Physics PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title: Physics
1
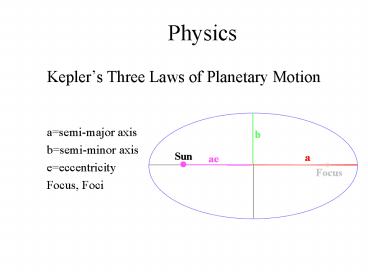
Physics
- Keplers Three Laws of Planetary Motion
- asemi-major axis
- bsemi-minor axis
- eeccentricity
- Focus, Foci
2
- Distance, Velocity from the Sun at any given
time - qangle from perihelion
3
- Keplers second law rate of orbit changes (fast
at perihelion, slow at aphelion) - Keplers third law
- P2 k a3
- Newtons version (correct version)
4
- Orbits arent that simple
- More terms needed
- a Semi major axis
- e - eccentricity
- i - inclination
- q perihelion distance
- W longitude of the ascending node
- w argument of the perihelion
5
- Non-elliptical/circular orbits
- Depends upon velocity, direction
- Velocities lt Escape velocity elliptical/circular
6
- Velocity Escape Velocity
- Orbit becomes parabolic
- e1, qclosest approach
- Velocity gt Escape Velocity
- Orbit is hyperbolic
- egt1
7
Gravity
- Current formula two objects
- Three objects disaster!
- 3-body problems
8
3-Body Effects
- Simplifications good!
- Perturbations
- Predicatable (periodic)
- Commensurable orientations (orbits)
- Beat Phenomena
- Ratios of orbits ½, 1/3, ¼, 2/3, 2/5, etc.
- Increases influence
- examples Asteroid belt, Planetary rings
9
Lagrangian Points
- Gravitational Peaks Valleys associated with two
objects.
10
L1, L2, L3 Unstable L4, L5 Stable
11
- Lagrangian Objects
- Jupiter Sun system
- Trojan Asteroids
- Earth Moon system
- Dust
- Earth Sun system
- L1 - SOHO
- L2 - WMAP, JWST
- L4, L5 mainly dust, satellites maybe
12
- Mars Sun system
- L4, L5 - 6 asteroids
- Saturn Dione system
- L4, L5 - Helene, Polydeuces
- Saturn Tethys system
- L4, L5 - Calypso, Telesto
- Neptune - Sun system
- L4, L5 - about 6 asteroids
13
Horseshoes Tadpoles
- Horseshoe orbits
- Not really how things move
- Matter of perspective
- Janus/Epimetheus
14
Cruithne
15
2002 AA29
16
(No Transcript)
17
Tadpole Orbits
- Objects trapped in L4, L5 move around
18
- Who controls all of this?
- The Sun?
- Not necessarily sphere of influence
- Hill Sphere distance where an object controls
motion of other objects - All satellites within each planets Hill sphere
19
Tides
- Force that depends on object size/distance3
- Strong distance effect!
- Earth-Moon system
- High/Low tides
- Earths rotation
- Synchronous rotation of Moon (11)
- Moons migration away
- Sun contributes 20
20
Killer Tides!
- Not really
- When do they hurt?
- When you get within the Roche Limit
- No precise limit
- Tensile strength (Composition, density, etc)
21
- Tidal Heating
- Io, Europa, Ganymede
- Enceladus
- Triton
22
Ring
- Resonances
- Perturbations
23
(No Transcript)
24
Light/Gas Influences
- Does effect motion small objects mainly
- For sub-micron (10-7 m or less)
- Corpuscular drag
- Solar Winds particles from the Sun
- Gas drag
- Atmospheric effect
25
- For micron sized ( 10-6 m)
- Radiation pressure
- Photons energy influence
- Fradradiation force
- Qcorrection factor
- aparticle size
- rdistance
- Lluminosity
26
- For centimeter sized objects (0.01 m)
- Poynting-Robertson Drag
- Relativity effect
- Motion of particle effects re-emission of light
- Causes decreasing orbit
- Decaying orbits
- Particles that make up the Zodiacal light
- Need to be replenished!
27
- For meter sized objects
- Yarkovsky (Yarkovski) effect
- Hot objects give off light
- When they give off light alters motion
- Influenced by temperature variation across it
- diurnal effects (rotation)
- seasonal effects
- albedo/composition variations
- Yarkovsky-O'Keefe-Radzievskii-Paddack effect
(YORP) - Irregular shape alters motion
28
Light
- Other things you may have forgotten
- Types of light wavelength order
- Radio longest - lowest energy
- Microwave
- Infrared
- Visible (ROYGBIV)
- Ultraviolet
- X-ray
- Gamma-ray shortest - highest energy
29
- clf
- Speed wavelength x frequency
- Wiens law for black bodies
- Peak type of light emitted - temperature
- lmax 0.0029/T
- Doppler effect
- Change of wavelength due to motion
30
- Spectrum of planets
- Absorption due to atmosphere, surface material
31
(No Transcript)
32
Element Spectra
33
Albedo
- How light is absorbed reflected measured by the
albedo - Bond Albedo averaged over all wavelengths, all
directions most commonly used - Total reflected/total absorbed
- If it equals 0, what does that mean?
- If it equals 1, what does that mean?
34
- Albedo effects temperature
- Light coming in primarily visible
- Light emitted primarily IR
- Difference of incoming/outgoing influences
environment of object (Greenhouse effect)