Consider the wedge used to PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Consider the wedge used to
1
????
- ??????????????????????????????????????????????????
???????????????? - ????????????????
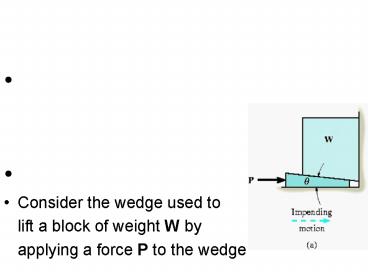
- Consider the wedge used to
- lift a block of weight W by
- applying a force P to the wedge
2
- FBD of the block and the wedge
- Exclude the weight of the wedge since it is small
compared to weight of the block
3
- Frictional forces F1 and F2 must oppose the
motion of the wedge - Frictional force F3 of the wall on the block must
act downward as to oppose the blocks upward
motion - Location of the resultant forces are not
important since neither the block or the wedge
will tip - Moment equilibrium equations not considered
- 7 unknowns - 6 normal and frictional force and
force P
4
- 2 force equilibrium equations (?Fx 0, ?Fy 0)
applied to the wedge and block (4 equations in
total) and the frictional equation (F µN)
applied at each surface of the contact (3
equations in total) - If the block is lowered, the frictional forces
will act in a sense opposite to that shown - Applied force P will act to the right if the
coefficient of friction is small or the wedge
angle ? is large
5
- Otherwise, P may have the reverse sense of
direction in order to pull the wedge to remove it - If P is not applied or P 0, and friction forces
hold the block in place, then the wedge is
referred to as self-locking
6
- Example 8.7
- The uniform stone has a mass of 500kg and is held
- in place in the horizontal position using a wedge
at - B. if the coefficient of static friction µs
0.3, at the - surfaces of contact, determine the minimum force
- P needed to remove the wedge. Is the wedge self-
- locking? Assume that the stone does not slip at A.
7
- Solution
- Minimum force P requires F µs NA at the
surfaces of contact with the wedge - FBD of the stone and the wedge
- On the wedge, friction force opposes the motion
and on the stone at A, FA µsNA, slipping does
not occur
8
- Solution
- 5 unknowns, 3 equilibrium equations for the stone
and 2 for the wedge
9
- Solution
- Since P is positive, the wedge must be pulled out
- If P is zero, the wedge would remain in place
(self-locking) and the frictional forces
developed at B and C would satisfy - FB lt µsNB
- FC lt µsNC
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.