Transport Phenomena - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Transport Phenomena
Description:
to a modulus ? = stress = Fx / dux. strain A dz. Viscosity ... Summary: Q/?T ~ dT/dx heat. l ~ n number. ? ~ dux/dz velocity. Jx ~ dn/dx number ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:251
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Transport Phenomena
1
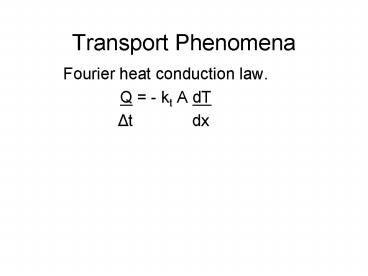
Transport Phenomena
- Fourier heat conduction law.
- Q - kt A dT
- ?t dx
2
Transport Phenomena
- Fourier heat conduction law.
- Q - kt A dT
- ?t dx
- kt thermal conductivity.
3
Transport Phenomena
- Fourier heat conduction law.
- Q - kt A dT
- ?t dx
- kt thermal conductivity.
- Heat Equation
- ?T K ?2T
- ?t ?x2
4
Transport Phenomena
- Fourier heat conduction law.
- Q - kt A dT
- ?t dx
- kt thermal conductivity.
- Heat Equation
- ?T K ?2T
- ?t ?x2
- K kt /?c
5
Transport Phenomena
- Fourier heat conduction law.
- Q - kt A dT
- ?t dx
- kt thermal conductivity.
- Heat Equation
- ?T K ?2T
- ?t ?x2
- K kt /?c ? density, c specific heat
6
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
7
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
- in FGT ? ? 1/(v2 ns)
8
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
- in FGT ? ? 1/(v2 ns) where s 4pr2
- and n
N/V
9
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
- in FGT ? ? 1/(v2 ns) where s 4pr2
- and n
N/V - Thermal conductivity of an ideal gas is
- kt ½ CV l vave V
10
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
- in FGT ? ? 1/(v2 ns) where s 4pr2
- and n
N/V - Thermal conductivity of an ideal gas is
- kt ½ CV l vave vave vT
- V
11
Conductivity of an ideal gas
- Mean Free Path ? l 1/4pr2 V/N
- in FGT ? ? 1/(v2 ns) where s 4pr2
- and n
N/V - Thermal conductivity of an ideal gas is
- kt ½ CV l vave vave vT
- V
- where CV f Nk f P
- V 2 V 2T
12
Viscosity
- Viscosity transfers momentum in a fluid.
13
Viscosity
- Viscosity transfers momentum in a fluid.
- Motion of one layer sliding on another, if slow
and the motion is laminar the resistance to
shearing is viscosity
14
Viscosity
- Viscosity transfers momentum in a fluid.
- Motion of one layer sliding on another, if slow
and the motion is laminar the resistance to
shearing is viscosity - The equation for the coefficient is similar
- to a modulus ? stress
- strain
15
Viscosity
- Viscosity transfers momentum in a fluid.
- Motion of one layer sliding on another, if slow
and the motion is laminar the resistance to
shearing is viscosity - The equation for the coefficient is similar
- to a modulus ? stress Fx / dux
- strain A
dz
16
Viscosity
- Viscosity transfers momentum in a fluid.
- Motion of one layer sliding on another, if slow
and the motion is laminar the resistance to
shearing is viscosity - The equation for the coefficient is similar
- to a modulus ? stress Fx / dux
- strain A
dz - ? vT and independent of P
17
Diffusion
- Movement of particles is diffusion
18
Diffusion
- Movement of particles is diffusion
- Jx - D dn/dx (Ficks Law)
19
Diffusion
- Movement of particles is diffusion
- Jx - D dn/dx (Ficks Law)
- D is the diffusion coefficient n N/V
20
Diffusion
- Movement of particles is diffusion
- Jx - D dn/dx (Ficks Law)
- D is the diffusion coefficient n N/V
- D ranges from 10-5 for CO to 10-11 for
large molecules SI unit is m2 /s.
21
Diffusion
- Movement of particles is diffusion
- Jx - D dn/dx (Ficks Law)
- D is the diffusion coefficient n N/V
- D ranges from 10-5 for CO to 10-11 for
large molecules SI unit is m2 /s. - Summary Q/?T dT/dx heat
- l n
number - ? dux/dz
velocity - Jx dn/dx
number