Coverage: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Coverage:
Description:
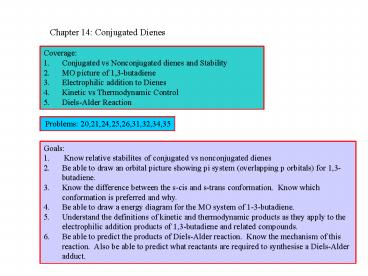
Coverage: Conjugated vs Nonconjugated dienes and Stability. MO ... Also be able to predict what reactants are required to synthesise a Diels-Alder adduct. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:22
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Coverage:
1
Chapter 14 Conjugated Dienes
- Coverage
- Conjugated vs Nonconjugated dienes and Stability
- MO picture of 1,3-butadiene
- Electrophilic addition to Dienes
- 4. Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Control
- Diels-Alder Reaction
Problems 20,21,24,25,26,31,32,34,35
- Goals
- Know relative stabilites of conjugated vs
nonconjugated dienes - Be able to draw an orbital picture showing pi
system (overlapping p orbitals) for
1,3-butadiene. - Know the difference between the s-cis and s-trans
conformation. Know which conformation is
preferred and why. - Be able to draw a energy diagram for the MO
system of 1-3-butadiene. - Understand the definitions of kinetic and
thermodynamic products as they apply to the
electrophilic addition products of 1,3-butadiene
and related compounds. - Be able to predict the products of Diels-Alder
reaction. Know the mechanism of this reaction.
Also be able to predict what reactants are
required to synthesise a Diels-Alder adduct.
2
Dienes two double bonds a. Nonconjugated
diene double bonds are separated by at least
two C-C single bonds.
1,4-pentadiene
b. Conjugated diene double bond separated by
only one C-C single bond.
1,3-pentadiene
c. Allenes - cumulated double bonds.
1,2-pentadiene
3
Stabilites of dienes measured by heats of
hydrogenation, -?H
-?H, kcal/mol
30.0
27.4
60.2
53.7
Are the values for dienes what you expect?
4
- 1,4-pentadiene contains two monosubstituted
double bonds. - Predicted -?H 2 x 30.0 60.0 kcal/mol
- Actual -?H 60.2 kcal/mol
- 1,3-pentadiene contains one monosubstituted
double bond and - one disubstituted double bond.
- Predicted -?H 1 x 30.0 1 x 27.4 57.4
kcal/mol - Actual -?H 53.7 kcal/mol
Conclusion 1,3-pentadiene is more stable than
predicted.
Why? Answer Conjugation
sp2 sp2 sp2 sp2 sp3
5
Why? Conjugation the two double bonds form a
continuous overlap of the p orbitals. This
results in delocalization of the pi electrons and
extra stability
sp2 sp2 sp2 sp2 sp3
Conformations of 1,3-butadiene
1 2 3 4
1,3-butadiene exists in two conformations that
are in equilibrium
180o
s-trans
s-cis
6
s - single bond s-cis - double bonds are cis
with respect to single bond s-trans double
bonds are trans with respect to single bond
All atoms (including C and H) lie in the same
plane for these conformations. Any nonplanar
conformations results in disruption of the
continuous overlap of p orbitals and raises the
energy.
7
(No Transcript)
8
Steric repulsion makes the s-cis conformation
adopt a slightly nonplanar conformation.
9
1,2- and 1,4-addition reactions to 1,3-butadiene
1,2-product 1,4-product
Mechanism Markovnikov Addtion of HBr (see
Alkenes)
Allylic carbocation resonance stabilized
Br-
10
-80 C 80
20 40 C 15
85
The product distribution is temperature
dependent. Low Temperature The product that
forms the fastest will be the major product.
This product is termed the kinetic product.
Thus, 1,2-product is the kinetic product and
forms faster than than the 1,4-product.
High Temperature The product that is more
stable will be the major product. This product
is termed the thermodynamic product. The
1,4-product is the thermodynamic product and is
more stable.
11
- Further explanation
- At low temperature, the reaction is not
reversible. The 1,2-product forms faster - because attack by Br- at the 20 carbon, which
bears a larger positive charge, has - a lower energy of activation, Ea. So the
1,2-product builds up and it does not - revert back to reactant.
- At high temperature, the reaction is reversible.
Although the 1,2-product forms - faster, once it forms, it reverts back to
reactant, which then reacts to form - 1,4 product, which is more stable. The 1,2-
and 1,4-product are in equilibrium - at high temperature, with the 1,4-product
predominating.
12
Molecular Orbital Picture of 1,3-butadiene
Nodes 3 2 1 0
?4 Antibonding ____ ?3Antibonding
____ ?2 Bonding ____ ?1
Bonding ____
LUMO HOMO
E
13
UV-Visible Spectroscopy
UV 200-400 nm Visible 400-800 nm
- Electronic transitions of ? or nonbonding
electrons - Follows Beers Law
- A ? c l A absorbance
- ? molar absorptivity of molecule
- c concentration
- l path length of light
- Absorption characterized by ?max wavelength of
maximum absorption - ?max increases with
- 1. Conjugation - 30 nm per
double bond - 2. Alkyl substitution - 5 nm per
alkyl group
14
___ ___ ___ ___
UV
217 nm
Ground State Excited State
15
(No Transcript)
16
495 nm
603 nm
483 nm
17
Why are my jeans so blue?
Reduced water-soluble yellow form of Indigo
applied to jeans
Oxidized form of Indigo responsible for blue
color
18
Phenolphthalein Acidic and Basic Forms
Phenolphthalein is an pH indicator dye used in
titrations. It is also an ingredient in Ex-lax!
When the solution is acidic, the molecule is
colorless. Under basic conditions, it turns red.
Increased conjugation is responsible for the red
color.
sp3
Acid Form less conjugation, absorbs in
UV and colorless
OH-
Basic Form more flat and conjugated, absorbs
in visible region and red
sp2
3-D structures
19
Diels-Alder Reaction
- Method for synthesis of 6-membered ring
- One-step, concerted reaction
- Termed 42 cycloaddition reaction where 4? and
2? - electrons react.
Otto Diels
Kurt Alder
? ?
?
Diene electron-rich nucleophile
electron-donating groups make it more reactive.
20
Dienophile electron poor electrophile
electron-withdrawing groups make it
more reactive
acrylonitrile maleic anhydride
Reaction
21
Mechanism of Diels-Alder one-step, simultaneous
(concerted) bond-making
and bond-breaking involving
6 ? electrons
Diels Alder Movie
22
Stereochemical Requirements of Diels-Alder
Reaction 1. Diene must be in the s-cis
conformation in order to react.
s-trans
s-cis
unreactive
Explain the following reactivities of dienes.
Very Unreactive Reactive!
100 s-cis Cannot adopt s-cis
23
2. Syn Stereochemistry due to its concerted
nature, the reaction is syn with respect to
both the diene and dienophile.
T toward you in product A away from you in
product
cis cis
trans
trans
Conclusion The reaction stereospecific with
respect to the dienophile. cis
cis trans trans
24
What about the diene?
trans, trans
cis
cis, trans
trans
severe steric crowding
s-cis
s-trans - much
more stable
cis, cis Unreactive!!!! Why?
25
Conclusion Diels-Alder is stereospecific with
respect to the diene. trans, trans
? cis product trans, cis ?
trans product cis, trans ? trans
product cis, cis ? unreactive
3. Endo Rule when substituted bicyclic
structures form ,the endo product
is favored over the exo product.
Endo Exo favored
26
Explanation of Endo Rule There are two possible
approaches between the diene and dienophile in
this reaction.
HOMO diene
LUMO dienophile
Additional interaction lowers Ea reacts faster
Endo - major Exo
- minor