Cell Reproduction PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: Cell Reproduction
1
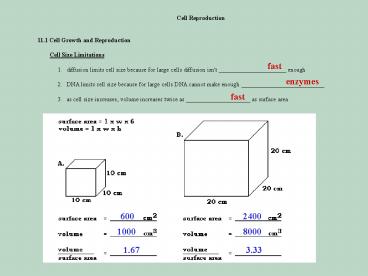
Cell Reproduction 11.1 Cell Growth and
Reproduction Cell Size Limitations
1. diffusion limits cell size because
for large cells diffusion isn't
______________________ enough
2. DNA limits cell size because for large cells
DNA cannot make enough ___________________________
3. as cell size increases,
volume increases twice as _____________________
as surface area
fast
enzymes
fast
600
2400
1000
8000
1.67
3.33
2
When Do Cells Divide? 1. cells divide
when a. cells get too
________________________ b.
tissues _____________________ and need to be
______________________ or _______________________
Cell Reproduction The Role of
Chromosomes 1. in non-dividing cells,
DNA and proteins in the nucleus form
_________________________________ 2. in
dividing cells, DNA and proteins that were in the
nucleus form __________________________________
big
wear out
replaced
repaired
chromatin
chromosomes
The Cell Cycle Phases of
Interphase G1 phase S
phase G2 phase
Phases of Mitosis
Prophase Metaphase
Anaphase Telophase
3
The Cell Cycle (continued) 1. all
stages of a cell's life make up the
____________________________________
2. cells grow during ___________________________
___________ 3. the nucleus divides
during ________________________ the cell divides
during ________________________
Interphase 1. during the G1 phase, the
cell __________________ this includes
a. making __________________,
___________________, _____________________, and
_____________________ b. and
excreting _________________________
2. during the S phase, the DNA is
_________________________________
3. during the G2 phase, the growth involves
making structures necessary for
__________________________
cell cycle
interphase
mitosis
cytokinesis
grows
ATP
proteins
new organelles
repairs
wastes
replicated (doubled)
mitosis
4
nucleus
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleolus
centrioles
5
The Phases of Mitosis Prophase Main
Features 1. the chromatin coils
to form _____________________________________
2. the ______________________________
______ and ____________________________________
disappear 3. centrioles (animal
cells only) migrate to opposite
_______________________ of the cell
4. the _____________________________ forms
chromosomes
nuclear envelope
nucleolus
poles
spindle
chromosome
centromere
chromatid
6
Prophase (continued)
7
Prophase (continued)
8
Metaphase Main Features 1. spindle
fibers attach to _________________________________
___ 2. the chromosomes ___________________
_________ along the equator
centromeres
line up
9
Metaphase Main Features 1. spindle
fibers attach to _________________________________
___ 2. the chromosomes ___________________
_________ along the equator
centromeres
line up
10
Anaphase Main Features 1. the sister
chromatids ___________________ to opposite poles
move
11
Anaphase Main Features 1. the sister
chromatids ___________________ to opposite poles
move
12
Telophase Main Features 1. the
_____________________________________ uncoil to
form chromatin 2. the ____________________
_________ disappears 3. the
_____________________________________ and
____________________________________ reappear
4. the _____________________________________
starts to form between the nuclei
chromatids
spindle
nuclear envelope
nucleolus
plasma membrane
nucleus
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleolus
plasma membrane
13
Cytokinesis Main Features 1. the
_________________________________________ pinches
inward 2. the ____________________________
________ gets divided in half 3. for
plant cells, a ______________________________
forms between the daughter cells
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
cell plate
nucleus
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleolus
plasma membrane