Classes of Mutations PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Classes of Mutations
1
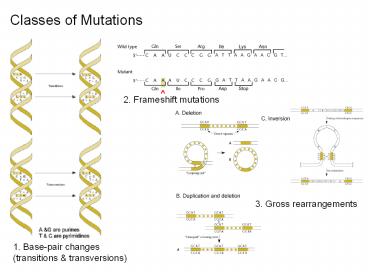
Classes of Mutations
2
Consequences of mutations
- Base substitutions lead to nonsense, missense,
neutral or silent mutations - Frameshift mutations alter the translational
reading frame - Rearrangements reduce or eliminate protein
function
3
Methods for Inducing Mutagenesis
4
Methods for Detecting Mutagenesis
Variety of test systems available that are based
on acquisition or loss of a specific genetic
marker, e.g. antibiotic resistance.
5
UV-induced mutagenesis (using rif-resistance)
- Score for rifS to rifR.
- Rifampin (rif) targets the bacterial RNA Pol,
blocking transcription. - 69 possible single base substitutions confer rif
resistance. These are concentrated in the first
half of the protein, and are distributed among 24
coding positions (Garibyan et al. DNA Repair 2
(2003) 593-608).
6
The strains
Wild-type strain -- provides reference for
frequency of mutation when repair and coping
systems are intact.
Excision repair mutant (uvrA) -- unable to remove
DNA lesions.
Mutant in damage-inducible DNA polymerase (umuC)
-- umuC allows mutagenic bypass of UV lesions.
Mismatch repair mutant (mutS) -- impairs removal
of mismatched base pairs that have passed through
proof-reading step of DNA replication
7
UV irradiation and plating protocol
8
Pull-down Assay
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.