Habitual Decision Making PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title: Habitual Decision Making
1
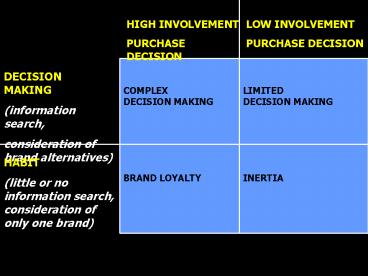
HIGH INVOLVEMENT PURCHASE DECISION
LOW INVOLVEMENT PURCHASE DECISION
COMPLEX DECISION MAKING
LIMITED DECISION MAKING
DECISION MAKING (information search, consideration
of brand alternatives)
BRAND LOYALTY
INERTIA
HABIT (little or no information search,
consideration of only one brand)
2
Low Involvement Decision Making
- Low Involvement Theories and Implications
- Krugmans Passive Learning Theory
- Sherifs Social Judgment Theory
- Petty and Cacioppos Elaboration Likelihood Model
3
Understand Inertia by Contrasting with Complex
Decision-Making
4
Complex Decision Making
Information Acquisition
Information Processing Belief Formation
Problem Recognition/Need Arousal
Comparative Evaluation/ Purchase
Post-Purchase Evaluations
Hierarchy of Effects Beliefs, (information
processing), evaluations, behavior
5
Krugman Passive Learning
- Exposure to TV ads passive learning (not active
learning) - WHY??
- So TV ads create brand recall without changing
attitudes - May only remember brand name (Bubble Yum) and
some basic beliefs about the brand name. But
havent decided whether you like it or dislike
it. - So how does exposure to TV advertising lead to
buying the brand??? - Hierarchy of effects says evaluation has to
come before
6
Low Involvement Products Different Hierarchy of
Effects (Krugman)
- Memory of Brand name and some beliefs
- Can be enough to create Product Purchase
- When you are in the store you see the brand --
you remember seeing an ad for it remember some
beliefs - And you buy the brand without really knowing
whether you like it or dislike it.
7
Hierarchy of Effects
- High Involvement
- Beliefs (Awareness) Attitude
Behavior - Low Involvement
- Beliefs (Awareness) Behavior
Attitude - Belief can simply be I remember this brand name
(no evaluation) - Implications for Marketing Strategies????
- What should you do if youre selling a
low-involvement product?
8
Implications
- Repeated Advertising
- Memorable brand name (Bubble Yum)
- Point-of-purchase (POP) display in store
- Putting brand at end of shelf position in store
9
Sherifs Social Judgment Theory
- Latitude of Acceptance (LOA)
- range of positions with which individual agrees
- Latitude of Rejection (LOR)
- range of positions with which individual
disagrees - Latitude of Noncommitment (LON)
- range of positions with which individual is
neutral - High Involvement Narrow LON Narrow LOA Wide
LOR. - Low Involvement Wide LON Wide LOA Narrow LOR
10
Opinions of HK universities (bad, good, neutral)
- Difference between highly-involved person
- Vs.
- Low-involved person
11
Universities LOA, LON, LOR
- High Involvement
- HKUST
- CUHK
- HKU
- City U
- HK Poly
- Baptist
- Lingnan
- Low Involvement
- HKUST
- CUHK
- HKU
- City U
- HK Poly
- Baptist
- Lingnan
12
Implications
- High involvement
- Wide LOR Narrow LOA only willing to accept a
few brands I.e., very few brands make it past
the acceptable level - Implication Brand quality important
- Low involvement
- Wide LOA Narrow LOR willing to accept a lot of
brands but passively -- wont go searching for
different brands - Implication availability important
13
Assignment
14
Elaboration Likelihood Model
- How people watch Advertising under low vs. high
involvement
15
Elaboration Likelihood Model
- High involvement
- consumers evaluate ad and product carefully
- what the ad says about the products attributes
- peripheral cues (non-product material such as??)
less important - Low involvement
- consumers do not evaluate ad carefully
- what the ad says about attributes not so
important - peripheral cues quite important (e.g., endorser,
music, nice pictures, etc.)
16
Implications for Advertising
- High Involvement
- Ad should have lot or little information?
- Use of attractive non-product features (cues) or
product benefits? - Print ads or tv ads?
- High or low Repetition?
- Low Involvement
- Ad should have lot or little information?
- Use of attractive non-product features (cues) or
product benefits? - Print ads or tv ads?
- High or low Repetition?
17
Creating A Model of Low Involvement Decision
Making
- (using the three theories discussed )
18
Complex Decision Making
Information Acquisition
Information Processing Belief Formation
Problem Recognition/Need Arousal
Comparative Evaluation/ Purchase
Post-Purchase Evaluations
Hierarchy of Effects Beliefs, (information
processing), evaluations, behavior
19
Low vs. High Involvement
- Low Involvement
- Problem Recognition
- Routine
- Search
- few sources (ad) passive
- Evaluation and Decision
- few attributes like price and awareness
peripheral cues - decision at point of purchase
- acceptable solution
- often, liking after trial
- High Involvement
- Problem Recognition
- Planning
- Search
- many sources active
- Evaluation and Decision
- many attributes (peripheral cues not important)
- decision before point of purchase
- optimal solution
- liking before trial
20
Marketing Implications for Low Involvement
Purchases
- Not too many attributes used in decision. Often
only price used. - marketing implication??
- Decision often made in the store (not before)
- marketing implications?
- Will not actively search for brands or visit many
stores - Distribution implication?
- Liking for brand may only come after product
trial - So if you want to make them like the product?
21
Marketing Implications Contd...Advertising
- Advertising should focus on key points
- High repetition
- TV advertising
- captive audience
- extended coverage
- Use of likable peripheral cues
- visual cues pleasant music
22
Other Low Involvement Issues
23
HIGH INVOLVEMENT PURCHASE DECISION
LOW INVOLVEMENT PURCHASE DECISION
COMPLEX DECISION MAKING
LIMITED DECISION MAKING
DECISION MAKING (information search, consideration
of brand alternatives)
BRAND LOYALTY
INERTIA
HABIT (little or no information search,
consideration of only one brand)
24
Limited Decision Making
- Low involvement, but not buying same brand again
- Switching to different brand so some
consideration of other brands some effort in
decision making - Switching occurs because of
- boredom what is this type of limited decision
making called? - new product attribute
25
Final topic Unplanned purchases
- Low involvement purchases are often unplanned
- Not all unplanned purchases are low involvement
- impulse purchases (examples??)
26
Quiz 2 Wednesday (March 19)
- 6-7 pm be in your seats by 5.55 pm!!
- Venue LTJ
- No dictionaries allowed
- Multiple choice questions (1 for correct -.25
for incorrect 0 for no answer) - Same rules pick best answer professors
decision final - Materials all lecture notes after Quiz 1 (not
including Project lecture). - Book
- Chapter 4 pg. 103-134
- Chapter 5 pg. 141-173 (except for types of
unplanned purchases -- pg. 152 and FCB grid
on pp 164-165) - GOOD LUCK!!!