Rotations in R2 PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 63
Title: Rotations in R2
1
Rotations in R2
2
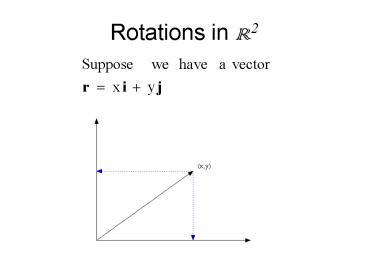
Rotations in R2
3
(1)
Definition If the components of the quantity A
transform under a rotation accoring to (1) then A
is said to be a vector
4
(No Transcript)
5
Matrix
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Rotation
9
(No Transcript)
10
Classical Physics
- Newtons Laws
- 1.Every body remains at rest or in constant
rectilinear motion unless acted on by a force - 2
11
Newtons third law
12
Comments
- Makes perfect sense for electrostatics and
gravity - e.g
13
- There is an implicit assumption of an absolute
time here, i.e absolute simulantiety - There is a suggestion of static interaction at a
distance
14
Inertial frames
15
(No Transcript)
16
Maxwells equations together with force
law FqEvxB Contains all of Classical
Electrodynamics
17
m/s
18
m/s
Exactly the speed of light
19
- Static charges and charges in motion at a
constant rate do not radiate, accelerated charges
radiate
20
Consider the circuit shown . There is an energy
sourcethat restores the energy that is radiated
or lost as heat in the resistor. If the
resistance loses are small the current in the
circuit varies sinusodially with resonance
angular frequency w( ?1/?LC ). The oscillator is
coupled through a transformer to a transmission
line which carries the current to an anteena, in
this case it is a simple dipole antenna
21
- An electric charge at rest sets up a pattern of
electric field lines. A charge in motion sets up
a pattern of magnetic field lines in addition to
the electric field. Once a steady condition has
been reached (after the charge is in motion and
the fields are established in space)there is an
energy density associated with the electric and
magnetic fields but the energy density remains
constant in time. However if you wiggle the
charge back and forth you can send a signal.
22
- Static charges and charges in motion at a
constant rate do not radiate, accelerated charges
radiate
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
- The more important fundamental laws and facts of
physical science have all been discovered, and
these are now so firmly established that the
possibility of their ever being supplanted in
consequence of new discoveries is exceedingly
remote . . . Our future discoveries must be
looked for in the sixth place of decimals. - Albert A. Michelson, 1894
26
Lorentz Transformation
27
Lorentz Transformation
28
Lorentz Transformation
29
(No Transcript)
30
- There is no motion in the y or z directions hence
31
- Now assume that observers in S and S
- Measure a flash of light moving along the
- x(x) directions
- The speed of light is constant so
32
(No Transcript)
33
- For a general outgoing spherical pulse
34
hence
35
Linear Transformation equation
36
(No Transcript)
37
Speed of light is constant
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
Lorentz transformation
41
Inverse Lorentz transformation
42
Properties and Consequences of the Lorentz
transformation
43
- Then
44
If the differences are infinitesmalwe can go
over to differentials
- Then
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
Length Contraction
48
Length Contraction
49
Simulaniety
- Suppose We have two diodes fixed at a distance L
apart in and fixed to a single circuit so that
both light at the same time
50
Causality
Causality is perserved!!
51
Time Dilation
52
- Be careful to think operationally
- What we mean is time goes slower
- As measured by the observer at rest when looking
at an event occurring in the frame - S
- If you run very fast you will appear to live
longer to an observer at rest but to you you
will live exactly the same amount of time as if
you had stayed at rest!
53
Properties and Consequences of the Lorentz
transformation
54
- Then
55
If the differences are infinitesmalwe can go
over to differentials
- Then
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
Length Contraction
59
Length Contraction
60
Simulaniety
- Suppose We have two diodes fixed at a distance L
apart in and fixed to a single circuit so that
both light at the same time
61
Causality
Causality is perserved!!
62
Time Dilation
63
- Be careful to think operationally
- What we mean is time goes slower
- As measured by the observer at rest when looking
at an event occurring in the frame - S
- If you run very fast you will appear to live
longer to an observer at rest but to you you
will live exactly the same amount of time as if
you had stayed at rest!