Exploratory research PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Exploratory research
1
Exploratory research
2
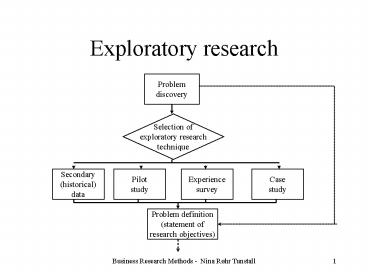
Exploratory research
- diagnosing the situation
- screening alternatives
- discovering new ideas
- mainly qualitative
3
Primary Data
- Data which is collected in order to enlighten the
company's specific problem via field research - Qualitative - complex situations, expresses
opinions and attitudes - often, but not only, in
Exploratory research - Quantitative - can be measured, often large
volumes of data, results are often accurate,
support quantitative decisions - mostly used in
Descriptive research
4
Measurement error
Nonresponse error
Acquiescence bias
Respondent error
Deliberate falsification
Extremity bias
Random sampling error
Response bias
Interviewer bias
Unconscious misrepresentation
Total error
Auspices bias
Social desirability bias
Systematic error (bias)
Data processing error
Sample selection error
Administrative error
Interviewer error
Interviewer cheating
5
Measurement error(types and examples)
Measurement influenced by related
characteristics. Willingness/ability to
answer depends on interest/IQ
Measurement influences by temporary
conditions. Morning mood/just won the national
lottery
Initial setup of measuring equipment. Who is
asking, how is the questionnaire designed
Administration of the measuring
equipment. Temporary tiredness, noise light etc.
Coding process of answers/ measurements. Different
people will code the same answer differently
Differences in interpreting the answers. How
should an unclear answer be interpreted - sense
of irony
6
Errors and Security
- Validity
- Do we measure what we want to measure?
- Reliability
- Do we get the same result each time?
- Degree of details
- Accuracy
- Comparison
7
Validity
- Concept - Do we measure what we really want to
measure? - Statistical
- Can we draw conclusions?
- Internal
- Historical event
- Maturity - respondent changes attitudes
- Selection - wrong respondents
- Faulty - not at home, invalid responds
- External
- Can the results be generalised?
8
Reliability
- Concept - Can the same results be achieved in
other circumstances or if another person is
repeating the observations - Equipment
- The ruler always measure the same distance, but
the measurement may not be correct - Data Collection
- Is the interviewer reliable?
- Data processing
- Coding error?
9
Random sampling error - chapters 15 16
Sample 1
Population
inference
sampling
Sample 2
10
Systematic Sampling Error
- Sampling bias
- consistent deviation from true value
- SSE - also called nonsampling errors
- Can be explained by
- Respondent error
- Administrative error
11
Non Response Error
- No information at all
- Nonrespondents - especially mail surveys
- Not-at-home - when do you call?
- Refusals - follow up procedures, incentives
- Incomplete information
- Refusals
- Self-selection bias - extreme responses
- Cultural bias - Copenhagen/Thy
12
Response Bias - p 171
- Deliberate falsification
- Unconscious misrepresentation
- acquiescence bias - always agrees
- extremity bias - Copenhagen rather than Thy
- interviewer bias - impress interviewer
- auspices bias - who is asking (which
organisation?) - social desirability bias - exceed level of salary
13
Administrative error
- data processing error
- sample selection error
- interviewer error
- interviewer cheating
14
Corrections/reductions
- Rule-of-thumbs
- weighting ex. only 50 will buy the product
- Questionnaire interview design
- structure or disguise questions
- Sample selection