oxidation PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: oxidation
1
? - oxidation
2
Fatty acid storage
- Dietary fatty acids form triacylglycerols in
intestinal cells - Released into lymphatic system as chylomicrons
- Lipoprotein lipase
- present in capillaries supplying adipocytes (and
skeletal muscle) - Hydrolyse fatty acids from triacylglycerols in
chylomicrons/lipoproteins - Fatty acids flow down concentration gradient via
facilitated transport - Stored as triacylglycerols
From Matthews, CK van Holde KE (1990)
Biochemistry. Redwood CityBenjamin Cummings
p.301.
3
Fatty acid release
- Triacylglycerols hydrolysed in adipocytes (and
skeletal muscle) by hormone sensitive lipase - Stimulated by sympathetic hormones and
neurotransmitters - Inhibited by insulin
From Matthews, CK van Holde KE (1990)
Biochemistry. Redwood CityBenjamin Cummings
p.301.
4
Fatty acid release
- Glycerol released by adipocytes and skeletal
muscle - Adipocytes and SM do not contain glycerol kinase
- Glycerol converted to glycerol 3-phosphate in
cells containing glycerol kinase (i.e. liver) - G-3-P converted to DHAP
- Glycolysis
- Gluconeogenesis
- New data suggest that SM may metabolise some
glycerol despite not containing glycerol kinase - Fatty acids
- In adipocytes
- Some reesterified to triacylglycerols
- Some released and attach to albumin to form FFA
- In skeletal muscle
- Used as fuel
5
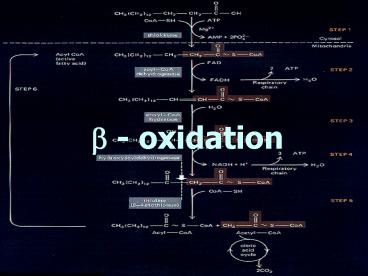
Fatty acid oxidation
- Fatty acids oxidised in mitochondria
- Must be activated before entering mitochondrial
matrix - Combine with CoA on outer membrane to form Acyl
CoA - Energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
6
Fatty acid oxidation
- Acyl CoA transported across inner mitochondrial
membrane by carnitine transporter - Rate limiting step for fatty acid break down
From Stryer, LS (1988) Biochemistry (3rd Ed).
New York WH Freeman Co. p471
7
Fatty acid oxidation
- Once inside mitochondria Acyl CoA oxidised via
?-oxidation - Two carbons at a time removed from hydrocarbon
tail to form acetyl CoA - Split between ? and ? carbons
From Stryer, LS (1988) Biochemistry (3rd Ed).
New York WH Freeman Co. p470
8
Fatty acid oxidation
- Acyl CoA dehydrogenated to form enoyl CoA
- Produces
- double bond between ? and ? carbons
- FADH
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
9
Fatty acid oxidation
- Enoyl CoA hydrated to form hydroxyacyl CoA
- Saturates double bond between ? and ? carbons
- Changes energy distribution within molecule
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
10
Fatty acid oxidation
- Hydroxyacyl CoA oxidised to form ketoacyl CoA
- H removed from hydroxyl group on ? carbon
- Produces NADH H
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
11
Fatty acid oxidation
- ketoacyl CoA split between ? and ? carbons and
another CoA added - Produces
- Acetyl CoA
- Acyl CoA which has been shortened by 2 carbons
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
12
Fatty acid oxidation
- Acyl CoA which has been shortened by 2 carbons
- Process continues until final product is two
acetyl CoA - Acetyl CoA and propionyl CoA (3C) final products
of odd chain fatty acids - Propionly CoA converted to succinyl CoA and
enters KC
From Summerlin LR (1981) Chemistry for the Life
Sciences. New York Random House p 559.
13
Ketone bodies
- When body CHO stores low blood glucose also low
- decreased insulin production
- Insulin inhibitor of lipolysis
- Low insulin leads to accelerated lipolysis
- High blood FFA leads to increased extraction by
liver - acetyl CoA production via ?-oxidation increased
- Liver cells use oxaloacetate to synthesise
glucose to combat falling blood glucose levels - Leaves less to combine with acetyl CoA for entry
into KC - Liver contains enzymes that make ketone bodies
from acetyl CoA - Acetoacetate
- reduced to form D-3-hydroxybutyrate
- Spontaneous decarboxylation forms acetone
- Ketone bodies used as fuel by other tissues
- ketoacidosis - reduced pH can be fatal in
uncontrolled diabetes mellitus