Three Metabolic Pathways PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title: Three Metabolic Pathways
1
2
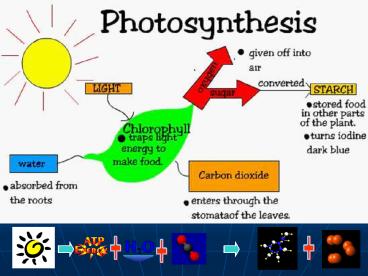
Three Metabolic Pathways
Glucose
Glycolysis
NADH2
ATP
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
NADH2 / FADH2
ATP
Electron Transport System (ETS)
3
Overall Carbohydrate Metabolism
4
Glycolysis ATP
NADH2
Gluconeogenesis Glucose from Amino
Acids
Pentose Phosphate Pathway Ribose
NADPH2
5
Glycolysis Citric Acid Cylcle
Electron Transport System
Glucose
6
Glucose
Glycolysis
Pyruvate
7
Glycolysis
4 ATP Substrate Level Phosphorylations of ADP
Use 2 ATP to add PO4 to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphat
e
Net 2 ATP for Biological Work
Make 2 NADH2 -- reduced 2 NAD
Make 2 Pyruvates (Pyruvic Acid)
8
How is the ATP Made?
4 ATP Substrate Level Phosphorylations of ADP
Glycerate-1,3-diPO4 ADP
Glycerate-3-PO4 ATP
Phosphoenolpyruvate ADP Pyruvate
ATP
o'
What do you know about G ?
gt 7.3 kcal/mole
9
The Gyceraldehyde-3-PO4 Dehydrogenase Reaction
10
The Gyceraldehyde-3-PO4 Dehydrogenase Reaction
Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 NAD
Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 NADH2
NADH2 NAD NAD NADH2
Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 PO4
Glyceraldehyde-1,3-Di (bis) PO4
11
Anaroebic
Aroebic
12
Lactate Produced Anaroebically
Lactate is a Metabolic Deadend
13
Anaerobic Glycolysis
14
A
Glycogenolysis
A
15
Fates of Pyruvate
- b
Combine with Acetylcoenzyme A and enter the
Citric Acid Cycle
Can form Lactate (Lactic Acid)
Fermentation Muscle
16
Fates of Pyruvate
17
(No Transcript)
18
Coenzyme A
O
CoA CoASH CoASCCH3
19
Kreb's Cycle
20
Kreb's Cycle
21
Kreb's Cycle
22
Reduced Coenzymes
ATP CO2
23
2
H
2
H
2
2
Electron Transport Chain
H
H2O
24
Isoprene
Co-Q10
25
Electron Transport System
H
H2
O
H
26
Electron Transport System
27
The 4 Complexes
28
Cytochromes
29
Cytochrome c
30
Non-heme Iron Proteins
Complex 1
31
ATP
Synthase
32
ATP Synthase
33
Electron Transport System
34
ETS Complex 1 2
35
ETS Complex 3
36
From NADH2 get 3 ATP
Complex 1
Complex 2
Complex 3
From FADH2 2 ATP
Complex 4
37
Electron Transport System
Its function is to make ATP!
From NADH2 ATP in Complexes 1,3,4
Glucose
Citric Acid Cycle
ETS
ATP
ATP
ATP
MOST
38
Energy
- 52 kcal
e -
39
Total ATP from Glucose
40
Anaerobic Glycolysis
41
Carbohydrate Metabolism
42
Other Hexoses
43
Pentose or HMP Shunt
NADPH2
44
AA's
AA's
AA's
AA's
AA's
AA's
45
Two Types of Metabolism
Make NADH2 Make ATP
Catabolic Anabolic
USE NADPH2 USE ATP
46
END