Transformation PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title: Transformation
1
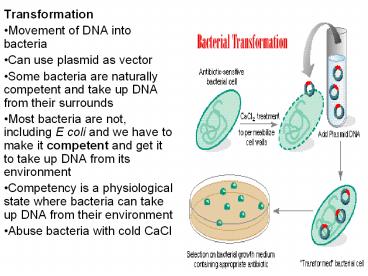
- Transformation
- Movement of DNA into bacteria
- Can use plasmid as vector
- Some bacteria are naturally competent and take up
DNA from their surrounds - Most bacteria are not, including E coli and we
have to make it competent and get it to take up
DNA from its environment - Competency is a physiological state where
bacteria can take up DNA from their environment - Abuse bacteria with cold CaCl
2
(No Transcript)
3
- When do the cutting and sticking of plasmid and
foreign DNA there are several possible outcomes - Successful sticking of the plasmid and foreign
DNA - Recircularization of plasmid without the foreign
DNA - Circulization of plasmid with other plasmids or
several inserts to make huge circular molecule - Many inserts sticking together to make long
linear molecule - All of these outcomes occur and could be taken up
into bacteria - Possibility 3 is less likely to happen as big
plasmids are more difficult to take up and also
less stable when they are taken up - Possibility 4 can occur but linear DNA is usually
broken down very quickly in a bacterial cell as
it is recognised as non self
4
- Selection
- A mechanism is required to select for the
bacterial cells that have taken up the plasmid
with one inserted foreign DNA piece - Usually bacterial cells are used that are
sensitive to a particular antibiotic - The recombinant plasmid that is used usually
carries antibiotic resistance and also a gene for
Beta galactosidase. - Beta galactosidase is an enzyme that acts on a
substrate called X gal to yield a coloured
product. - The foreign DNA is inserted into a site in the
middle of the beta galactosidase gene. This
disrupts it and makes it inactive and unable to
perform the colour reaction with X gal.
Nutrient agar with ampicillin and X gal
5
(No Transcript)
6
- Plasmid vectors
- small circular dsDNA molecules capable of
autonomous replication inside cells. - Usually of bacterial origin (there are some
eukaryotic plasmids).
Designed Plasmids must have origin of replication (Ori), Termination seqs Selective marker (usually antibiotic resistance gene) to select for bacteria containing plasmid. Polycloning site (unique restriction target sites useful for inserting donor fragments Many plasmids allow for blue/white selection for distinguishing between recombinant vs nonrecombinant plasmids polycloning site inserted inframe into beta-galactosidase gene (product of this gene converts colorless X-gal into blue product) Fragments inserted into this polycloning site disrupt function of b-galactosidase gene product, resulting in white colonies.
7
- plasmids used as vector when fragments of DNA to
be inserted are smaller than 20 kb. - Some plasmid vectors constructed such that cloned
genes can be transcribed and translated. These
are called expression vectors .
8
- Types of Naturally occurring Plasmids
- All plasmids carry genes for their own
replication what other genes? - No apparent function cryptic plasmids
- for conjugation
- For antibiotic production
- Bacteriocin production
- Resistance genes
- Virulence genes
- Physiological functions degradation of
chemicals/herbicides, production of acetone,
nodulation in symb N2 fixation
9
- Resistance Plasmids
- R plasmids resistance to antibiotics and other
growth inhibitors - Genes encode proteins that inactivate Ab or
affect its uptake - Can transfer resistance via conjugation
- Many drug resistance elements are on transposons
- Plasmid R100 carries resistance to sulfonamides,
streptomycin, spectinomycin, chloramphenicol etc
and can transfer itself to Klebsiella, Proteus,
Salmonella and Shigella
10
(No Transcript)
11
- Transfer of DNA between Cells
- In prokaryotes DNA transferred to recipient cell
by 1 of 3 processes - Transformation involves donor DNA free in
environment - Transduction donor DNA transfer mediated by a
virus - Conjugation involves cell to cell contact
between donor and recipient i.e. acquisition
directly from another bacterium