The Code For Life - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Code For Life
Description:
Inject mutant gene in to one of the pronuclei of the fertilized mouse oocyte ... Harvest quiescent cells. Starve cells. Suction. Suction Pipette. Glass pipette ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:28
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Code For Life
1
The Code For Life
2
The Code For Life
Big nose
Brown eyes
Straight hair
3
Structural Biology Medicine and Biology at the
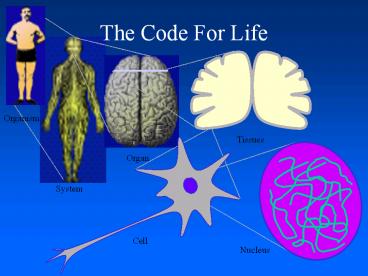
Atomic Scale
Organ ? Tissue ? Cell ? Molecule ? Atoms
- A cell is an organization of millions of
molecules - Proper communication between these molecules is
essential to the normal functioning of the cell - To understand communication between molecules
determine the arrangement of the atoms
4
Advanced Cell Developmental Biology
5
- Gene, Recombinant DNA Cloning Analysis
6
Restriction Enzymes
- Restriction enzymes are DNases (nucleases) found
in bacteria that recognize specific DNA sequences
as 4mers,6mers or 8mers and make double stranded
breaks in DNA . - This enables cutting of genome in specific ways
to generate restriction site maps and the
development of approaches for pasting pieces of
DNA together in specific ways.
A
Separation of EcoR1 segments on an agarose gel
B
C
D ,E
F
7
DNA Hybridization
- DNA hybridization is the process whereby
complementary strand of DNA anneals (to form a
double helix) with the single stranded DNA - Hybridization can be measured by labeling the
complementary strand either with 32P
nucleotides or fluorescent probes . - There is also DNA-RNA hybridization
8
Southern Blotting
- Southern Blotting enables identification of
specific DNA sequences (gene - fragments) from among the total sequence of DNA
Hybridize with a labeled DNA or RNA of interest (
e.g., 32P labeled DNA) followed by
autoradiography or phosphoimaging for detection
9
Northern Blotting
- Northern Blotting is where RNA is blotted and
then probed labeled DNA (cDNA) - synthesized from the mRNA isolated from the
cell - Enables identification and quantification of
specific mRNAs from among the vast - population of RNAs in the cell
10
DNA cloning
- DNA cloning enables specific pieces of genome to
be inserted into bacteria as plasmid or phage
lambda vectors and grown in large quantity. - The first step is to generate a library of
bacteria with inserted DNA fragments. This could
either be a genomic(DNA)or a cDNA (mRNA) library
11
Replica plating and in situ hybridization
- Techniques used to identify a bacterial colony
that contains the gene (DNA sequence) - of interest. The isolated colony can be grown
up in large quantities.
CsCl centrifugation for separation of plamid DNA
from chromosomal DNA
Replica plating and in situ hybridization
12
cDNA libraries
- They are generated to isolate particular genes
of interest or to identify a gene based on the
protein expression of that gene cloned in the
bacterial cell - The latter procedure is called reverse
genetics whereby the protein product is used to
identify the gene followed by DNA sequencing
13
DNA sequencing
- Sangers dideoxy method DNA to be sequenced is
mixed with each of 4 ddNTPS (chain terminators)
in separate reactions for DNA synthesis and later
separation of the products by electrophoresis - Can now be done automatically via sequencing
machines that work with different flurochromes
attached to each of dideoxy nucleotides - To determine the sequence of a gene of many
kilobases overlapping DNA fragments of 400-800 bp
must be sequenced
14
Protein expression vectors
- These are specially designed plasmid
- vectors for fusion protein expression
- to isolate large quantities of protein of
- interest for antibody production or
- other studies of purified protein.
- The proteins are produced as fusion
- proteins of the cDNA gene coding
- sequence ligated to a protein
- expression marker or reporter protein
- e.g. beta-galactosidase
- They can also be used as a major tool
- in cell biology to study the expression
- of proteins in cells following DNA
- transfection
15
DNA transfection and Polymerase chain reaction
(PCR)
- DNA transfection is used to track the properties
of individual proteins in a cell - Construct a plasmid expression system that
contains the protein of interest fused with a
reporter gene such as a beta- galactosidase or a
short peptide sequence such as HA 9 mer peptide
or FLAG epitope for antibody localization with
anti HA or anti FLAG or fluorescent localization
in living cells with GFP-constructs (GFP-actin)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Is used as an
alternative to cloning for purifying a particular
DNA (gene sequence It enables the production of
microgram quantities of the DNA sequence of
interest in the test tube Provides an
alternative for preparing DNA probes to screen
genomic or cDNA library for clones encoding a
protein of interest
16
DNA Microarrays and chips
- Enable via fluorescence in situ hybridization
(FISH) to measure expression of 1000s of genes
on each array/ chip.
Actual chip size
Yeast genome microarray The array is hybridized
to cDNA labeled with a green fluorescent dye
prepared from cells grown in glucose and with red
labeled cDNA from cells grown in ethanol. Spots
were detected with a scanning confocal microscope
17
Antibody production
- Polyclonal antibodies are
- generated by injecting
- antigen into an animal and
- purifying the antibody
- titer from blood
- Monoclonal antibody
- technique enables to obtain
- a single clone of cells that
- recognizes one epitope
- ( usually 9 a.a.) of the
- total protein
Monoclonal antibody production
18
Genetic Engineering
- Introduction of exogenous genes ( mutant or
normal) in to normal cells or organisms to study
gene expression - Used to study the role of the protein coded by
the gene in the cell/organism function or for
engineering gene expression for improving food
production or reducing the destrcutive damage of
human diseases
19
Site Directed Mutagenesis
- Alterations in nucleotides (substitutions or
deletions) in vitro at known (directed) sites to
create mutant genes - These mutant genes can be transfected into cells
as previously discussed and enables study of gene
function at the individual cell level. The
transfected genes are also called transgenes
20
Production of transgenic mouse
Inject mutant gene in to one of the pronuclei of
the fertilized mouse oocyte
Transfer oocyte to surrogate mother. 10-30 of
offspring contain the transgene in equal amounts
in all tissues
21
Gene Knockout or replacement
- Form of trangenics
- Occurs following homologous recombination of the
transgene at the site of the endogenous gene - Occurs readily in yeast cells but in mammalian
cells the rate of recombination is very slow and
hence a double selection marker approach is
adopted where the first marker e.g. neomycin
resistance selects for all cells with homologous
recombination while the second marker allows
growth of only those cells that carried out
homologous recombination
22
Knockout protocol
ES cells are isolated from the inner blastocyst
and culture
ES cells are tranfected with the gene of interest
Enables direct study of gene function in an
intact organism
ES cells successfully transfected via homologous
recombination are selected and grown in culture
and injected into a host blastocyst. Chimeras
develop which contain ES cells from both the
transfected and the host cells.
23
Gene Replacement/therapy
- Replace an abnormal
- gene with a normal one
- at a very early stage of
- development
- It has the potential for
- curing or alleviating the
- symptoms of a wide
- variety of human
- diseases, e.g.,Parkinsons
- disease
Procedure for gene replacement
24
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 1Making Quiescent Cells
Culture mammary cells
Starve cells
25
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 2Collecting The Donor
Nucleus
26
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 2Collecting The Donor
Nucleus
Glass pipette
27
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 3Egg Preparation
An egg is collected then placed into a dish where
it can be manipulated
28
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 3Egg Preparation
Egg
29
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 3Egg Preparation
Glass pipette
Egg
30
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 4Inserting The Donor
Nucleus
31
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 4Inserting The Donor
Nucleus
Glass pipette
32
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 4Inserting The Donor
Nucleus
33
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
34
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Zygote
35
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Cleavage
36
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Cleavage
37
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Cleavage
38
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Cleavage
39
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 5Initiating Development
Morula
40
How Ian Wilmut Made Dolly 6Development