Lecture notes 1, 4910 spring 2005, FRF Spatial environmental models PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Lecture notes 1, 4910 spring 2005, FRF Spatial environmental models
1
Lecture notes 1, 4910 spring 2005, FRFSpatial
environmental models
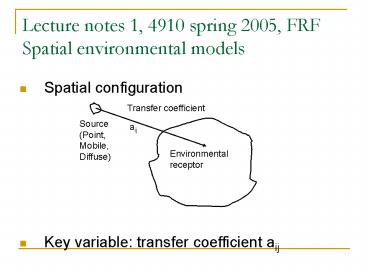
- Spatial configuration
- Key variable transfer coefficient aij
2
The Generic model of spatially distributed
pollutants
- Source abatement cost function
- Deposition of pollutants in the environment
3
Uniformly distributed pollutants
- Uniform mix multiple recipients
4
Non-uniformly distributed pollutants
- Non-uniform mix
5
Structured transfer river pollution
- At receptor j a ranking of transfer coefficients
starting upstream at source 1 and ending at
nearest source Nj
6
The spatial social problem
- General social problem formulation with damage
function
7
The spatial social problem, cont.
- The general first order condition
- Non-uniformly mixed Source marginal abatement
cost equal to social marginal damage weighted
with transfer coefficients. NB! In general
different marginal costs between sources.
8
Cost effective solutions, cont.
- River pollution
- Uniformly mixed
- Marginal abatement cost equal for all sources and
equal to total marginal damage
9
The pollutant tax solution
- Source decision problem
- The tax on pollutants is source specific, and
should be set equal to the weighted marginal
damage in the optimal case. - Uniform distribution tax rate equal for sources
10
Ambient standard
- Environmental service of receptors
- Damage function
- The physical ambient standard is the level of
deposition of pollutants, dj
11
Environmental policy in practice
- Formulating limits for dj dj
- Social problem
- The Lagrangian (Economists mathematical manual
Kuhn Tucker, maximisation)
12
Environmental policy in practice, cont.
- First order conditions
- Interpretation Marginal abatement costs equal to
shadow prices on ambient constraints weighted
with transfer coefficients
13
Environmental policy in practice, cont.
- Interpretation of shadow price
- Envelope theorem
- Shadow price positive for binding constraints
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.