T Cell Subsets PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: T Cell Subsets
1
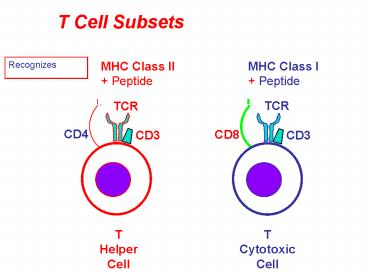
T Cell Subsets
MHC Class II MHC Class I Peptide Peptide
Recognizes
TCR
TCR
CD4
CD8
CD3
CD3
T Helper Cell
T Cytotoxic Cell
2
Antigen Processing and Presentation to T
Lymphocytes
Lecture 7
3
Immune Responses are initiated in the Peripheral
lymphoid organs
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Dendritic Cell Migration and Antigen Presentation
7
- How do antigenic peptides end up binding to MHC?
- What determines whether Ag. Is presented by MHC I
or II? - How can you target CD4 vs. CD8 T Cells?
- Physiological Significance
8
Bacteria Candida Helminths (Worms)
Mycobacteria Salmonella Leishmania Trypanosoma His
toplasma Yersinia pestis
Viruses Listeria Chlamydia sps. Rickettsia sps.
9
Vesicular
Cytosolic
10
Exogenous/Endocytic Pathway
11
Virus
Endogenous/cytosolic Pathway
12
(No Transcript)
13
Cell Biology of Antigen Processing
14
Antigen Presentation to CD8 T Cells
15
Which cells can present antigen to CD8 T cells?
And Why?
- All nucleated cells
16
Endogenous/Cytosolic Pathway
MHC I Pathway of Processing of Cytosolic Proteins
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
Antigen Presentation to CD4 T Cells
20
Which cells can present antigen to CD4 T Cells?
And Why?Professional Antigen Presenting
Cells Dendritic Cells Macrophages B cells
21
Exogenous/Endocytic Pathway
Invariant Chain
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
Antigen Presentation by Macrophage
Macrophage
T Cell
25
Numerous T Cells Interacting with a Single
Macrophage
26
Physiologic Significance of MHC II-Associated
Antigen Presentation
27
Bacteria Candida Helminths (Worms)
Mycobacteria Salmonella Leishmania Trypanosoma His
toplasma Yersinia pestis
Viruses Listeria Chlamydia sps. Rickettsia sps.
CD4 T Cells
CD8 T Cells
CD4 T Cells
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.