Money and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Money and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run
Description:
In the long run. Prices are flexible. As a first ... Expected depreciation of the Swiss Franc relative to the Euro = expected inflation differential ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Money and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run
1
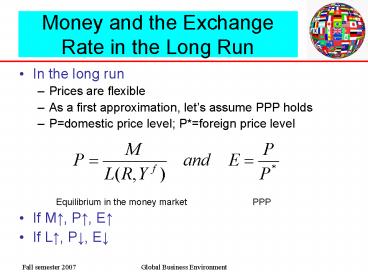
Money and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run
- In the long run
- Prices are flexible
- As a first approximation, lets assume PPP holds
- Pdomestic price level Pforeign price level
- Equilibrium in the money market
PPP - If M?, P?, E?
- If L?, P?, E?
2
Case Study Money Supply Growth in Bolivia
- Hyperinflation inflation rate of 50 a month or
higher - Bolivia experienced hyperinflation between April
1984 and October 1985 - During hyperinflations, the long-run effects of
money on the price level occur very quickly
3
Money growth, Inflation and Depreciation in
Bolivia 1984-85
4
Money growth, Inflation and Depreciation in OECD
economies
5
Money and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run
- In the short run the price level is fixed (strong
assumption) - If M?, L?
- How can money demand fall?
- Money has no effect on output in the long run,
i.e. Yf is not affected by M - Hence, R?
6
Money and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run,
cont.
- UIPC
- R R (Ee - E)/E
- E adjusts instantaneously to achieve UIPC
- Suppose M? permanently
- Ee ? (long-run effect)
- Given R, if R?, this implies (Ee - E)/E ?
- Hence, E ? more than Ee?
- This is the exchange rate overshooting
7
A Long-Run Exchange Rate Model Based on PPP
- PPP
- ECHF/ PCHF/ P
- Differentiate to obtain relative PPP
- (EeCHF/ - ECHF/)/ECHF/ ?eCHF - ?e
- Expected depreciation of the Swiss Franc relative
to the Euro expected inflation differential - UIPC
- RCHF R (EeCHF/ - ECHF/ ) / ECHF/
- Combine relative PPP with UIPC to obtain the
Fisher relationship - RCHF - R (EeCHF/ - ECHF/)/ECHF/ ?eCHF
- ?e - The international interest rate differential is
the difference between expected national
inflation rates
8
Empirical Evidence on the Fisher Relationship
Switzerland
9
Empirical Evidence on the Fisher Relationship
The United States
10
Empirical Evidence on the Fisher Relationship
Switzerland and the United States
11
Empirical Evidence on the Fisher Relationship
12
Does PPP Really Hold in the Long Run? For All
Goods?
- It does, but in the very long run
- The speed of convergence is very slow deviations
appear to damp out at a rate of roughly 15 per
year
13
Empirical Evidence on PPP and the Law of One
Price
- Big Mac Currencies, published by The Economist
- Started in 1986 it is a survey of Big Mac
hamburger prices at McDonalds restaurants around
the world - It is a homogeneous good. Hence the Law of One
Price would apply - Evidence The Economist
14
(No Transcript)
15
Big Mac
- Column 1 Big Mac price in local currency Px
- Column 2 Px multiplied by E/x, the U.S.
dollar/local currency price exchange rate. This
is the dollar price of the Big Mac in country X - Column 3 Px/ PUS. This is the implied PPP of
the U.S. dollar, EPPP/X - Column 3 (EPPP/X - E/X)100 / E/X
- This is the under(-)/over() valuation of
currency X against the U.S. dollar - The CHF is 53 overvalued relative to the US
Dollar
16
Big Mac (cont.)
- China most undervalued, Iceland the most
overvalued - If you can keep the Big Mac fresh, buy it in
China for the equivalent of 1.45 and sell it in
Iceland for 7.6! - Trade barriers, transport costs and differences
in taxes - Use of non-traded goods and services, like labor
and rent contribute about 60 of the price of the
Big Mac - Most expensive Big Mac Iceland, Norway,
Switzerland, Denmark - Least expensive Big Mac Sri Lanka, Indonesia,
Hong Kong
17
Explaining the Problems with PPP
- The failure of the empirical evidence to support
the PPP and the law of one price is related to - Trade barriers and transport costs
- Non-tradable goods
- Departures from free competition
- International differences in price level
measurement
18
Trade Barriers and Transport Costs
- Transport costs and governmental trade
restrictions make trade expensive - Equivalent to 170 tariff in advanced economies
19
Non-tradable goods
- The domestic prices of non-tradable goods can be
very different when expressed in the same
currency - Example housing price in Lausanne and in New
Delhi - No arbitrage
- Non-tradable goods account for about 50 of GNP
and hence 50 of the CPI - Non-tradable goods are more expensive in richer
countries
20
Balassa-Samuelson Hypothesis
- In poorer countries, productivity in tradable
goods and therefore wages are lower - Prices of non-tradable goods are lower
- PN gt E PN
- Where PN is the foreign price of non-tradable
goods - Because non-tradable goods account for almost 50
of the CPI (consumer price index) - P gt E P
21
Price Levels and GDP per capita