AC i-V relationship for R, L, and C PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: AC i-V relationship for R, L, and C
1
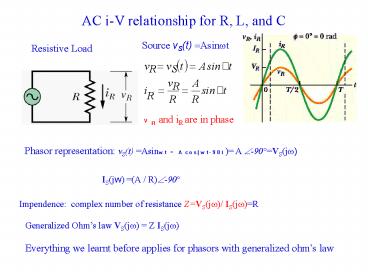
AC i-V relationship for R, L, and C
Source vS(t) Asinwt
Resistive Load
VR and iR are in phase
Phasor representation vS(t) Asinwt
Acos(wt-90) A ?-90VS(jw)
IS(jw) (A / R)?-90
Impendence complex number of resistance
ZVS(jw)/ IS(jw)R
Generalized Ohms law VS(jw) Z
IS(jw) Everything we learnt before applies for
phasors with generalized ohms law
2
Capacitor Load
ICE
VC(jw) A ?-90
Notice the impedance of a capacitance decreases
with increasing frequency
3
Inductive Load
ELI
Phasor VL(jw)A ?-90 IL(jw)(A/wL)
?-180 ZLjwL
Opposite to ZC, ZL increases with frequency
4
AC circuit analysis
- Effective impedance example
- Procedure to solve a problem
- Identify the sinusoidal and note the excitation
frequency. - Covert the source(s) to phasor form
- Represent each circuit element by its impedance
- Solve the resulting phasor circuit using previous
learnt analysis tools - Convert the (phasor form) answer to its time
domain equivalent.
Ex. 4.16, p180
5
Ex. 4.21 P188
R1100 W, R275 W, C 1mF, L0.5 H,
vS(t)15cos(1500t) V. Determine i1(t) and
i2(t). Step 1 vS(t)15cos(1500t), w1500
rad/s. Step 2 VS(jw)15 ?0 Step 3 ZR1R1,
ZR2R2, ZC1/jwC, ZLjwL Step 4 mesh equation
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.