Dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory:
Description:
... of realloc() often leads to dangling pointers! extending node c: ... Extension was not possible, reallocation was necessayr, right child of node a is dangling! ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:152
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory:
1
Dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory
Chapter 4, Slide 1
2
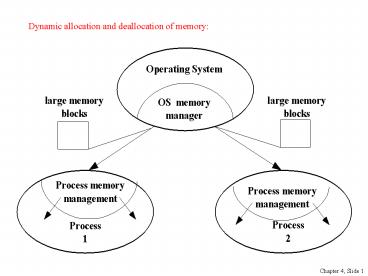
- Memory management is a simple accounting of
what process owns what part(s) of the memory. - Memory allocation is making an entry in the
accounting book that this segment is given to
this process for keeps. - Memory deallocation is an entry that this
segment is not needed by this process and hence
free. - The operating system process manager usually
keeps track of allocated blocks in a data
structure called binary heap (in which each node
is labeled by a label that is smaller than labels
of all its descendants). Its purpose is to
facilitate fast and efficient searching for a
suitable free block. - This heap is sometimes referred to as system
heap or free store.
Chapter 4, Slide 2
3
- The process memory manager usually keeps a
dynamic list of free segments. - One of the implications is that every time your
program requests more memory, the process memory
manager has to search through the list to find a
suitable segment if none is found, more memory
must be requested from the operating system
memory manager that must search the system heap
for a suitable block and when delivered to the
process memory manager, a suitable segment must
be carved out from the freshly allocated block. - The time delay cannot be determined. Thus, if a
program does a significant number of allocations
and deallocations, the unpredictable delays
caused by these may affect the program's
performance. - These issues must be considered for real-time
software systems and for all programs where
performance is essential. We will look at these
issues when we discuss the concept of allocation
from arena.
Chapter 4, Slide 3
4
The memory manager in C programs is engaged
through various interfaces (standard functions)
include ltstdlib.hgt void malloc(size_t size)
The size of the allocated segment is at least
size, the contents are arbitrary!
include ltstdlib.hgt void calloc(size_t
nelem,size_t elsize)
The size of the allocated segment is at least
nelemelsize, the contents are cleared!
include ltstdlib.hgt void realloc(void
ptr,size_t size)
Chapter 4, Slide 4
5
If the reallocated segment can be extended, it is
done so, otherwise a new segment is created, the
contentrs of the old segment are copied to the
new one, and the old segment is
deallocated. Careless use of realloc() often
leads to dangling pointers! extending node c
Chapter 4, Slide 5
6
Extension was possible, all is fine!
Chapter 4, Slide 6
7
Extension was not possible, reallocation was
necessayr, right child of node a is dangling!
Chapter 4, Slide 7
8
Deallocation
include ltstdlib.hgt void free(void ptr)
End of slides for chapter 4
Chapter 4, Slide 8