Ch. 6 Application Specific Processors - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 61
Title:
Ch. 6 Application Specific Processors
Description:
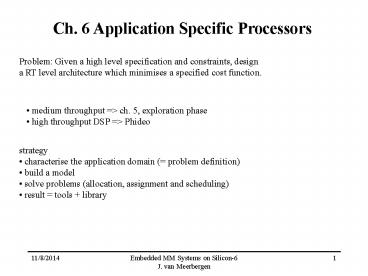
Problem: Given a high level specification and constraints, design ... PUk. AG1. AG2. AGi. Routing Network. M1. M2. Mj. Routing Network. C. O. N. T. R. O. L. 9/3/09 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:28
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ch. 6 Application Specific Processors
1
Ch. 6 Application Specific Processors
Problem Given a high level specification and
constraints, design a RT level architecture which
minimises a specified cost function.
- medium throughput gt ch. 5, exploration phase
- high throughput DSP gt Phideo
- strategy
- characterise the application domain ( problem
definition) - build a model
- solve problems (allocation, assignment and
scheduling) - result tools library
2
outline
- domain analysis
- model of periodic operations
- overview of Phideo (once over lightly)
- basic steps
- PU generation
- scheduling
- memory synthesis
- address synthesis
- controller synthesis
- extensions hierarchy and parameters
- example progressive scan
Goal to show importance of modeling
to discuss basic steps that are more generally
applicable
3
Domain analysis
proc
orig
output
Line merge
input
proc
Key stream oriented processing Use this as a
basis for the approach adapt the method to the
way designers are thinking. (not the opposite)
4
regular execution no overlap between loops no
overlap between loop bodies
maintain allow overlap allow overlap
5
Model of periodic operations
A periodic operation O is executed periodically
in time. The operation can have multiple
dimensions and is characterised by
s1
6
Model of periodic operations
(i0 0 .. 1 ) 16 (i1 0 .. 3 ) 2
operation ()
s1
p0
p1
time
1
5
10
15
20
starts counting from 0
7
Model of periodic operations execution time
(i0 0 .. 1 ) 16 (i1 0 .. 3 ) 2
operation ()
t 1 16i0 2i1 s pTi
8
Model of periodic operations data dependencies
For j0 0 to 4 115 For j1 0 to 7 10
For j2 0 to 6 1 g(X5j0j21
6j18)
For i0 0 to 5 50 For i1 0 to 14 2
X2i0i1 3i15 f()
X....
f
g
n A i b
9
Model of periodic operations minimum distance
between starttimes
For i 0 to 4 pp2 x i
For k 0 to 4 pc ... x k
Production Consumption
10
for i0 0 to 1 5 for i1 0 to 2 1 x
i0i1
for j0 0 to 2 3 for j1 0 to 1 1 ...
x j1j0
g
f
Production Consumption
time
sf
sg
for each DD tg gt tf
Example
11
Model of periodic operations conflict detection
Stream 1