Standard form: PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Standard form:
1
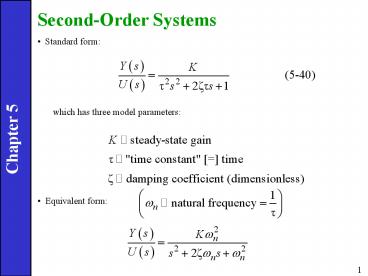
Second-Order Systems
- Standard form
which has three model parameters
Chapter 5
- Equivalent form
2
Block Notation
Composed of two first order subsystems (G1 and G2)
Chapter 5
2nd order ODE model (overdamped)
roots
3
- The type of behavior that occurs depends on the
numerical value of damping coefficient,
It is convenient to consider three types of
behavior
Chapter 5
- Note The characteristic polynomial is the
denominator of the transfer function
- What about ? It results in an unstable
system
4
Chapter 5
5
Chapter 5
6
Several general remarks can be made concerning
the responses show in Figs. 5.8 and 5.9
- Responses exhibiting oscillation and overshoot
(y/KM gt 1) are obtained only for values of
less than one. - Large values of yield a sluggish (slow)
response. - The fastest response without overshoot is
obtained for the critically damped case
Chapter 5
7
Chapter 5
8
- Rise Time is the time the process output
takes to first reach the new steady-state value. - Time to First Peak is the time required for
the output to reach its first maximum value. - Settling Time is defined as the time
required for the process output to reach and
remain inside a band whose width is equal to 5
of the total change in y. The term 95 response
time sometimes is used to refer to this case.
Also, values of 1 sometimes are used. - Overshoot OS a/b ( overshoot is 100a/b).
- Decay Ratio DR c/a (where c is the height of
the second peak). - Period of Oscillation P is the time between two
successive peaks or two successive valleys of the
response.
Chapter 5
9
Second Order Step Change
- Overshoot
- time of first maximum
- c. decay ratio (successive maxima not min.)
- d. period of oscillation
Chapter 5
10
Sinusoidal
Chapter 5
11
Chapter 5
12
Chapter 5
13
Chapter 5
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.