SLOWING DOWN - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
SLOWING DOWN
Description:
Fast fission. Resonance abs. Non-fuel abs. Leakage. Non-fissile abs. Fission. Slowing down ... Fast reactors: lp = 10-7. HT2004: Reactor Physics. Reactor Kinetics. 4 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:18
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: SLOWING DOWN
1
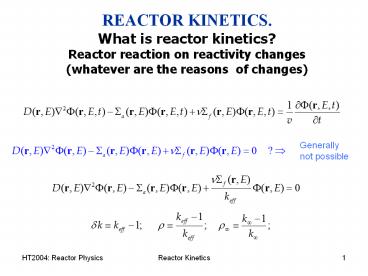
REACTOR KINETICS. What is reactor
kinetics? Reactor reaction on reactivity changes
(whatever are the reasons of changes)
Generally not possible
2
Principles of a Nuclear Reactor
Leakage
E
N2
2 MeV
N1
Fast fission
n n/fission
Energy
Slowing down
Resonance abs.
? 2.5
Non-fuel abs.
Non-fissile abs.
1 eV
Fission
200 MeV/fission
Leakage
3
Graphite-moderated lp 10-3 Water-moderated
lp 10-4 Fast reactors lp 10-7
4
Homogeneous infinite reactor
5
Group Half-life T1/2(s) Mean life tmi (s) Decay constant li (s-1) Fraction of total fission neutrons, bi
1 55.7 80.2 .0124 .000215
2 22.7 32.7 .0305 .001424
3 6.2 8.9 .111 .001274
4 2.3 3.3 .301 .002568
5 .61 .88 1.14 .000748
6 .23 .33 3.01 .000273
6
Kinetic Equations
7
Solution of Kinetic Equations
8
Delayed neutrons ignored
n(t)/n(0)
?0 gt 0
C(t)/C(0)
?0 lt 0
?0
Time
9
Inhour Equation
Unit inverse hour inhour 1 inhour amount of
reactivity needed to make the reactor period
equal to one hour 1 pcm (per cent mille) 10-5
of ?k/k 1 is equal to ? ß
10
(No Transcript)
11
Special Cases
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
n(t)/n(0)
?0 0.5
?0 5
?0 10
15
The END
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)