Root: Functions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Root: Functions
Description:
Movement into the vascular cylinder: Casparian strip: waterproof strip that ... Pith: parenchyma cells inside the ring of vascular tissue in dicot stems ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:68
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Root: Functions
1
Root Functions
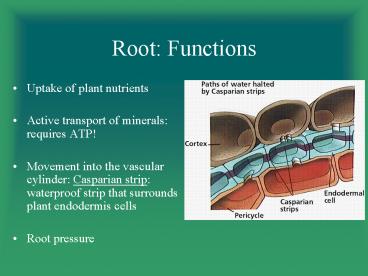
- Uptake of plant nutrients
- Active transport of minerals requires ATP!
- Movement into the vascular cylinder Casparian
strip waterproof strip that surrounds plant
endodermis cells - Root pressure
2
Stem Structure and Function
- Produce leaves, branches and flowers
- Hold leaves up in the sunlight
- Transport substances between roots and leaves
3
Stem Structure and Function
- Node point on a stem where a leaf is attached
- Internode region between nodes on plant stems
- Bud plant structure containing undeveloped
tissue that can produce new stems and leaves
4
Monocot and Dicot Stems
- Monocot Stems vascular bundles are scattered
throughout the stem - Dicot Stems (and most gymnosperms) vascular
bundles are arranged in
a cylinder - Pith parenchyma
cells inside
the ring
of vascular tissue
in
dicot stems
5
Primary Growth of Stems
- Type of plant growth that occurs at the tips of
roots and shoots - Cell divisions in the apical meristem
- Takes place in all seed plants
6
Secondary Growth of Stems
- Pattern of plant growth in which stems increase
in width - Enables the plant to support more weight and more
fluid through the vascular tissues
7
Formation of the Vascular Cambium
- New layers of vascular tissue are created each
year after secondary growth begins - New meristematic tissue forms between the xylem
an phloem of each vascular bundle - Divisions in the vascular cambium give rise to
new layers of xylem and phloem
8
Formation of Wood
- Most of what we call wood is actually layers of
xylem - Heartwood older xylem near the center of a woody
stem that no longer conducts water darkens with
age - Sapwood area in plants that surrounds heartwood
and is active in fluid transport lighter in
color - Heartwood and sapwood make up tree rings
9
Formation of Bark
- Tree structure that includes all tissues outside
the vascular cambium, including phloem, the cork
cambium, and cork
10
(No Transcript)
11
Leaf Structure
- Optimized for absorbing light and carrying out
photosynthesis - Blade thin, flattened section of a plant leaf
that collects sunlight - Petiole thin stalk by which a leaf blade is
attached to a stem
12
Leaf Functions
- Photosynthesis
- Transpiration
- Gas Exchange
13
Water Transport in Plants
- Root pressure
- Capillary Action
- Transpiration
- Together provide enough force to move water
through the xylem tissue of even the largest
plant!
14
(No Transcript)
15
Capillary Action
- Tendency of water to rise in a thin tube
- Adhesion attraction between unlike molecules
16
Transpiration
- The evaporation of water from leaves
- Controlled by the guard cells
- The biggest contributor to moving water in the
plant
17
Nutrient Transport
- Water is pulled upward in plants nutrients are
pushed through phloem - Phloem In cold climates, sugar is stored in the
roots in the winter and in the trunk and branches
in the springhow does it move?
18
Movement from Source to Sink
- Pressure-Flow Hypothesis When nutrients are
pumped into or removed from the phloem system,
the change in concentration causes a movement of
fluid in that same direction - As a result, phloem is able to move nutrients in
either direction to meet the nutritional needs of
the plant