Properties of Nucleic Acids - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Description:
Abbreviations. Bases, nucleosomes, and nucleotides have related names. Abbreviations of the form NMP stand for nucleoside monophosphate; 'd' indicates ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:544
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Properties of Nucleic Acids
1
Properties of Nucleic Acids
- Lecture 1 of
- Introduction to Molecular Biology
- ??? ???
2
The Discovery of DNA
The idea that genetic material is nucleic acid
had its roots in the discovery of transformation
by Griffith in 1928.
In 1944, Avery and colleagues showed chemically
that the isolated transforming principle is
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
3
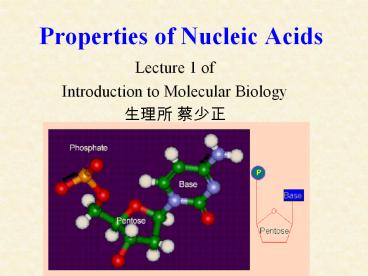
The components of DNA
- A nucleic acid consists of a) nitrogen base, b)
pentose, and c) phosphate.
Two types of pentose are found in nucleic acids.
They distinguish DNA (contains 2-deoxyribose) and
RNA (contains ribose).
4
Pyrimidine Purine
- Two types of nitrogenous bases pyrimidine
(six-member ring) and purine (fused five-and
six-member rings).
5
Building block for nucleic acid
- A base linked to a sugar is called a nucleoside
when a phosphate group is added, the
base-sugar-phosphate is called a nucleotide
(building block for nucleic acid).
6
Polynucleotide chain
- The nucleotides are linked together into a
polynucleotide chain by a backbone consisting of
an alternating series of sugar and phosphate
residues. - The terminal nucleotide at one end of the chain
has a free 5' group the terminal nucleotide at
the other end has a free 3' group. - Traditionally, we write nucleic acid sequences in
the 5' to 3' direction, i.e. 5' terminus at the
left and 3' terminus at the right.
7
(No Transcript)
8
Abbreviations
- Bases, nucleosomes, and nucleotides have related
names. Abbreviations of the form NMP stand for
nucleoside monophosphate "d" indicates the
2-deoxy form.
9
AMP, ADP, and ATP
ADP
ATP
Adenosine
10
Secondary Structure of Nucleic Acid
11
Double Strand DNA
- Watson and Crick proposed that the two
polynucleotide chains in the double helix
associate by hydrogen bonding between the
nitrogenous bases. In their usual forms, G can
hydrogen bond specifically only with C, while A
can bond specifically only with T.
12
Complementary bases
- These reactions are described as base pairing,
and the paired bases (G with C, or A with T) are
said to be complementary. The two polynucleotide
chains run in opposite directions (antiparallel)
therefore, one strand runs in the 5'-3'
direction, while its partner runs 3'-5'.
13
DNA Denatured
- DNA can be denatured and renatured. The mid
point of the temperature range over which the
strands of DNA separate is called the melting
temperature (Tm). Tm depends on the proportion of
G C base pair (GC content).
14
Forms of DNA
DNA can exist in several types of structure
families.
Type Base/Turn Length/turn Distance /2
bases Rotation B 10 3.4 nm 0.34 nm A 11 2.3
nm 0.21 nm Z 12 4.5 nm 0.33 nm -
Rotation per base pair is indicated as () for a
right-handed duplex and (-) for a left handed
duplex.
15
B DNA
16
B form vs. Z form DNA
17
A Nucleotide
18
a helix conformation
Left-handed
Right-handed
19
Base-pairing
20
(No Transcript)