Example Managing Research Process - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Example Managing Research Process
Description:
Research and Development (R&D) Committee ... Each committee consists of up to 18 members - at least one third are lay members ... knew what support they would ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:34
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Example Managing Research Process
1
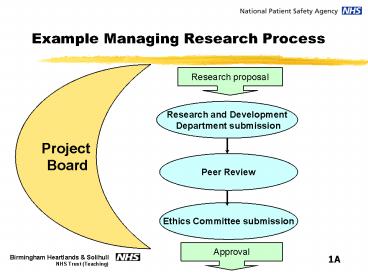
Example Managing Research Process
Project Board
Research proposal
Research and Development Department submission
Peer Review
Ethics Committee submission
Approval
1A
2
Project Board/Review and Reference Group - RRG
- This board or group is a number of health and
social services professionals (and lay members)
with experience and knowledge of the research
topic and methodology - They are usually set up prior to submitting a
research project for peer review - Their role is to support the project until its
completion and dissemination
1B
3
Purpose of the Project board/RRG
- Monitor, support and guidance
- Develop and comment on the design and methods
used - Ensure timing and budget are adhered to
- Develop a strategy to ensure the results are
disseminated and findings put into practice
1C
4
Research and Development (RD) Committee
- Most trusts/organisation has an Research and
Development (RD) department that is responsible
for the research activity within the Trust - Each RD department has a RD committee that
meets regularly to assess research projects - All research projects should be approved by a RD
committee before applying to an ethics committee
1D
5
Peer Review
- At peer review the project is assessed on the
- Skill and experience of the project team
- Adequacy of timing and resources
- Sufficient supporting evidence for the project
- Aims and objectives clear and appropriate
- Research questions fulfil the aims
- Appropriate numbers to fulfil the aims
- Appropriate methods to fulfil the aims
1E
6
Research Ethics Committee
- NHS ethics committees provide independent advice
to participants, researchers, funders, sponsors,
employer, care organisations and professionals
about issues of quality and safety in the
research proposal - They are governed and supported by the department
of Health and local Health Authority - Each committee consists of up to 18 members - at
least one third are lay members - Each committee has a broad range of ages,
diversity, experience and expertise - scientific,
clinical and research
1F
7
Purpose of the Ethics Committee
- The primary purpose of the ethics committee is
to - protect the dignity, rights, safety and
well-being of participants and concerned
communities - take into account the interests, needs and safety
of researchers, but this is secondary to
participants - ensure the burden and benefits of research are
fairly distributed across all classes and groups
within society (age, gender, economic status,
culture and ethnicity)
1G
8
The Ethics Committee Review
- Ethics committees assess the project for
- Scientific design and conduct
- Recruitment of participants
- Protection of participants
- Community considerations
- They are also responsible for agreeing any
changes to the research protocol at any stage
throughout the project
1H
9
Opportunities for user involvement in managing
research
- There are potentially several areas where users
can become involved with managing research - Member of a project board/RRG
- Peer Reviewer for new projects
- Member of an ethics committee
1I
10
Why is the managing research stage important?
- User involvement in managing research and
development is important because having users and
carers involved can - change the focus, design and content of a study
- raise new research questions that professionals
may not know or think about - ensure interventions and outcomes are kept
user-friendly - encourage stronger commitment to dissemination of
the project
1J
11
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Purpose The Primary Care Group in Newcastle
wanted to find out more about the needs of their
Pakistani and Bangladeshi communities so they - understood how they described emotional distress
from a cultural perspective - knew what support they would need to deal with
distress - could use the findings to improve local services
2A
12
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Setting up the project
- Pakistani and Bangladeshi community members were
invited to join the project team through
community advertisements - Seventeen people submitted applications and were
interviewed - Thirteen were employed and joined the project
team as paid Community Project Workers (CPWs)
2B
13
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Roles of the user consultants After training,
they co-designed the project under the
supervision of experienced service managers and
researchers and - developed the interview guides and interview
process, - advised on cultural matters,
- used their community networks to gain
participants for the interviews who then
encourage others to participate, - did the interviews,
- analysed the information with a researcher,
- shared outcomes with community members/organisatio
ns.
2C
14
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Support provided to user consultants
- Went through a 6 month training period 6
hrs/week the training was accredited through
the National Open College - Were supervised by experienced service managers
and researchers on a regular basis - Were paid project members on a part-time basis
able to work flexible hours
2D
15
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Level of influence or decision-making The CPWs
were paid members of the project team and had
strong influence on all aspects of the project
design. They - were the main decision-makers about what
questions to ask, how to ask them and how to run
the interviews - were partners in the project analysis
- guided the researcher in understanding what was
said and why in the interviews - reviewed and confirmed the final descriptions of
what the information meant about community
members experiences and changes in services.
2E
16
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Activities that happened
- Discussions about why services needed to be
improved for these community members - Initial training period
- Designed how to gain the information
- Did 104 interviews with community members
- Analysed information gained in interviews
- Shared information with different primary care
groups, other local services and community
members through regular meetings and formal
presentations
2F
17
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Outcomes achieved The project led to these
outcomes - found out how mental health services were working
for local ethnic minority groups - better location of support workers where
community members could reach/visit them - brought in and trained more counsellors from
Asian backgrounds to offer more culturally
appropriate services - worked on a way to address racism in the local
area
2G
18
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Strategies for success The main strategies were
- recruiting people directly from the community who
understood how to involve community members - listening to their cultural advice with respect
and building this into all parts of the project - providing extensive training and then doing a
test run to help build the CPWs confidence - providing ongoing supervision for CPWs to help
with any problems that occurred - communicating the outcomes back to the community
so they know what had happened to their input.
2H
19
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Problems that occurred
- Staff wanted to ask personal details that CPWs
said community members would not give - Staff learned to balance information they
expected they could ask with what was culturally
sensitive. - If not they would lose valuable information
because people would not participate or speak in
detail. - There was tension between staff supervising the
CPWs and senior staff about how quickly the
project should happen - Senior staff realised they were so familiar with
wider health service issues that they forgot they
were working with people who knew little about
this - they needed to be more patient
2I
20
Example 1 The needs of Pakistani and Bangladeshi
communities in Newcastle
- Benefits achieved
- employed workers from Asian backgrounds in a
community with a high unemployment rate - got good participation from a mostly non-English
speaking disadvantaged population who had low
literacy levels - gained in depth information because the process
was appropriate to the group - had solid information they could use to make
service changes - learned about different views of what emotional
distress is and how people show it this will
reduce misunderstanding between staff and
community members
2J
21
Thinking about practical issues what does it
mean for you?
- Number of user consultants involved
- Costs of involvement
- What is the user consultant role description?
- Being prepared for the role
- At what stage are user consultants involved?
- Office space or equipment
- Number of methods for gaining user involvement
used
3A
22
Thinking about practical issues what does it
mean for you?
- How much information you receive
- Handling confidential information
- Training
- Mentoring
- Your connection to a network of other users,
carers, the public - Debriefing opportunities or support
- Opportunity to reflect on what you learn
- Dealing with personal difficulties
3B