Electromagnetic Waves PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title: Electromagnetic Waves
1
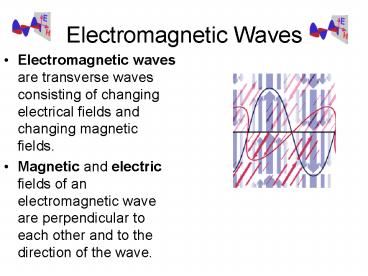
Electromagnetic Waves
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves
consisting of changing electrical fields and
changing magnetic fields. - Magnetic and electric fields of an
electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each
other and to the direction of the wave.
2
What are they?
- An electrical field is a region of space that
exerts an electrical forces on charged particles. - A magnetic field is a region of space that
produce magnetic forces. - Electromagnetic waves are produced when an
electric charge vibrates or accelerates. - Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum
or empty space, as well as through matter.
3
Properties
- The speed of light in a vacuum (c)
- 3.00 x 108 meters per second
- In a vacuum all electromagnetic waves travel at
the same speed, but their wavelength and
frequency vary. - The wavelength is inversely proportional to the
frequency. - s f? (speed c)
4
Wave or Particle?
- Electromagnetic radiation behaves sometimes like
a wave and sometimes like a stream of particles. - Wave
- Light demonstrates it experiences interference.
- Particle
- Photoelectric Effect a metal plate can emit
electrons if a high energy light
(Blue-Ultraviolet) strikes it. - The intensity of light decreases as photons
travel farther from the source.
5
The Waves of the Spectrum
- The full range of frequencies of electromagnetic
radiation is called the Electromagnetic Spectrum.
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Large ? Low f
- Radio Waves are used in radio and television
technologies, as well as in microwave ovens and
radar. - AM and FM radio waves has the lowest frequencies.
- Amplitude modulation (AM), the amplitude of the
wave is varied, but the frequency stays the same.
- Frequency modulation (FM), the frequency of the
wave is varied, but the amplitude stays the same. - AM can be heard for a greater distance
9
Detection
- The shortest wavelength radio waves are called
microwaves. - f300 MHz-300,000MHz
- Cook Food
- Cell Phone Communication
- Water and fat molecules absorb microwaves and
their thermal energy increases.
- Radar (Radio Detection And Ranging)
- Radio waves are sent out in short bursts and the
waves reflect off the objects and bounce back to
the receiver. - Doppler is used to determine speeds of moving
objects.
Right Now on Doppler
10
Infrared Rays
- Infrared rays have a wavelength of 1 mm 1nm
- Infrared rays are used as a source of heat and to
discover areas of heat differences. - Thermograms are color-coded pictures that show
variation in temperature.
11
Visible Light
- Visible light is light is the part of the EM
spectrum the human eye can see. - Each color corresponds to a specific frequency
and wavelength.
12
Ultraviolet Rays
- Ultraviolet rays have applications in health and
medicine, and in agriculture. - The wavelengths vary from 400nm-4nm.
- Ultraviolet rays have a higher frequency than
violet light. - Sun Rays
- Kills bacteria and other microorganisms
13
X-Rays
- X-Rays have high energy and can penetrate matter.
- Used in medicine, industry and transportation to
make pictures of the inside of a solid object. - Wavelength of 12nm 0.005 nm
14
Gamma Rays
- Gamma rays are the shortest wavelength (About
0.005nm or less). - They have the highest amount of energy.
- They are used in the medical field to kill cancer
and take pictures of the brain, and in industrial
situations as an inspection tool.
15
Light and Materials
- Materials can be transparent, translucent or
opaque. - A transparent material transmits light, which
means it allows most of the light that strikes it
to pass through it. - A translucent material scatters light. The
object does not appear clear or distinct. - An opaque material either absorbs or reflects all
the light that strikes it.
16
Interactions of Light
- When light strikes a new medium, the light can be
reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. When light
is transmitted, it can be refracted, polarized,
or scattered.
- Reflection is the bouncing off of waves.
- An image is a copy of an object formed by
reflected or refracted waves of light
17
Types of Reflection
- Regular Reflection occurs when parallel light
strike a surface and reflect all in the same
direction.
- Diffuse reflection occurs when parallel light
waves strike a rough, uneven surface, and reflect
in many different directions.
18
Refraction
- Lights waves refract, or bend, when it passes at
an angle from one medium to another. - A mirage is a false or distorted image caused by
differences in temperature
19
Polarization
- When light waves vibrate in only one plane the
light is polarized. - Used in sunglasses and in film
20
Scattering
- Earths Atmosphere contains many molecules that
scatter light. - Scattering means that light is redirected as it
passes through a medium. - Why is the sky blue?
21
White ROYGBV
- Sunlight is made up of all the colors of the
visible spectrum. - The process in which white light separates into
colors is called dispersion.
22
Color
- The color of an object depends on what the object
is made of and on the color of light that strikes
the object. - The color reflected is the color you see. The
colors absorbed are not visible.
- Primary colors are three specific colors that can
be combined in varying amounts to create all
possible colors. (Red, Green, Blue) - Secondary colors are combinations of two primary
colors. (Magenta, Cyan, Yellow)
23
Color Wheel
24
Mixing Pigments
- A pigment is a material that absorbs some colors
of light and reflects other colors. - The primary colors of pigments are cyan, magenta
and yellow. - Any two colors of pigments that combine to make
black pigment are complementary colors of
pigment.