines to the constructor).
21
Extra Class Exercises
- Use help files to find dwstyle for
- CFrameWndCreate
- CStaticCreate
- Load the source file demoHCPP into a VC Win32
Application project. - Separate the code into two files within the
project, demo.cpp and demo.h - Run the program and observe its output
- Experiment with the options for Create w/
CStatic, what do SS_CENTER and WS_BORDER do? - Modify the program so that Alabama is in the
upper right corner, and Crimson Tide in the
lower left (in a box appropriately sized for the
text) - Comment CRect defines upper-left and lower-right
endpoints of the rectangle in question
22
Windows Coding Overview
- Using Visual C and MFC
- Basic concepts
- Build off of what already exists in MFC classes
- Naming convention is Hungarian notation
- No main routine, the actual main is hidden in
routines that are invoked for us by the framework - To build a windows application
- CFrameWnd
- Derive a specific windows class that does what
you want it to do - CWinApp
- Derive and instantiate a specific application
class that instantiates the CFrameWnd derived
class
23
How do these programs run?
- // part of your code
- class CMyApp
- public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance()
- m_pMainWnd new CMyWin
- m_pMainWnd-gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)
- m_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow( )
- return TRUE
- myApp
- The CWinApp class controls application startup,
execution, and termination - Every MFC application has one instance of a class
derived from CWinApp, this code replaces main - As the program is loaded
- Calls CMyApp constructor (if exists)
constructors for parent (CWinApp) - CWinApp constructor stores this objects address
as the entry point as WinMain (beginning point of
execution) - When execution begins
- WinMain calls InitInstance
- InitInstance creates CMyWin
- Make CMyWin visible, update screen
- Just out of curiousity, when is m_pMainWnd
declared????
24
Adding Menus
- Most windows have a set of menus across the top
of them (various actions users perform) - Can custom-build menus in an application
- Use some built-in MFC features to make it easier
to develop menus - Utilize MFC macro to declare a message map
- This is a data structure that maps message
identifiers to the appropriate message handling
method - Walk through a sample menu program
25
Our Application with Menus
- What do we need to handle our Toggle application
- An application to act as main and instantiate the
window - Derive and instantiate a class from CWinApp
- A window that displays a menu
- Derive and instantiate a class from CFrameWnd
- The constructor should specify which menu
resource to use - Some way to describe the menu items
- A menu resource file (menu.rc)
- Some mechanism of associating a menu item
(message or event) to a method (message or event
handler) - This is done via an MFC macro called a message
map - It maps a menu item ID to its corresponding
method - A way to display the contents of our window
- Some way to represent the information (string)
- Some way to represent the color (RGB)
26
Windows menu example
- Two menus
- First allows user to exit
- Second allows user to toggle text on screen
- Basic construction
- Routines OnExit and OnToggle do processing of
menu items - String variables hold the two messages
- Need the DECLARE stanza in header
- // MenuWin.h file
- include ltafxwin.hgt
- include ltstringgtusing namespace std
- class CMenuWin public CFrameWnd
- publicCMenuWin()afx_msg void
OnExit()afx_msg void OnToggle() - privateint m_iTogglestring m_sOnestring
m_sTwoDECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
27
MenuWin.cpp (1)
- include demo.h"
- include "menus.h"
- CMenuWinCMenuWin() m_sOne("Roll"),m_sTwo("Tid
e"),m_iToggle(0) - Create(NULL, Menu example",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, CRect(100,100,500,500),
NULL, "MyMenus") - afx_msg void CMenuWinOnExit()
SendMessage(WM_CLOSE)
- Include files
- Constructor code
- initialize three variables
- create a window, note the one additional
parameter that defines how menus are to look in
this window (will see the MyMenus definition
later) - OnExit Message Handler Function detailing what
to do when you process an exit request (you
quit the program) CWndSendMessage
28
MenuWin.cpp (2)
- afx_msg void CMenuWinOnToggle() CClientDC
dc(this)string sTextif (m_iToggle)
sTextm_sOne m_iToggle0 dc.SetTextColor(
RGB(255,0,0))else sTextm_sTwo
m_iToggle1dc.SetTextColor( RGB(0,
0,255))dc.TextOut(50,50, sText.c_str() )
- OnToggle Message Handler Function detailing what
to do when the user selects the toggle menu
option - A method for referring to the current window (dc
device context), enables drawing in the window - Check state of variable
- Either set text message to string one or string
two, set color to either red or blue - Copy the string to the window at location
specified
29
MenuWin.cpp (3)
- // new, this is needed to handle messages (this
is a set of macros, so it does not follow
standard C syntax) - // identify a message and the routine that should
process it - BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP (CMenuWin, CFrameWnd)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_EXIT, OnExit)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_TOGGLE, OnToggle)
- END_MESSAGE_MAP()
- // already seen the following in the previous
example, its role in this program is the same - class CMenuApp public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance() m_pMainWnd new
CMenuWinm_pMainWnd-gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)m
_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow()return TRUE - menuApp
30
Need two more files
- // menus.rc file
- // defines menu and associates identifiers with
message items - include ltafxres.hgt
- include ltmenus.hgt
- MyMenus MENU
- POPUP "File"
- MENUITEM "Halt", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Stop", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Quit", IDM_EXIT
- POPUP "Options
- MENUITEM "Toggle", IDM_TOGGLE
- // menus.h file, links identifiers in our
resource file with the C code - define IDM_EXIT 5050
- define IDM_TOGGLE 5500
31
Summary of menu program
- Declare a derived class from CFrameWnd
- Basic idea same as before (last program)
- Contains macros for defining menus and what
methods in the class are to process menu items - Declare a resource file for menu format
- menus.rc, outlines what menus are in program
- Declare mnemonic names for messages
- menus.h, clean way to refer to messages in pgm
- Declare a derived class from CWinApp
- Same as before, sets program starting point
32
Windows menu example
- Two menus
- First allows user to exit
- Second allows user to toggle text on screen
- Basic construction
- Routines OnExit and OnToggle do processing of
menu items - String variables hold the two messages
- Need the DECLARE stanza in header
- // demo.h file
- include ltafxwin.hgt
- include ltstringgtusing namespace std
- class CMenuWin public CFrameWnd
- publicCMenuWin()afx_msg void
OnExit()afx_msg void OnToggle() - privateint m_iTogglestring m_sOnestring
m_sTwoDECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
33
Body of the menu program (1)
- include demo.h"
- include "menus.h"
- CMenuWinCMenuWin() m_sOne("Roll"),m_sTwo("Tid
e"),m_iToggle(0) - Create(NULL, Menu example",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, CRect(100,100,500,500),
NULL, "MyMenus") - afx_msg void CMenuWinOnExit()
SendMessage(WM_CLOSE)
- Include files
- demo.h from previous slide
- menus.h contains definitions (see shortly)
- Constructor code
- initialize three variables
- create a window, note the one additional
parameter that defines how menus are to look in
this window (will see the MyMenus definition
later) - Function detailing what to do when you process an
exit request (you quit the program)
34
Body of the menu program (2)
- afx_msg void CMenuWinOnToggle() CClientDC
dc(this)string sTextif (m_iToggle)
sTextm_sOne m_iToggle0dc.SetTextColor(
RGB(255,0,0))else sTextm_sTwo
m_iToggle1dc.SetTextColor( RGB(0,255,0))dc.
TextOut(50,50, sText.c_str() )
- Function detailing what to do when the user
selects the toggle menu option - A method for referring to the current window (dc
device context), enables drawing in the window - Check state of variable
- Either set text message to string one or string
two, set color to either red or blue - Copy the string to the window at location
specified
35
Body of the menu program (3)
- // new, this is needed to handle messages (this
is a set of macros, so it does not follow
standard C syntax) - // identify a message and the routine that should
process it - BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP (CMenuWin, CFrameWnd)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_EXIT, OnExit)
- ON_COMMAND
- (IDM_TOGGLE, OnToggle)
- END_MESSAGE_MAP()
- // already seen the following in the previous
example, its role in this program is the same - class CMenuApp public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance() m_pMainWnd new
CMenuWinm_pMainWnd-gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)m
_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow()return TRUE - menuApp
36
Need two more files
- // menus.rc file
- // defines menu and associates identifiers with
message items - include ltafxres.hgt
- include ltmenus.hgt
- MyMenus MENU
- POPUP "File"
- MENUITEM "Halt", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Stop", IDM_EXIT
- MENUITEM "Quit", IDM_EXIT
- POPUP "Options
- MENUITEM "Toggle", IDM_TOGGLE
- // menus.h file, links identifiers in our
resource file with the C code - define IDM_EXIT 5050
- define IDM_TOGGLE 5500
37
Summary of menu program
- Declare a derived class from CFrameWnd
- Basic idea same as before (last program)
- Contains macros for defining menus and what
methods in the class are to process menu items - Declare a resource file for menu format
- menus.rc, outlines what menus are in program
- Declare mnemonic names for messages
- menus.h, clean way to refer to messages in pgm
- Declare a derived class from CWinApp
- Same as before, sets program starting point
38
Class Exercises
- Build our menu program (from previous slides)
- demo.h
- demo.cpp
- menus.h
- menus.rc
- Create menus.rc as a text file, not a resource
file!!!!! - Create a new VC project and insert these files
into this project. Run the program - Modify the program so it initially displays some
message (either roll or tide) when the
program starts (add lines to the constructor).
39
Our Application with Clicks
- What do we need to display the locations of our
clicks - An application to act as main and instantiate the
window - Derive and instantiate a class from CWinApp
- Some mechanism of associating a mouse click
message (or event) to a method (message or event
handler) - Well need another Message Map to do this
- A way to display the contents of our window
- Some way to represent get the coordinates of our
click - Clean way to convert these numerical points to a
character array
40
Capturing Mouse Clicks
- System has built-in routines to capture mouse
clicks - OnLButtonDown, OnLButtonUp
- OnRButtonDown, OnRButtonUp
- All four routines take two parameters
- UINT flags, a 32-bit unsigned integer
- CPoint point, a class for points, x and y
coordinates are available (can retrieve), as well
as other operations
41
Program captures mouse clicks
- include ltafxwin.hgt
- include ltstringgt
- using namespace std
- class CMouseWin public CFrameWnd
- publicCMouseWin()afx_msg void
OnLButtonDown(UINT, CPoint)afx_msg void
OnRButtonDown(UINT, CPoint)afx_msg void
OnLButtonUp(UINT, CPoint)afx_msg void
OnRButtonUp(UINT, CPoint) - privatevoid showUp(CPoint)void
showDown(CPoint)DECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP( )
- Our class will provide new methods for processing
the various mouse click events - Utilizes two private methods to process these
mouse clicks (showUp and showDown)
42
Program Body (part one)
- include ltstrstrea.hgt
- include "example.h"
- CMouseWinCMouseWin()
- Create(NULL, "Mouse Click Example",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, - CRect(100,100,500,500))
- afx_msg void CMouseWinOnLButtonDown(UINT
uFlags, CPoint point) showDown(point) - afx_msg void CMouseWinOnLButtonUp(UINT uFlags,
CPoint point) showUp(point) - afx_msg void CMouseWinOnRButtonDown(UINT
uFlags, CPoint point) showDown(point) - afx_msg void CMouseWinOnRButtonUp(UINT uFlags,
CPoint point) showUp(point)
- One new header file (will use it shortly)
- Constructor creates a standard window
- Four methods defined to capture each of the four
mouse actions - Two methods call the showDown method (press mouse
button) - Two methods call the showUp method (release mouse
button)
43
Program Body (part two)
- void CMouseWinshowDown(CPoint point)
- CClientDC dc(this)
- ostrstream s
- s ltlt "(" ltlt point.x ltlt ", ltlt point.y ltlt ")"
- dc.TextOut(50,50,s.str(), s.pcount())
- void CMouseWinshowUp(CPoint point)
- CClientDC dc(this)
- char carText32
- ostrstream s(carText, sizeof(carText))
- s ltlt "(" ltlt point.x ltlt ", ltlt point.y ltlt ")"
- dc.TextOut(200,200,carText, s.pcount())
- New concept here (writing to a string)
- Already seen writing to files and stdout
- Can also write to an array of chars
- Process
- Declare array
- Declare output stream
- Write to it (s.pcount has count of chars written)
- Take this array (with the output that was written
to it) and display it in the window
44
Program Body (part three)
- BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP
- ( CMouseWin, CFrameWnd )
- ON_WM_LBUTTONDOWN( )
- ON_WM_RBUTTONDOWN( )
- ON_WM_LBUTTONUP( )
- ON_WM_RBUTTONUP( )
- END_MESSAGE_MAP( )
- class CMouseApp public CWinApp
- public
- BOOL InitInstance( )
- m_pMainWnd new CMouseWin
- m_pMainWnd -gtShowWindow (m_nCmdShow)
- m_pMainWnd-gtUpdateWindow()
- return TRUE
- mouseApp
- Message map section defines four events that this
program is watching out for (all related to mouse
buttons). All four are built into the system,
you dont need to define further - Standard clause at the end of the program to get
things started (register mouseApp with WinMain
and have it invoked when the program starts)
45
Class Exercises
- Modify the code from the previous catching mouse
clicks example so that - The right mouse button down and up locations are
printed at the top of the window (in the left and
right corners) - The left mouse button down and up locations are
printed at the bottom of the window (in the left
and right corners) - Files
- MouseWin.h
- MouseWin.cpp